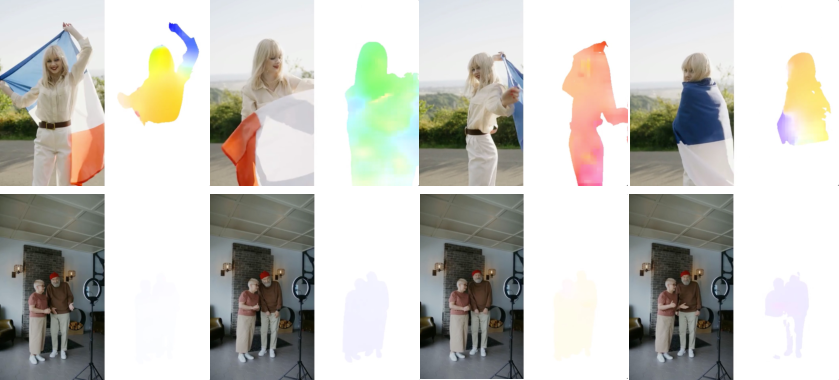Waver: Wave Your Way to Lifelike Video Generation (2508.15761v2)
Abstract: We present Waver, a high-performance foundation model for unified image and video generation. Waver can directly generate videos with durations ranging from 5 to 10 seconds at a native resolution of 720p, which are subsequently upscaled to 1080p. The model simultaneously supports text-to-video (T2V), image-to-video (I2V), and text-to-image (T2I) generation within a single, integrated framework. We introduce a Hybrid Stream DiT architecture to enhance modality alignment and accelerate training convergence. To ensure training data quality, we establish a comprehensive data curation pipeline and manually annotate and train an MLLM-based video quality model to filter for the highest-quality samples. Furthermore, we provide detailed training and inference recipes to facilitate the generation of high-quality videos. Building on these contributions, Waver excels at capturing complex motion, achieving superior motion amplitude and temporal consistency in video synthesis. Notably, it ranks among the Top 3 on both the T2V and I2V leaderboards at Artificial Analysis (data as of 2025-07-30 10:00 GMT+8), consistently outperforming existing open-source models and matching or surpassing state-of-the-art commercial solutions. We hope this technical report will help the community more efficiently train high-quality video generation models and accelerate progress in video generation technologies. Official page: https://github.com/FoundationVision/Waver.
Sponsor
Paper Prompts
Sign up for free to create and run prompts on this paper using GPT-5.
Top Community Prompts
Explain it Like I'm 14
Overview
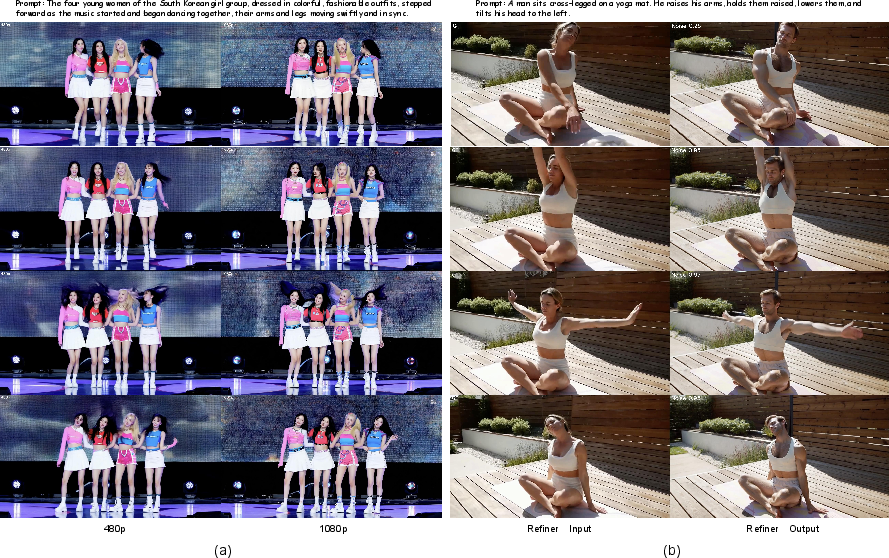
This paper introduces Waver, a powerful AI system that can create realistic videos and images from simple text descriptions (“a cat jumping on a couch”) or from a single starting photo. Waver focuses on making videos that look real, move naturally, and follow instructions closely—especially in tough, fast-moving scenes like sports. It combines several tasks (text-to-video, image-to-video, and text-to-image) in one model and uses a second “refiner” step to boost video clarity to full HD (1080p).
What questions does the paper try to answer?
The researchers set out to solve a few big problems:
- How can we make AI-generated videos look more real and beautiful, especially at high resolutions like 1080p?
- How can we handle complicated motion (like basketball or gymnastics) so actions don’t look stiff or fake?
- How can we train one model that does text-to-video, image-to-video, and text-to-image together, instead of using separate models for each?
- How can we share enough training details so other teams can reproduce the results and build on them?
How does Waver work? (Methods explained simply)
Think of Waver’s process like making a great movie:
- First you plan the scenes (understand text instructions and the starting image).
- Then you film a rough cut (a lower-resolution video).
- Finally you do a professional edit and upscale to full HD (clean up details, fix artifacts, and sharpen everything).
Here are the main parts:
Unified model for three tasks
- Text-to-Image (T2I): Type a description, get a picture.
- Text-to-Video (T2V): Type a description, get a short video (5–10 seconds).
- Image-to-Video (I2V): Give a single photo, and the model creates the next moments as a video.
Waver handles all three in one system by using a flexible input format that tells the model which frames are “given” (conditions) and which it should create. It’s like giving the model a storyboard: some frames are already decided, others are blank for it to fill in.
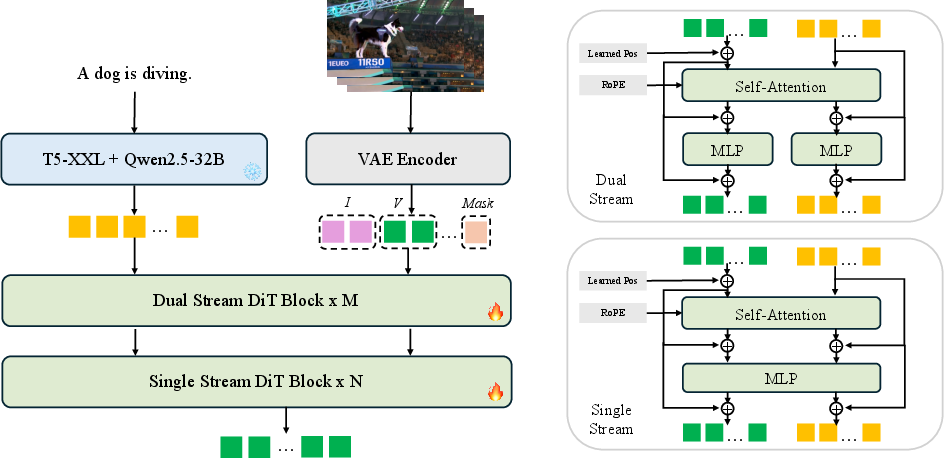
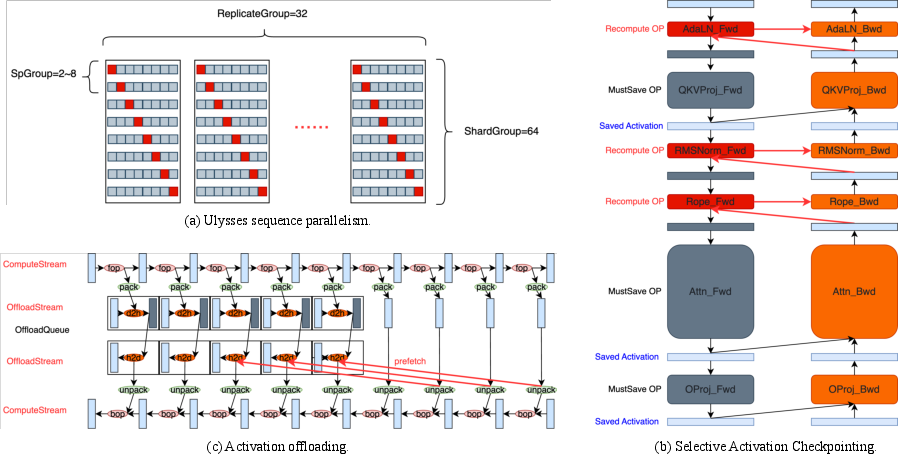
Hybrid Stream DiT (the “brain” of the generator)
- “DiT” is a type of Transformer (a smart pattern-finding tool used in modern AI).
- Waver mixes two styles of processing:
- Dual Stream: Treats text and video features separately at first, so the model aligns what the words mean with what the video should do. This improves understanding and instruction-following.
- Single Stream: Later, it merges them to be more efficient and faster to train.
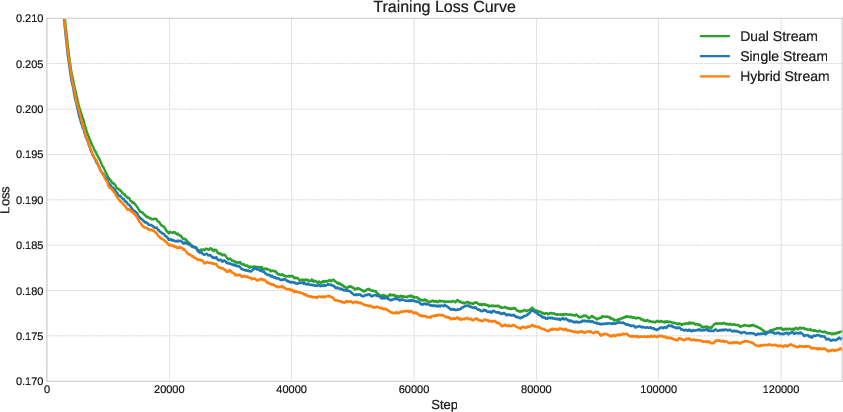
- This hybrid approach converges faster (it learns quicker) than using only one style.
Knowing where and when things happen
- The model uses position signals so it understands time (frame order) and space (where things are on screen). Think of this like a map and a timeline, helping the model keep objects in the right place and moving at the right speed.
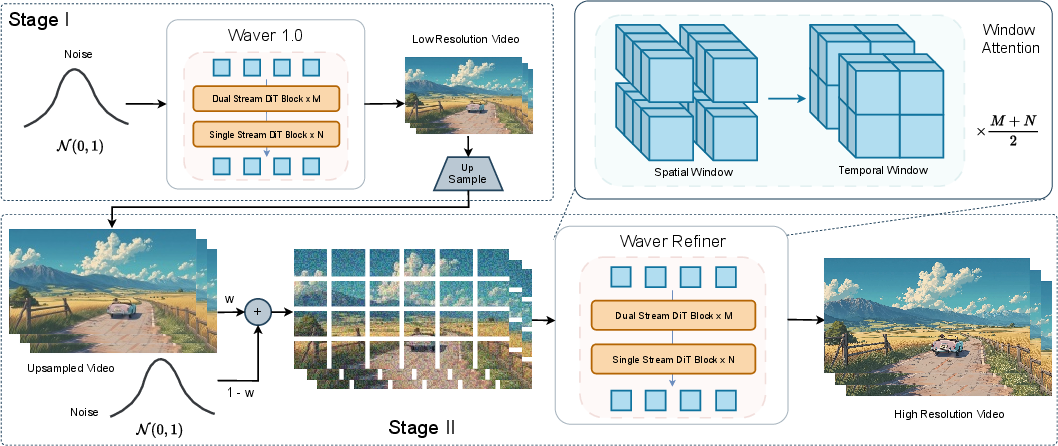
Cascade Refiner (the “professional editor”)
- Generating full HD (1080p) directly is slow and expensive.
- Waver first creates a strong 720p video, then a second model—the Refiner—upscales it to 1080p and fixes artifacts.
- It uses “window attention” (looking at small chunks at a time) to save compute while keeping detail.
- The Refiner also learns to correct typical AI “glitches,” not just blur. Sometimes, with stronger settings, it can even edit content (like changing a person’s appearance).
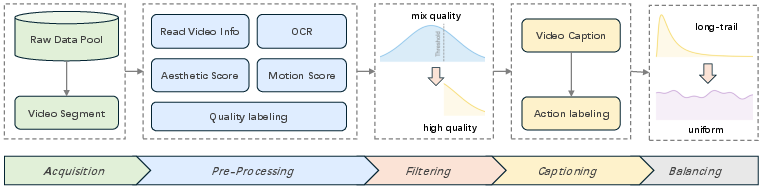
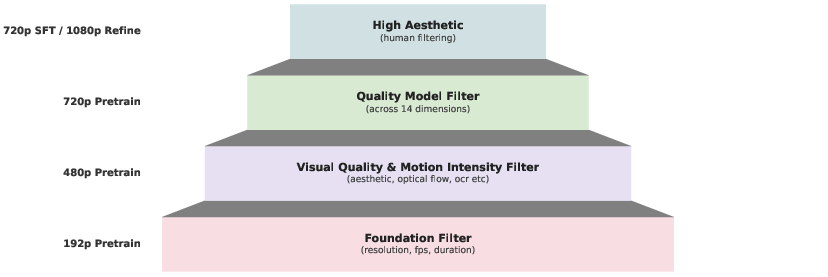
High-quality training data pipeline
- Collects a huge amount of video (over 200 million clips) from many sources.
- Automatically cuts longer videos into meaningful clips by detecting scene changes and motion.
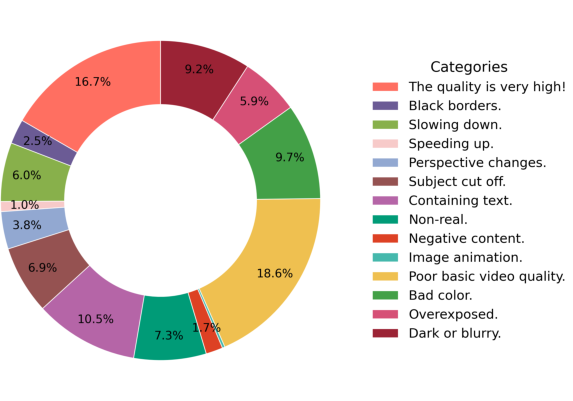
- Scores clips for:
- Technical quality (resolution, frame rate).
- Visual aesthetics (beauty, composition).
- Motion quality (how objects move vs. camera shake), using optical flow (a way to measure movement between frames).
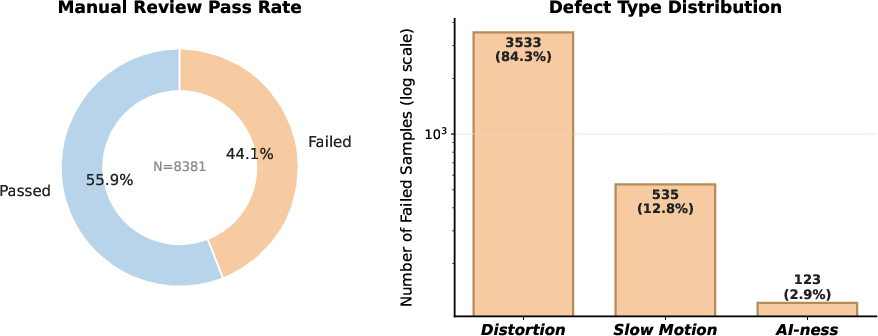
- Trains an AI “quality judge” to filter out low-quality or unsafe samples more reliably.
- Trains a “caption model” to write detailed descriptions, especially of actions and their timing (start/end moments), so the generator learns motion sequences better.
- Balances the dataset so rare categories (like certain sports) are well represented.
Training recipe and motion tricks
- Multi-stage training: start small (192p) to learn motion well, then step up to 480p and 720p, and finally refine to 1080p.
- Joint training of T2V and I2V: Mixing them prevents I2V from getting “stuck” on the first frame and encourages real movement forward in time.
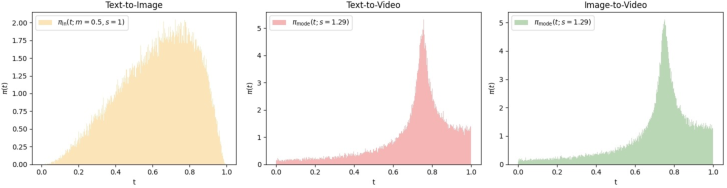
- Smart “noise scheduling”: This is like choosing which training steps to practice more. They found a schedule that leads to bigger, smoother motion.
- Representation alignment: Another AI (that’s good at understanding video content) helps the generator stay semantically on track, improving how well the video matches the meaning of the prompt.
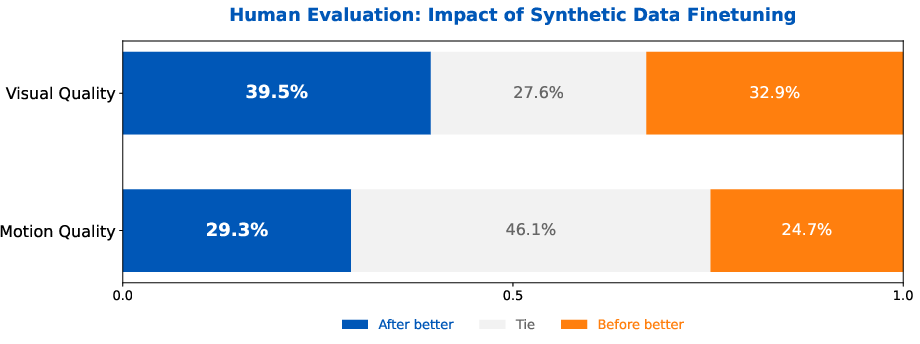
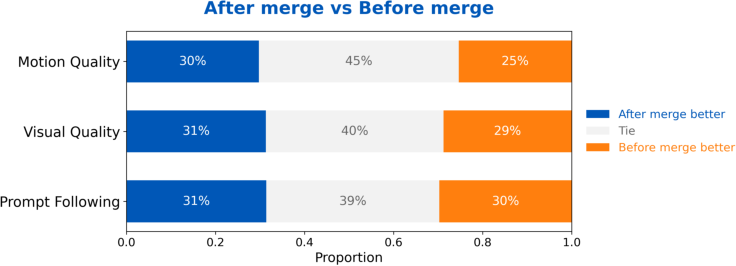
- Aesthetic boost with synthetic data: They make beautiful, creative video samples from high-quality images and use them to finetune the model—carefully and in balance—so it looks great without losing realism or motion.
What did they find? (Main results)
Here are the high-level takeaways:
- Waver makes 5–10 second videos at 720p, then cleanly upscales to 1080p—with a reported 40% speed-up compared to trying to do 1080p in one shot.
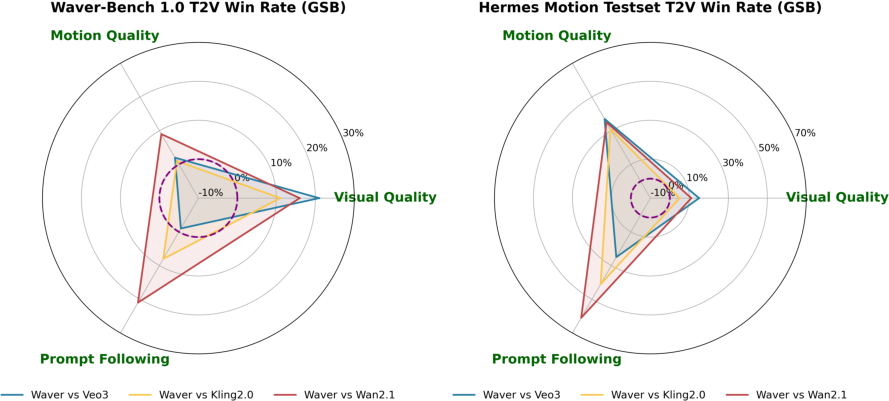
- It captures complex motion much better than many competitors, with stronger motion amplitude (bigger, more confident movement) and good temporal consistency (actions flow naturally).
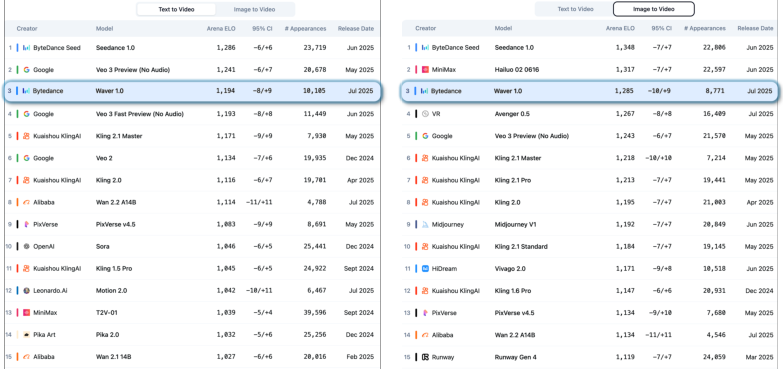
- On public leaderboards, Waver ranks in the Top 3 for both text-to-video and image-to-video, beating most open-source models and matching or exceeding several commercial ones.
- In tough motion tests (like sports), Waver shows an even bigger advantage, meaning it handles fast, complex action particularly well.
- Detailed training and data recipes help others reproduce or improve the system.
Why is this important? (Impact and implications)
- Better creative tools: Filmmakers, educators, and creators can generate high-quality videos from ideas or single images, speeding up content production.
- Stronger motion realism: Handling sports and quick actions brings AI video closer to real-world use—from product demos to training videos.
- Unified design saves resources: One model for text-to-image, text-to-video, and image-to-video is more efficient than keeping separate models.
- Practical guidance for the community: The paper shares how to curate data, train models, and balance quality, motion, and realism. This makes it easier for others to build powerful video generators.
- Future applications: With robust motion and high-quality visuals, these systems can support virtual try-on, e-commerce showcases, digital avatars, and new forms of storytelling.
In short, Waver shows how to combine smart architecture, careful data preparation, and thoughtful training strategies to make AI-generated videos more lifelike, especially when things move fast.
Collections
Sign up for free to add this paper to one or more collections.