- The paper demonstrates that integrating ChatGPT and REBEL significantly enhances the extraction of entities and relations for effective knowledge graph construction.
- The methodology leverages sequential processing and prompt engineering to manage token limitations and accurately extract semantic triplets from sustainability news articles.
- The results indicate ChatGPT's superior performance in recognizing entities while highlighting the need for improved structural consistency in the generated knowledge graphs.
Enhancing Knowledge Graph Construction Using LLMs
Introduction
The paper "Enhancing Knowledge Graph Construction Using LLMs" explores the integration of advanced LLMs with semantic technologies to improve the process of creating Knowledge Graphs (KGs) from unstructured text data. The research focuses on the application of foundational LLMs, such as ChatGPT, alongside specialized models like REBEL for joint entity and relation extraction. Through experiments centered around sustainability-related content, the study evaluates the efficacy of these models in automating the creation and enhancement of KGs, which are critical for various applications, including search engines and recommendation systems.
Methodologies
LLMs and Their Role in KG Construction
LLMs have shown promise in processing vast amounts of text data, achieving state-of-the-art results in multiple NLP tasks, including Named Entity Recognition (NER), Relation Extraction (RE), and Semantic Parsing. The paper employs two primary models: REBEL, a seq2seq model based on BART and specialized in end-to-end relation extraction, and ChatGPT, a conversational agent utilizing a generative approach. Both models, albeit with different strengths, are leveraged to construct KGs by parsing raw text into structured triplet formats.
Data Collection and Preprocessing
The data for experiments was sourced using the News API, collecting 94 articles related to sustainability. Due to input token limitations in LLMs, necessary preprocessing steps were employed to segment articles exceeding the manageable token length for effective processing by the models.
REBEL is utilized for its proficiency in generating triplets by tokenizing texts into batches, thus enabling the extraction of relations from lengthy documents. Despite challenges in relation extraction due to batch segmentation, REBEL's sequential processing reliably identifies subject-relation-object triplets.
ChatGPT's conversational model was employed in two experimental setups. The first used prompting to perform direct relation extraction, while the second aimed to automatically generate a comprehensive ontology and populate the KG. The second approach showed improved results by refining prompts to dictate KG construction procedures, showcasing ChatGPT's adaptability through prompt engineering.
Results and Evaluation
Comparative Analysis of Knowledge Bases
The performance of REBEL and ChatGPT was quantitatively assessed based on the number of entities, relations, and triplets extracted. ChatGPT outperformed REBEL in the number of recognized entities and relations. However, it lacked structure, often resulting in fragmented KGs with entities connected by ambiguous relations.
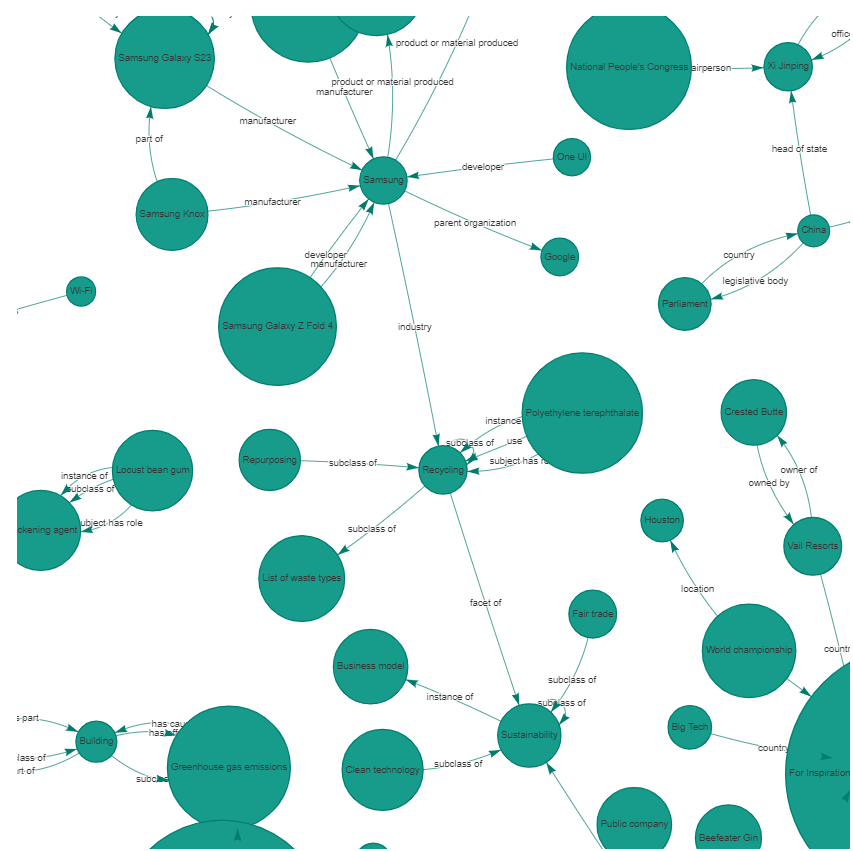
Figure 1: Subset of the Knowledge Base generated using the REBEL model. The Knowledge Base is displayed in a graph format where entities are represented as nodes and relations are represented as edges.

Figure 2: Subset of the Knowledge Base generated using the first experiment with ChatGPT. The Knowledge Base is displayed in a graph format where entities are represented as nodes and relations are represented as edges.
Qualitative Assessment
The qualitative evaluation, based on established principles for KG quality, indicated ChatGPT's potential to create more comprehensive and meaningful KGs by employing detailed prompts, although there remains room for improvement in refining automatic ontology generation and relation consistency.
Conclusions and Future Directions
The integration of LLMs for KG construction demonstrates significant potential in processing unstructured data into actionable knowledge representations. The paper highlights the advantage of using ChatGPT for generating more coherent KGs when prompted appropriately. Future research directions propose formalizing evaluation frameworks for KG quality and extending the methodology across different domains to create unified KGs with consistent ontological structures for enhanced query resolution.
In conclusion, LLMs like ChatGPT, with the right prompting techniques, represent a promising approach for advancing the construction of KGs, providing a foundation for their application in automated and empirical analysis across diverse fields.



