- The paper introduces a framework that cuts token consumption by replacing repetitive LLM inferences with learned policies.
- The methodology employs a two-stage Lifestyle Policy and a Social Memory that compresses inter-agent dialogues while maintaining behavioral fidelity.
- Experiments in simulated environments demonstrate up to 96.6% token cost reduction with comparable task performance and authentic agent interactions.
Affordable Generative Agents
The paper introduces the Affordable Generative Agents (AGA) framework, aimed at reducing the cost of creating believable interactions in LLM-based environments. It addresses the cost issues critically impeding the deployment of LLM agents for prolonged interactions by substituting repetitive LLM inferences with learned policies and compressing inter-agent dialogue information. Extensive experiments demonstrate the framework's efficacy in achieving significant cost reductions while maintaining performance, thereby facilitating more practical applications in dynamic, large-scale environments.
Introduction
The primary motivation for the Affordable Generative Agents framework is derived from the significant costs associated with maintaining prolonged interactions in LLM-based agents. Traditional use of LLMs incurs substantial costs due to frequent model invocations during agent-environment and inter-agent interactions. The AGA framework mitigates these costs by introducing two core components: the Lifestyle Policy for agent-environment interactions and the Social Memory for inter-agent engagements.
The Lifestyle Policy essentially replaces repetitive decision-making processes by reusing previously inferred strategies, while the Social Memory component optimizes dialogue information management by modeling and compressing social interactions. AGA proves advantageous in various environments, such as "Stanford Town" and VirtualHome, demonstrating a significant reduction in token consumption while retaining comparable performance levels.
Methodology
Agent-Environment Interactions
The AGA framework leverages the Lifestyle Policy to minimize redundant inference costs. The Lifestyle Policy operates in two stages: Plan Decomposition and Policy Reuse. During Plan Decomposition, LLMs generate high-quality plans for novel situations, breaking them down into executable actions. Policy Reuse identifies prior plans within the Lifestyle Policy library that match new scenarios, executing them based on predefined conditions, thereby reducing inference calls.
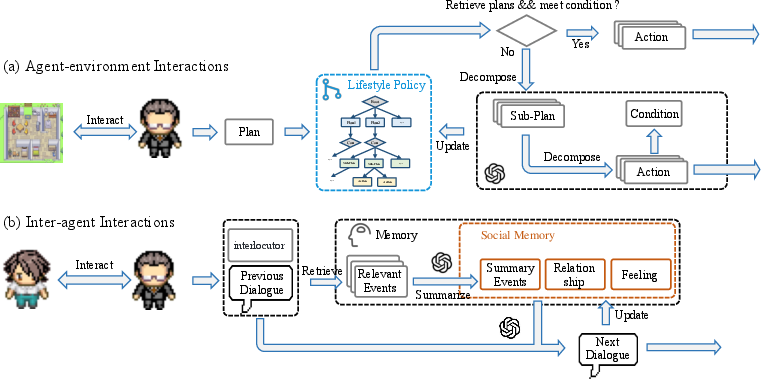
Figure 1: The AGA framework, including (a) Agent-environment interactions and (b) Inter-agent interactions.
Inter-Agent Interactions
The Social Memory module focuses on compressing auxiliary information required for inter-agent dialogues. It comprises components such as Relationship, Feeling, and Summary Events that succinctly represent social connections. The module updates dynamically, allowing agents to generate contextually relevant dialogues while minimizing prompt length, thus reducing computational costs.
An innovative aspect of the Social Memory is its ability to track relationship evolution over time, providing insights into the dynamics of agent interactions. These capabilities are essential for investigating the emergent social behaviors within agent populations.

Figure 2: An example of relational evolution driven by the updating of Social Memory following conversational interactions.
Evaluation
Generative Agents Case Study
In the Generative Agents simulations, AGA's implementation resulted in a drastic reduction in token consumption to 31.1% of the baseline in a 3-agent setup and 42.7% in a 25-agent setup. The AGA framework's efficacy was further corroborated through qualitative assessments, including agent interviews and specific event studies, confirming the preservation of behavioral authenticity despite cost reductions.
VirtualHome Application
For the VirtualHome environment, AGA reduced token costs to merely 3.4% of the baseline while achieving comparable task success rates. The Lifestyle Policy's integral role was evident in efficiently managing high-frequency, low-diversity tasks inherent to the household setting.

Figure 3: An activity generated by our AGA framework in VirtualHome.
Discussion
The research explores the emergence of believable behaviors in sandbox environments, revealing an inherent ceiling to such behaviors chiefly defined by the confines of agent profiles. This insight propels the proposal of strategies, like mind wandering, which incorporate unpredictable elements into decision-making, thereby enhancing behavioral diversity.

Figure 4: Cumulative number of activity types over run iterations in Generative Agents. The abbreviations ML, IR, and KM stand for the agents Maria Lopez, Isabella Rodriguez, and Klaus Rodriguez, respectively.
Conclusion
The Affordable Generative Agents framework represents a significant advancement in the sustainable deployment of LLM agents through cost reduction strategies without sacrificing behavioral fidelity. Future directions entail refining the Lifestyle Policy and addressing latency challenges. The framework is a stepping stone to broader LLM applications, particularly in extensive and dynamic environments, heralding more accessible and efficient agent-based simulations.



