- The paper introduces a knowledge-guided forgery detection module that aligns visual and textual embeddings for enhanced generalization and explainability.
- It employs a forgery prompt learner to convert detailed forgery features into effective prompt embeddings, facilitating multi-turn dialogues for accurate detection.
- The framework outperforms existing methods in both intra- and cross-dataset evaluations, significantly improving AUC scores across benchmarks.
Unlocking the Capabilities of Large Vision-LLMs for Generalizable and Explainable Deepfake Detection
Introduction
The paper presents a novel deepfake detection framework that leverages Large Vision-LLMs (LVLMs), integrating external knowledge for enhanced generalization and explainability. Traditional deepfake detection strategies focus on image-level or feature-level anomalies, often missing the interpretability crucial in real-world scenarios, particularly in judicial settings. This research introduces a Knowledge-guided Forgery Detection module with the ability for multi-turn dialogues, integrating both a forgery classifier and a forgery locator, designed to enhance the model's overall generalization capability while fulfilling interpretability requirements.

Figure 1: Comparison of existing deepfake detection methods, showing integration of external knowledge in new approach.
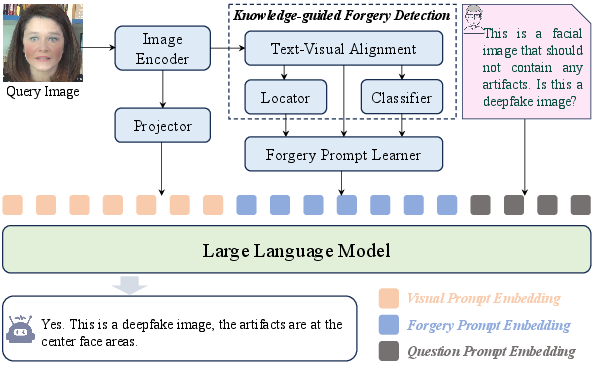
Figure 2: Overview of the proposed framework, detailing three main components for enhanced deepfake detection.
Methodology
Knowledge-guided Forgery Detection Module
The core of the framework is the Knowledge-guided Forgery Detection module, which relies on creating consistency maps between visual and textual embeddings. By leveraging pretrained image and text encoders, the module aligns visual features extracted at various layers with textual descriptions of real and fake images. This alignment is vital for generating visual-text correlations that improve the model's capability to discern forgery artifacts.

Figure 3: Overview of the Knowledge-guided Forgery Detector, showing the process of computing consistency maps from modalities.
Forgery Prompt Learner
The Forgery Prompt Learner plays a critical role in converting forgery-related features into forgery prompt embeddings. This approach ensures that the LLM receives fine-grained details necessary for accurate detection. This process involves a convolutional network and a fully connected layer that transforms localization maps and consistency maps into viable prompts for the LLM evaluation.

Figure 4: Architecture of the Forgery Prompt Learner, vital for capturing and embedding detailed forgery features.
Results and Evaluation
The proposed framework was extensively tested on multiple datasets, including FF++, CDF2, DFD, and DFDC. The results illustrated that the model not only outperformed existing deepfake detection methods on these benchmarks but also demonstrated a notable enhancement in generalization performance across unseen datasets. The cross-dataset evaluations highlighted significant improvements in AUC metrics, underscoring the framework's robustness in generalization capability.

Figure 5: GradCAM visualizations displaying forgery localization across datasets, proving the module's robustness.
Table 1 below summarizes the framework's performance, showing a clear edge over existing methods in both intra-dataset and cross-dataset settings.
| Method |
Intra-dataset AUC |
Cross-dataset Avg. AUC |
| Existing Methods |
97.23 - 99.87 |
69.90 - 95.40 |
| Proposed Framework |
99.53 |
92.39 |
Discussion
The integration of a Knowledge-guided Forgery Detector within the LVLM framework provides definitive enhancements in explainability without compromising generalization. The proposed model's ability to handle multi-turn dialogues aligns well with real-world applications, particularly within judicial or security frameworks. The document also illustrates the importance of fine-grained prompt tuning, using both real and simulated image-text pairs, to optimize the interactive capabilities of the LLM.
Conclusion
This study introduces a robust LVLM-based architecture for generalizable and explainable deepfake detection. By integrating a fine-tuned approach leveraging cross-modal encoders and a sophisticated prompt construction paradigm, the framework presents significant advancements in addressing the personalized deepfake threat. The findings pave the way for further exploration of LVLMs within interdisciplinary applications demanding high accuracy and interaction.






