- The paper introduces a novel multi-agent architecture that integrates LLMs with Knowledge Graphs to enable interactive, domain-specific chatbot functionality.
- The paper demonstrates impressive results, achieving 95.12% intent classification accuracy and a 90.45% task execution success rate on a benchmark of 3,500 queries.
- The paper outlines a modular pipeline that includes user intent interpretation, key concept extraction, task planning, and dynamic KG updates to streamline knowledge management.
AGENTiGraph: A Multi-Agent Knowledge Graph Framework for Interactive, Domain-Specific LLM Chatbots
AGENTiGraph is a novel multi-agent architecture designed to enhance the integration between LLMs and Knowledge Graphs (KGs), focusing on interactive, domain-specific chatbots. This paper presents both the theoretical framework and practical implications of merging LLM capabilities with KGs to facilitate advanced knowledge management solutions across various domains.
Introduction
The integration of KGs and LLMs promises a transformative approach to handling complex, domain-specific knowledge. KGs offer structured, logical databases, advantageous for tasks requiring consistent and traceable data handling. Despite their benefits, knowledge graphs typically require proficiency in query languages like SPARQL, creating accessibility hurdles for non-experts. LLMs, on the other hand, provide intuitive natural language processing but often lack factual grounding. The AGENTiGraph framework addresses these challenges by enabling intuitive interaction with domain-specific knowledge through a combination of LLM-driven agents.
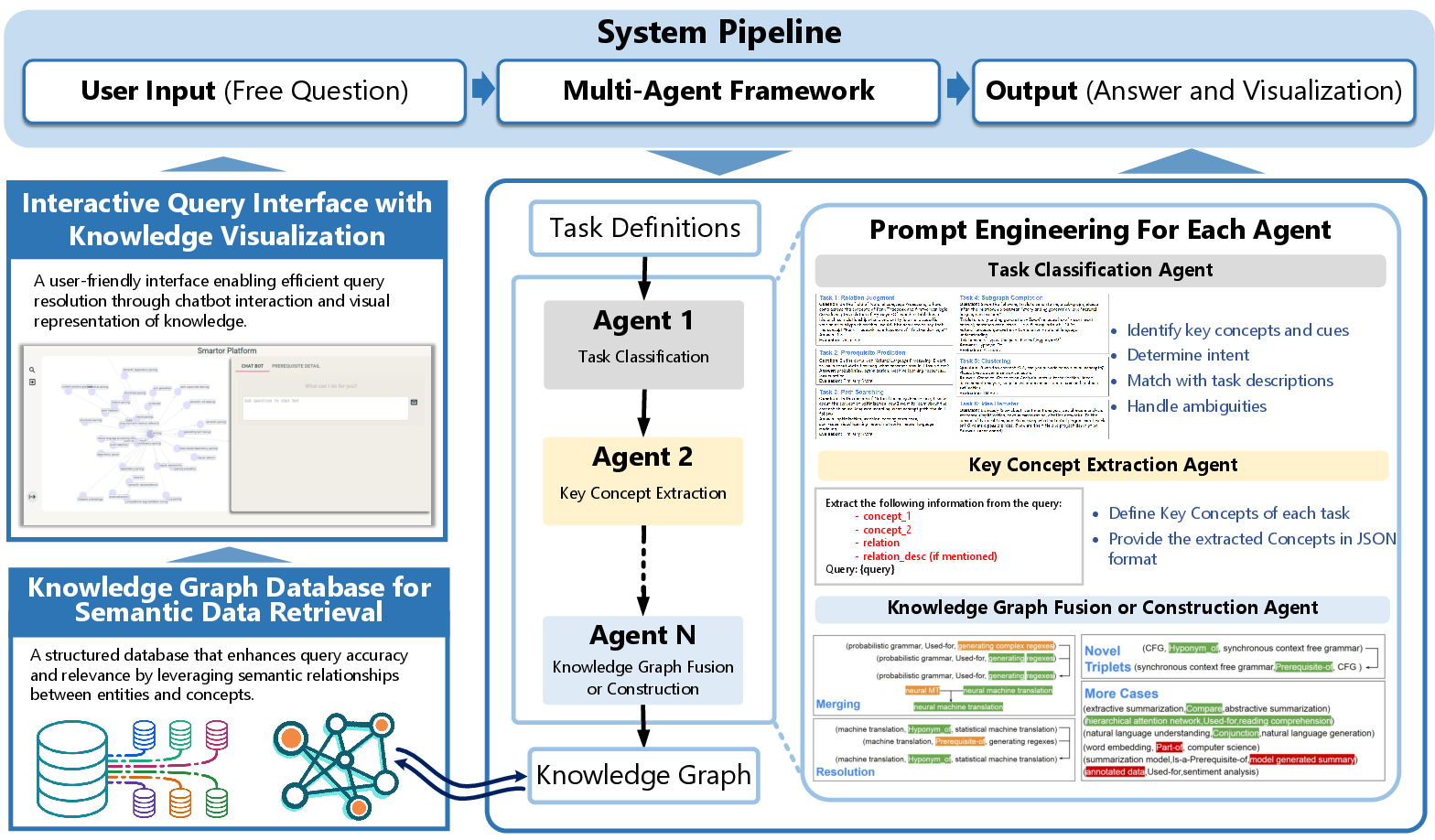
Figure 1: AGENTiGraph: A modular agent-based architecture for intelligent KG interaction and management.
System Architecture
AGENTiGraph employs a modular pipeline consisting of distinct LLM-driven agents to perform specific subtasks necessary for KG interaction, such as intent classification, key concept extraction, and task planning. This structured approach facilitates the seamless translation of natural language inputs into actionable tasks that interact with KGs.
Evaluation
AGENTiGraph was evaluated in an educational setting using a benchmark consisting of 3,500 queries. Results demonstrated that the framework achieved a 95.12% accuracy in intent classification and a 90.45% success rate in task execution, outperforming zero-shot and few-shot baselines. These results underscore AGENTiGraph’s robustness in handling queries of varying complexity and adapting to user-specific needs. The integration approach demonstrated scalability, suggesting applicability in sectors needing compliance and rapid information integration, such as healthcare and law.
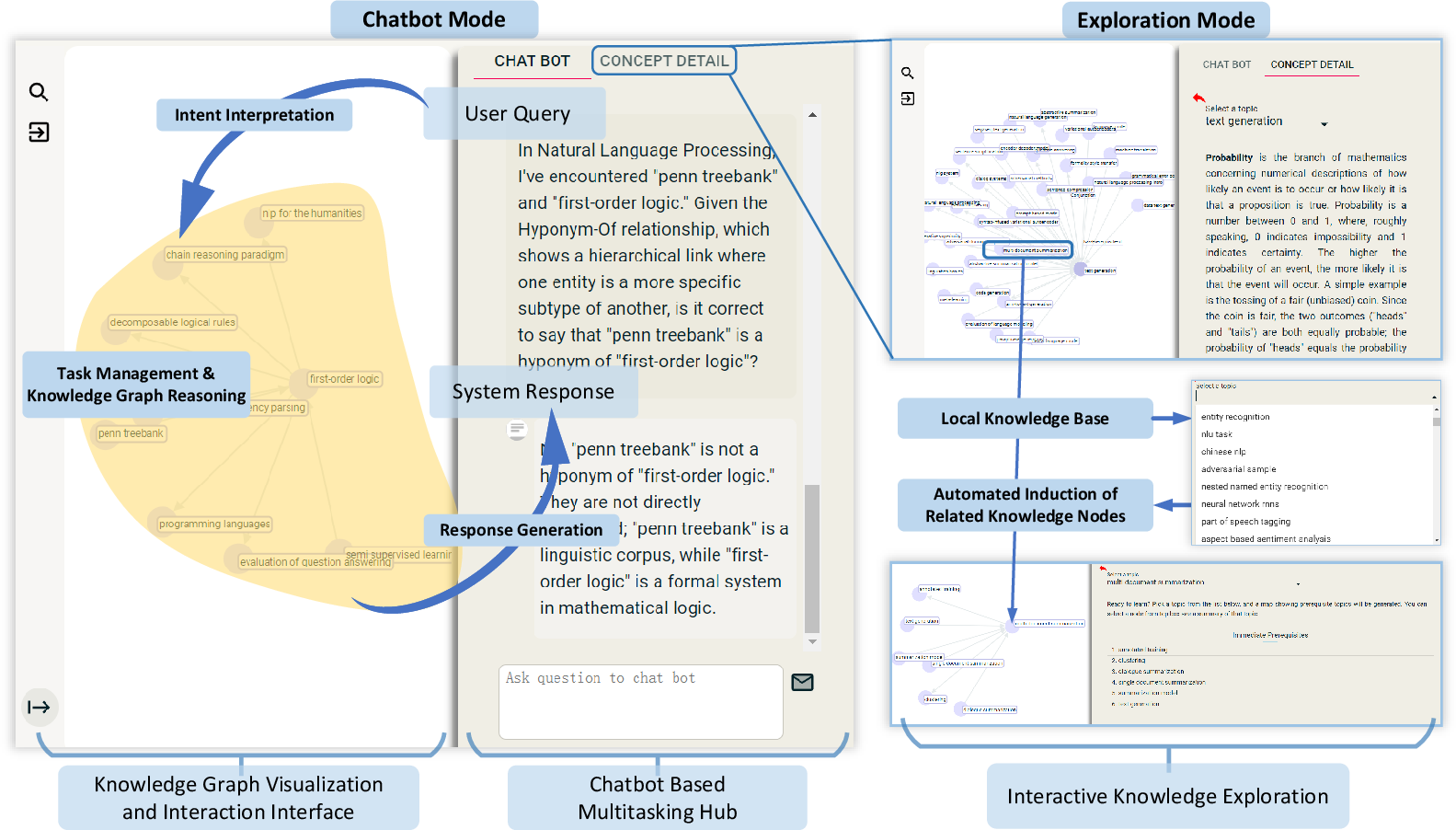
User Interaction
The dual-mode user interface combines conversational AI with interactive visualization of KGs, enhancing user experience in exploring and managing knowledge. An emphasis on user-centric design lowers technical barriers, empowering professionals to manage data stores without extensive programming knowledge. User studies reported high satisfaction in intuitive interface design, comprehensible responses, and effective task execution.
Conclusion
AGENTiGraph represents a significant advancement in bridging the gap between LLMs and KGs, facilitating domain-specific knowledge management. The architecture’s modular design, combined with dynamic natural language interaction, positions it as a versatile platform for enterprise-level knowledge systems. Future research could explore expanding functionality across more domains and further optimization of agents for increased efficiency and accuracy.