- The paper demonstrates that explicit spatiotemporal synchrony modeling via the SyncFusion module enhances joint audio-video comprehension and generation.
- It employs hierarchical learnable queries and a diffusion-based JavisDiT generator to effectively align multimodal inputs with output conditions.
- It achieves state-of-the-art performance in synchronization quality and data efficiency, validated across multiple audio-video benchmarks.
JavisGPT: A Unified Multi-modal LLM for Sounding-Video Comprehension and Generation
Overview
JavisGPT introduces a unified multimodal LLM (MLLM) architecture specialized for joint audio-video (JAV) comprehension and generation. Existing MLLM paradigms largely treat audio and video as decoupled modalities or perform late-stage feature integration, resulting in suboptimal temporal alignment and limited joint generation capacity. JavisGPT makes several key advances including the proposed SyncFusion module for explicit spatiotemporal synchrony modeling, hierarchical learnable queries for controlling a diffusion-based generator (JavisDiT), and the construction of JavisInst-Omni—a large, high-quality, synchrony-aware instruction-tuning dataset. Experimental results confirm JavisGPT's state-of-the-art performance across JAV comprehension and high-fidelity, synchronized audio-visual generation tasks, with significant efficiency in data usage.
Model Architecture and Synchronization Mechanisms
JavisGPT adopts an encoder–LLM–decoder architecture, with Qwen2.5 as the LLM backbone and a frozen vision encoder (Qwen2.5-VL) alongside the BEATs audio encoder. Inputs (text, audio, video) are processed in parallel and mapped into the LLM's token space, with further integration via several carefully designed modules:
- SyncFusion Module: Rather than simple concatenation or interleaving, SyncFusion aligns temporally segmented audio tokens to corresponding video frames, using cross-attention to inject audio cues into local video patches. This process yields SyncAV tokens with explicitly encoded spatiotemporal correlations.

Figure 1: SyncFusion aligns segmented audio tokens with video frames via cross-attention, generating tokens that capture local, temporally-synchronized audio-visual events.
- Hierarchical Learnable Queries: Two categories of learnable queries are used. Semantic queries bridge the LLM's final hidden states to the JavisDiT generator's condition embedding space; spatiotemporal-prior queries encode structured priors governing when and where audio-visual events should occur. These are projected with MLPs and optimized via alignment and diffusion losses that match the generated conditions to those from pretrained encoders and reference priors.
- JavisDiT Generator Integration: Rather than fine-tuning the Diffusion Transformer (DiT) itself, JavisGPT freezes it and instead learns to project LLM latent representations into the generative model's conditional space, greatly simplifying optimization and decoupling comprehension from generation.

Figure 2: Overall JavisGPT architecture, showing input processing, SyncFusion-based integration, instruction injection, and conditioning of the diffusion-based generator for synchronized audio-video output.
Training Pipeline and Instruction Dataset
The training procedure consists of three progressive stages:
- Multimodal Pretraining (MM-PreTrain): Introduces the audio branch and aligns LLM output with generative condition space.
- Audio-Video Fine-Tuning (AV-FineTune): Refines synchrony modeling via SyncFusion and hierarchical queries, optimizing comprehension and generation for joint AV data.
- Multimodal Instruction Tuning (MM-InstTune): Enables generalizable instruction following and cross-modal reasoning using the JavisInst-Omni dataset.
To support instruction tuning, the authors constructed JavisInst-Omni, a 200K-turn dataset of GPT-4o-curated, dialog-style multi-modal (audio-video-text) examples designed to explicitly test multi-level comprehension and synchronized audio-video generation capabilities.
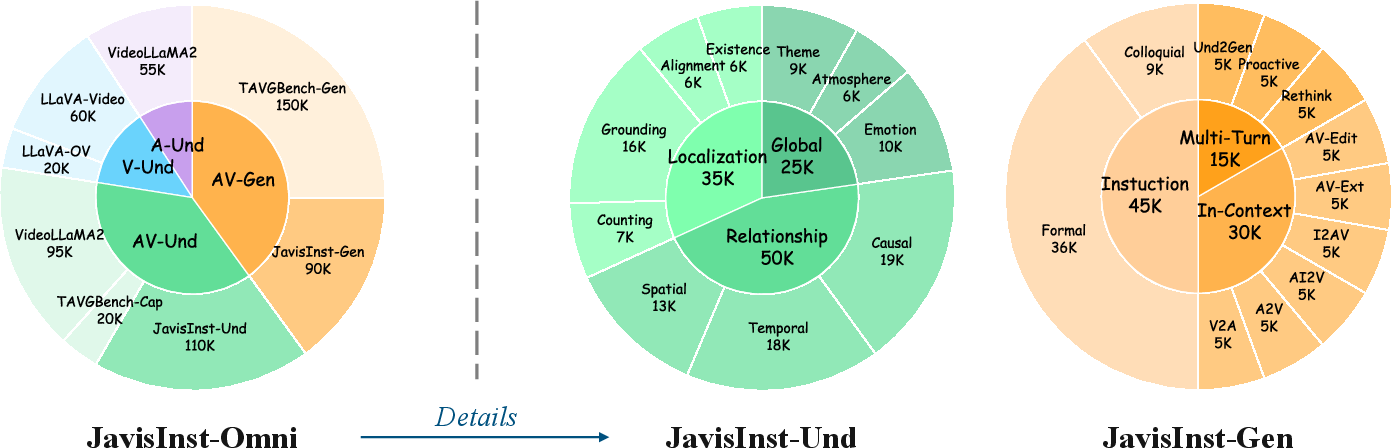
Figure 3: Distribution and content of JavisInst-Omni for comprehensive instruction-tuning in JAV scenarios.
Joint Comprehension and Synchronized Generation
During inference, the model can simultaneously process multiple modalities of input and produce multimodal outputs. Synchronized audio-video generation is controlled via hierarchical queries that encode both semantic and fine-grained spatiotemporal information. The approach allows for instruction-driven generation and in-context, interleaved conversation over multiple rounds, supporting both QA-style understanding and proactive content generation.

Figure 4: Instruction-followed and synchronization-enhanced generation pipeline, with queries interfacing LLM latent space and DiT condition embeddings, all optimized via combined alignment and diffusion objectives.
Experimental Results and Ablations
JavisGPT achieves or exceeds SOTA on a suite of benchmarks assessing both unimodal and joint audio-video comprehension (ActivityNet, Perception, MVBench, ClothoAQA, MU-AVQA, AVQA, etc.), as well as high-fidelity, temporally-aligned text-to-audio-video generation (JavisBench-mini). Particularly notable are:
- Superior Data Efficiency: SOTA results are achieved with fewer training samples than competitive models.
- AV Synchrony and Quality: JavisGPT outperforms both prior modular and unified MLLMs such as NExT-GPT and UnifiedIO-2 in generation quality (FVD=317.5, KVD=1.8, JavisScore=0.157), matching or slightly exceeding standalone generative baselines like JavisDiT in both quantitative and human studies.
- Joint Training Synergy: Ablation studies show that joint comprehension/generation training regimes mutually enhance both modalities, with the greatest gains in the generative track.

Figure 5: Case study demonstrating robust, context-aware joint AV understanding and generation over multiple dialog rounds, illustrating the model's ability to both ground and synthesize audio-visual content.
Design Rationale and Comparative Analysis
The design of JavisGPT reflects a careful balancing of modularity and integration. Analysis of possible architectures shows that the LLM+DiT combination, augmented with learnable queries and explicit synchrony modeling, is more scalable and tractable than monolithic AR models or architectures entirely unifying comprehension/generation losses, especially at current generative model scales.

Figure 6: Architecture comparison showing the tradeoffs between LLM+DiT (as in JavisGPT), monolithic AR-based approaches, and hybrid pipelines.
Further, retaining support for a pretrained text encoder in the DiT generator, in contrast to designs like MetaQuery that remove it, stabilizes training and preserves generalization to free-form, instruction-driven multimodal tasks.

Figure 7: Comparison of LLM+DiT bridging strategies, showing JavisGPT's hybrid query/encoder arrangement yields superior training stability and content diversity.
Implications and Future Directions
JavisGPT establishes that joint, tightly synchronized audio-video comprehension and generation are tractable and can benefit from explicit synchrony modeling, hierarchical condition control, and high-quality diverse instruction tuning. The model's efficient architecture and data pipeline offer a pragmatic blueprint for further research.
Potential future directions include:
- Scaling model and data magnitude to test the limits of this paradigm across much broader instruction and generation spaces.
- Tightening the unification of comprehension and generation, e.g., using AR-based continuous representations to more deeply fuse input/output modalities.
- Augmenting with more granular control signals for fine-editing and compositional content creation.
- Incorporating reinforcement learning post-training to improve reasoning and generation alignment in more open-ended dialog scenarios.
Conclusion
JavisGPT represents a significant technical advance in unified multimodal LLMs, achieving state-of-the-art accuracy and high-fidelity, synchronized sounding-video generation. Its modular, synchrony-aware architecture and comprehensive, diverse instruction-tuning data demonstrate a compelling path forward for research at the intersection of AV perception, reasoning, and controllable generation.

Figure 8: Additional qualitative results displaying the system's high-fidelity, synchronous AV comprehension and generation across a range of realistic scenarios.











