Whose LLM is it Anyway? Linguistic Comparison and LLM Attribution for GPT-3.5, GPT-4 and Bard
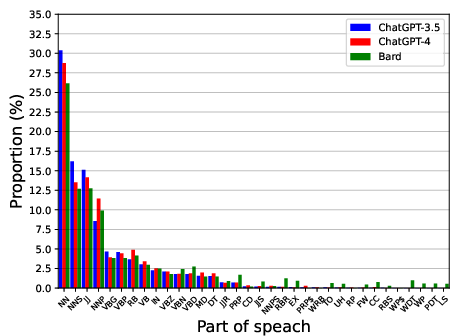
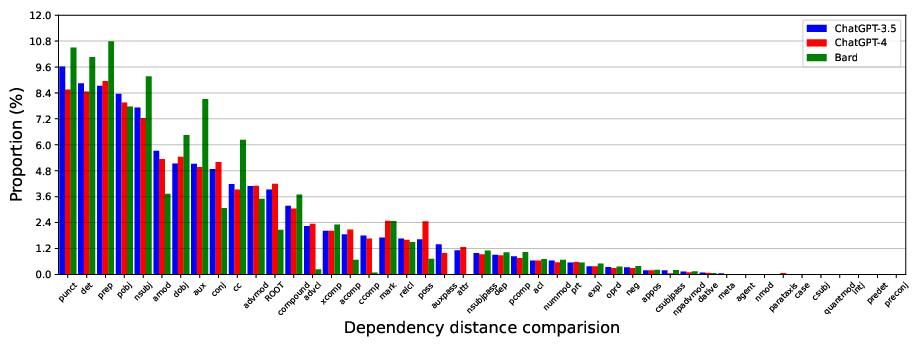
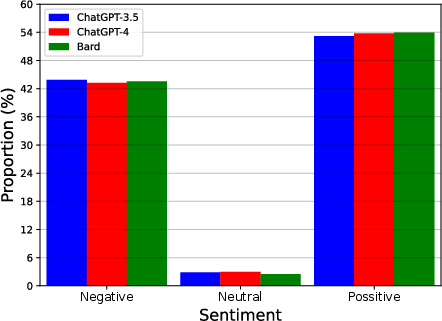
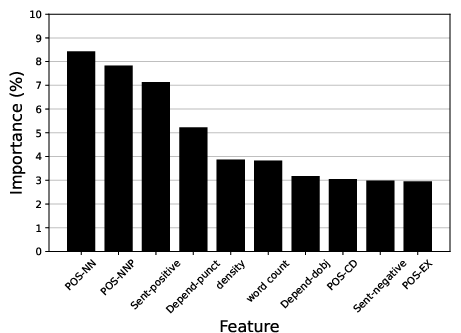
Abstract: LLMs are capable of generating text that is similar to or surpasses human quality. However, it is unclear whether LLMs tend to exhibit distinctive linguistic styles akin to how human authors do. Through a comprehensive linguistic analysis, we compare the vocabulary, Part-Of-Speech (POS) distribution, dependency distribution, and sentiment of texts generated by three of the most popular LLMs today (GPT-3.5, GPT-4, and Bard) to diverse inputs. The results point to significant linguistic variations which, in turn, enable us to attribute a given text to its LLM origin with a favorable 88\% accuracy using a simple off-the-shelf classification model. Theoretical and practical implications of this intriguing finding are discussed.
- Gpt-4 technical report. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.08774 (2023).
- Conda: Contrastive domain adaptation for ai-generated text detection. In Proceedings of the 13th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing and the 3rd Conference of the Asia-Pacific Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics (2023), Association for Computational Linguistics, pp. 598–610.
- Can linguists distinguish between chatgpt/ai and human writing?: A study of research ethics and academic publishing. Research Methods in Applied Linguistics 2, 3 (2023), 100068.
- Xgboost: A scalable tree boosting system. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (2016), p. 785–794.
- Efficient detection of llm-generated texts with a bayesian surrogate model. arXiv (2023).
- Distinguishing academic science writing from humans or chatgpt with over 99% accuracy using off-the-shelf machine learning tools. Cell Reports Physical Science (2023).
- ELI5: Long form question answering. In Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Florence, Italy, July 2019), A. Korhonen, D. Traum, and L. Màrquez, Eds., Association for Computational Linguistics, pp. 3558–3567.
- A survey on the possibilities & impossibilities of ai-generated text detection. Transactions on Machine Learning Research (2023).
- I slept like a baby: using human traits to characterize deceptive chatgpt and human text. In International workshop on implicit author characterization from texts for search and retrieval (IACT’23) (2023).
- Llm censorship: A machine learning challenge or a computer security problem? arXiv (2023).
- How close is chatgpt to human experts? comparison corpus, evaluation, and detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:2301.07597 (2023).
- Writing through time: longitudinal studies of the effects of new technology on writing. British Journal of Educational Technology 32, 2 (2001), 141–151.
- Using new technology to assess the academic writing styles of male and female pairs and individuals. Journal of Technical Writing and Communication 33, 3 (2003), 243–261.
- A large-scale comparison of human-written versus chatgpt-generated essays. Scientific Reports 13, 1 (2023), 18617.
- Outfox: Llm-generated essay detection through in-context learning with adversarially generated examples. arXiv (2023).
- A survey on stylometric text features. In 2019 25th Conference of Open Innovations Association (FRUCT) (2019), pp. 184–195.
- Multiple-attribute text rewriting. In International Conference on Learning Representations (2019).
- Authorship obfuscation in multilingual machine-generated text detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:2401.07867 (2024).
- Www’18 open challenge: financial opinion mining and question answering. In Companion proceedings of the the web conference 2018 (2018), pp. 1941–1942.
- Voice in academic writing: The rhetorical construction of author identity in blind manuscript review. English for Specific Purposes 26, 2 (2007), 235–249.
- Chatgpt and bard exhibit spontaneous citation fabrication during psychiatry literature search. Psychiatry Research 326 (2023), 115334.
- The linguistic features of writing quality. Written Communication 27 (2010), 57–86.
- Contrasting linguistic patterns in human and llm-generated text. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.09067 (2023).
- Natural language processing: an introduction. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association 18, 5 (2011), 544–551.
- Training language models to follow instructions with human feedback. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 35 (2022), 27730–27744.
- Can ai-generated text be reliably detected? arXiv (2023).
- Computer aided functional style identification and correction in modern Russian texts. Journal of Data, Information and Management 4 (2022), 25–32.
- You’ve got style: Detecting writing flexibility across time. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Learning Analytics And Knowledge (2015), Association for Computing Machinery, p. 194–202.
- Detectllm: Leveraging log rank information for zero-shot detection of machine-generated text. arXiv (2023).
- The science of detecting llm-generated texts. arXiv (2023).
- Ghostbuster: Detecting text ghostwritten by large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.15047 (2023).
- M4: Multi-generator, multi-domain, and multi-lingual black-box machine-generated text detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.14902 (2023).
- Fake news in sheep’s clothing: Robust fake news detection against llm-empowered style attacks. arXiv (2023).
- A survey on llm-gernerated text detection: Necessity, methods, and future directions. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.14724 (2023).
- WikiQA: A challenge dataset for open-domain question answering. In Proceedings of the 2015 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (Lisbon, Portugal, Sept. 2015), L. Màrquez, C. Callison-Burch, and J. Su, Eds., Association for Computational Linguistics, pp. 2013–2018.
- MedDialog: Large-scale medical dialogue datasets. In Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP) (Online, Nov. 2020), B. Webber, T. Cohn, Y. He, and Y. Liu, Eds., Association for Computational Linguistics, pp. 9241–9250.
- A survey of large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.18223 (2023).
Paper Prompts
Sign up for free to create and run prompts on this paper using GPT-5.
Top Community Prompts
Collections
Sign up for free to add this paper to one or more collections.