- The paper introduces the TUNES framework, which uses LLMs to identify entities and establish relationships for improved table understanding.
- It details a combined methodology of graph-based entity orientation, semantic search, and full-text search to enhance query accuracy.
- Results on WikiTableQuestions and TabFact demonstrate state-of-the-art performance with reduced computational load and improved precision.
Improving Table Understanding with LLMs and Entity-Oriented Search
This paper presents "Improving Table Understanding with LLMs and Entity-Oriented Search," focusing on addressing the complexities of table data comprehension using LLMs and an innovative entity-oriented search approach.
Introduction
LLMs have recently been leveraged for understanding tabular data by converting natural language queries into structured forms like SQL queries. However, the unpredictable structure of tabular data and limited contextual information pose significant challenges for accurate query execution. To tackle these issues, the paper proposes an entity-oriented search methodology that reduces reliance on preprocessing and keyword matching, focusing on semantic similarities and implicit relationships within tables. The integration of a graph query language, Cypher, is a novel contribution to this research, forming the cornerstone of TUNES (Table Understanding with Entity-Oriented Search).
Methodology
Framework Overview
The proposed TUNES framework consists of three main components:
- Entity Identification: Recognizes entities within tables using LLMs to identify primary keys and attributes. This component contributes to clarifying the implicit relationships that exist among data cells.
- Entity-Oriented Search: Combines full-text, semantic, and graph searches to enhance the relevance of retrieved data. Entities are represented as nodes in a graph, with relationships articulated through Cypher queries, establishing a rich semantic network.
- LLM-based Answer Generation: Extracts top relevant entities to generate accurate responses, making use of the entity relationships constructed in previous steps.
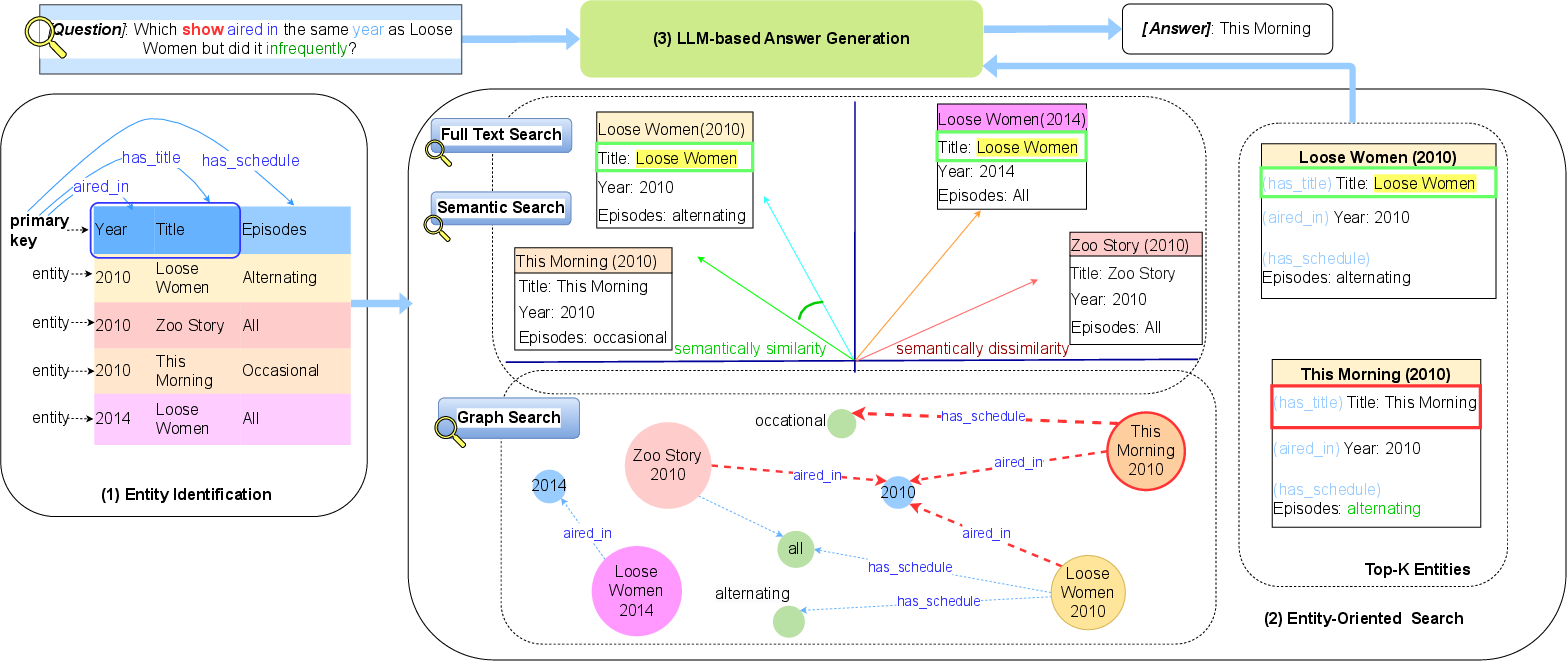
Figure 1: Overview of our proposed framework TUNES. The embedding space and the graph are simplified for illustration purposes.
Entity Identification
Entities are detected by analyzing table structures to discern primary keys and attributes, with LLMs prompting for attribute-entity relationships. Such structuring allows distinct context understanding and noise reduction in entity representations.
Entity-Oriented Search
- Graph Search: Graphs are constructed from identified entities and attributes, where nodes represent entities and attributes while edges represent relationships. Cypher queries enable accurate extraction by exploiting these relationships.
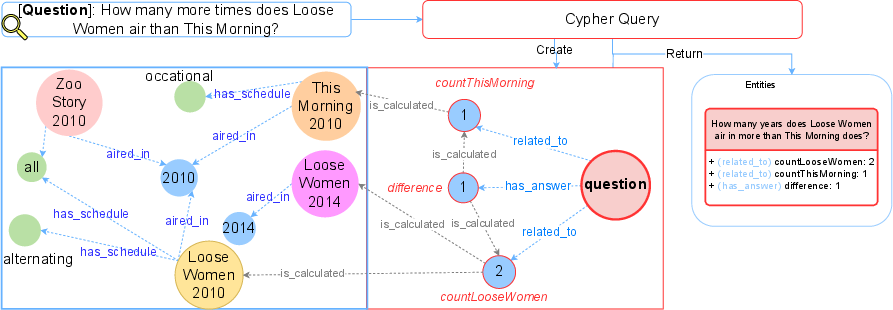
Figure 2: Cypher Query Execution Process. To answer a relational question, the query process creates a new entity representing the question and determines its relation to existing attributes.
- Semantic Search: Embeds entities and questions into a shared vector space, using cosine similarity to ascertain semantic relevance.
- Full-text Search: Employs the BM25 algorithm for keyword matching to refine entity relevance further.
LLM-based Answer Generation
The framework dynamically constructs a prompt incorporating the top K relevant entities which are processed by LLMs to derive accurate, contextually informed answers. This method significantly lowers the computational load compared to exhaustive keyword matching or preprocessing.
Experimental Setup and Results
The framework was evaluated using WikiTableQuestions and TabFact datasets, achieving state-of-the-art results. The method demonstrated significant cost efficiency by reducing the number of LLM calls while maintaining or surpassing accuracy compared to baselines using CoT or SC approaches.
Error Analysis
Common errors included insufficient entity retrieval and incorrect entity relations due to Cypher query execution. Numerical and logical errors in LLM output suggested areas for further improvement in reasoning and computation capabilities.
Conclusion
TUNES advances table comprehension by integrating entity-oriented search with LLMs, significantly reducing preprocessing needs. The results highlight the potential of integrating graph-based query systems like Cypher to handle implicit relationships within tables effectively. Future work could extend this approach to more complex table-dependent tasks, leveraging the adaptability and efficiency demonstrated in the experiments.



