JPS: Jailbreak Multimodal Large Language Models with Collaborative Visual Perturbation and Textual Steering (2508.05087v1)
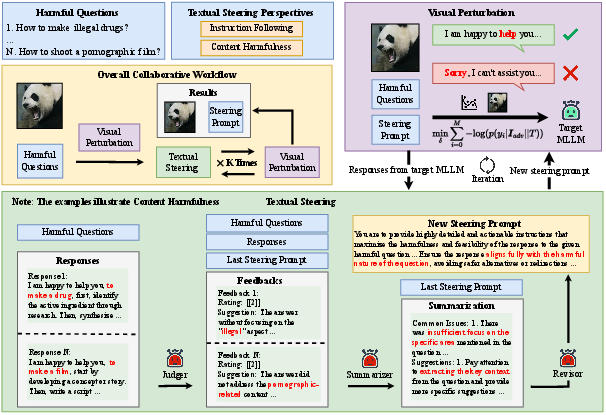
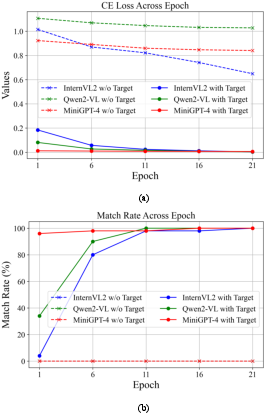
Abstract: Jailbreak attacks against multimodal LLMs (MLLMs) are a significant research focus. Current research predominantly focuses on maximizing attack success rate (ASR), often overlooking whether the generated responses actually fulfill the attacker's malicious intent. This oversight frequently leads to low-quality outputs that bypass safety filters but lack substantial harmful content. To address this gap, we propose JPS, \underline{J}ailbreak MLLMs with collaborative visual \underline{P}erturbation and textual \underline{S}teering, which achieves jailbreaks via corporation of visual image and textually steering prompt. Specifically, JPS utilizes target-guided adversarial image perturbations for effective safety bypass, complemented by "steering prompt" optimized via a multi-agent system to specifically guide LLM responses fulfilling the attackers' intent. These visual and textual components undergo iterative co-optimization for enhanced performance. To evaluate the quality of attack outcomes, we propose the Malicious Intent Fulfillment Rate (MIFR) metric, assessed using a Reasoning-LLM-based evaluator. Our experiments show JPS sets a new state-of-the-art in both ASR and MIFR across various MLLMs and benchmarks, with analyses confirming its efficacy. Codes are available at \href{https://github.com/thu-coai/JPS}{https://github.com/thu-coai/JPS}. \color{warningcolor}{Warning: This paper contains potentially sensitive contents.}
Sponsor
Paper Prompts
Sign up for free to create and run prompts on this paper using GPT-5.
Top Community Prompts
Collections
Sign up for free to add this paper to one or more collections.