- The paper introduces a formal PSN framework that leverages symbolic programs for continual, compositional skill learning in agents.
- It integrates mechanisms such as structured fault localization, maturity-aware update gating, and online canonical refactoring to optimize performance.
- Empirical results demonstrate PSN’s superior skill retention, efficient tech tree mastery, and robustness compared to competing methods.
Evolving Programmatic Skill Networks: Continual, Compositional Agent Skill Learning
Introduction and Framework
The paper "Evolving Programmatic Skill Networks" (2601.03509) articulates a formal framework for skill acquisition and continual improvement in embodied agents. The Programmatic Skill Network (PSN) is introduced as a symbolic, compositional skill library, where each skill is represented as an executable program (e.g., in JavaScript or Python) with explicit control flow, parameters, and logical pre/postconditions. Skills can invoke one another, establishing a dynamic invocation graph with explicit network structure, as shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1: The PSN framework manages a skill network N, wherein skills are synthesized, composed, executed, and continually refactored in interaction with an environment and a curriculum of tasks.
Three primary mechanisms underpin PSN:
- Reflect: A structured, LLM-based fault localization operator for symbolic credit assignment over nested skill compositions, decoupling credit propagation from code modification.
- Maturity-aware update gating: Adaptive modulation of optimization frequency, selectively stabilizing reliable skills while maintaining plasticity for immature or under-optimized skills.
- Canonical refactoring: Online, semantics-preserving graph rewrites (e.g., parameter extraction, common subskill factoring, deduplication) validated by rollback when network changes adversely impact performance.
Distinctly, the optimization behavior emerges not from the underlying LLM code model but from PSN’s architectural scaffolding, establishing parallels to neural network dynamics—symbolic backpropagation, freezing, and neural architecture search analogues.
Programmatic Learning and Symbolic Credit Assignment
PSN situates skill acquisition within an open-ended, sequential task stream, where each task is given in natural language and associated with a state predicate. Unlike flat or weakly-structured code repositories, the PSN’s codegraph enables formal manipulation: invocation traces are logged during skill execution, and in the event of failure, the Reflect operator recursively attributes credit by traversing call chains (akin to computational graph backpropagation).
Each skill s maintains an empirical quality score combining success rate and an uncertainty penalty, functioning as an explicit trust metric guiding both planning (via Boltzmann exploration) and update gating (through sigmoid-thresholded frequency modulation, parameterized by maturity). This supports selective freezing and targeted plasticity—a critical feature for mitigating catastrophic interference in continual skill learning.
Online Structural Refactoring and Abstractions
PSN systematically eliminates redundancy and discovers optimal program structure through five canonical refactor patterns:
- Parametric coverage: Specializations are replaced by parameterized abstractions.
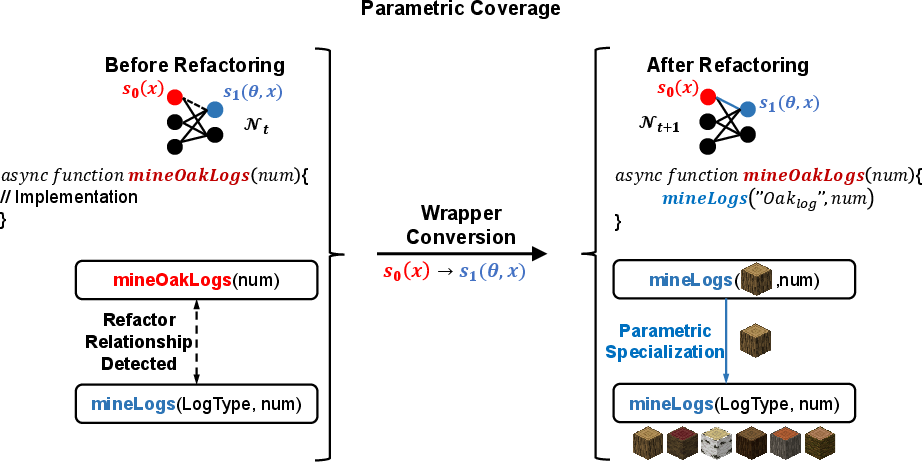
Figure 2: Parametric coverage—specialized skill is replaced with a parameterized generalization.
- Behavioral/subgraph coverage: Duplicated code blocks are abstracted via invocation of pre-existing skills.
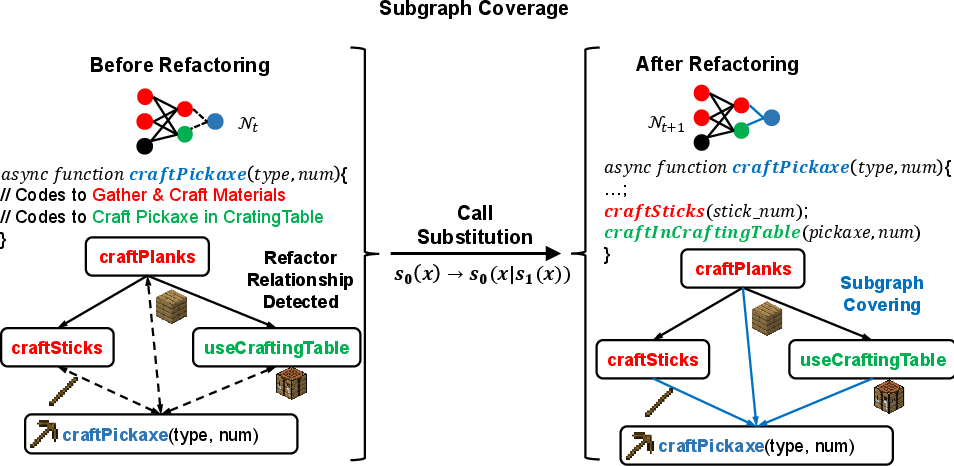
Figure 3: Behavioral coverage—internal duplication within a composite skill is replaced by reusable subskill invocation.
- Sibling specialization: Multiple specialized variants induce a missing abstraction identified and synthesized for reuse.

Figure 4: Sibling specializations highlight missing shared abstractions, which are synthesized and reused.
- Common subskill extraction: Repetitive subroutines are factored into shared subskills.

Figure 5: Common subskill extraction increases code reuse and reduces duplication by factoring out repeated logic.
- Duplication removal: Functionally equivalent skills are merged, unifying invocation and demoting aliases.

Figure 6: Duplication removal merges functionally identical skills, preserving only the canonical implementation.
Each refactor is applied online, subject to rollback validation: network changes are only retained if agent success on affected tasks is not significantly degraded, enforcing network compactness without compromising behavioral competence.
Empirical Results: Continual Learning, Generalization, and Robustness
Experiments are conducted on two challenging continuous-action embodied environments: MineDojo (an open-ended Minecraft environment) and Crafter (a survival/tech-tree environment with dense rewards and complex affordances).
- Skill acquisition efficiency: On MineDojo, PSN outpaces competing LLM-agent baselines (ReAct, Reflexion, AutoGPT, Voyager) in mastering long-horizon technology trees, successfully synthesizing deep, compositional skills with fewer iterations.

Figure 7: Tech tree mastery in Minecraft—PSN accelerates long-horizon technology acquisition compared to baselines.
- Dense reward performance: On Crafter, PSN demonstrates stable cumulative reward growth, consistently surpassing alternatives even under adverse survival scenarios.

Figure 8: PSN achieves robust cumulative rewards on Crafter, reflecting continual, stable progress.
- Skill retention and catastrophic forgetting: PSN maintains high skill retention rates across sequential curricula, contrasting with severe forgetting observed in Voyager as new tasks are introduced.
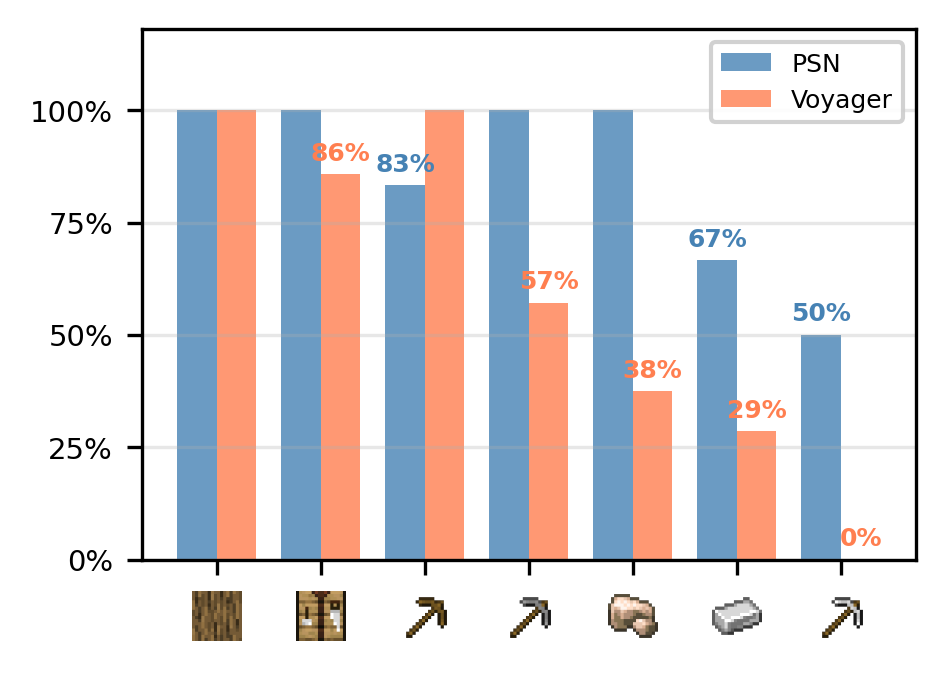
Figure 9: PSN preserves previously mastered skills during continual learning, while flat skill libraries exhibit catastrophic forgetting.
- Stabilization by maturity-aware update gating: Without update gating, skill libraries oscillate and degrade; with gating, cumulative success rates and network stability are significantly increased.

Figure 10: Maturity gating boosts cumulative success rates by reducing code churn on converged skills.
- Compositional generalization and network growth: Network-aware reuse, backward-chaining, and online refactoring enable PSN to maintain a compact yet expressive skill library. A variant without reuse grows unmanageably large skills with limited compositional generalization.

Figure 11: PSN controls skill repertoire growth via reuse and refactoring, maintaining compactness as task complexity increases.
Theoretical and Practical Implications
PSN establishes a discrete, programmatic variant of the structure-behavior tradeoff fundamental in neural networks. The analogy is evidenced in its:
- Symbolic backpropagation for local credit assignment
- Maturity-aware freezing for stability-plasticity arbitration
- Online symbolic neural architecture search for restructuring
These mechanisms demonstrate that continual skill learning is fundamentally architectural and not an artifact of neural parameterization. The explicit, inspectable programgraph provides strong interpretability advantages and paves the way for formal reasoning, correctness verification, and robust transfer. The modularity and abstraction in PSN also enable zero-shot adaptation to novel compositional tasks via code reuse and network rewiring, not observed in monolithic code memory systems.
Limitations and Future Directions
The current PSN instantiation is online, batch-size-one, with limited theoretical convergence guarantees. Scaling to parallel, high-throughput agents and developing formal optimality criteria for symbolic program-space projection remain open problems. The framework, however, is architecturally general: as code synthesis backends improve—through increasingly capable LLMs or mechanistic symbolic methods—PSN is expected to become more efficient.
Practically, PSN motivates future research into hybrid neuron-symbolic architectures, interpretable agent frameworks, and robust, lifelong compositionally adaptive skill learning at scale.
Conclusion
PSN presents a principled and scalable approach to continual, compositional skill learning via symbolic program evolution, structured credit assignment, adaptive stabilization, and formal refactoring. The work concretely demonstrates that well-founded architectural mechanisms are essential for robust skill acquisition and retention in embodied agents and highlights unifying optimization principles across differentiable and programmatic learning systems.












