- The paper introduces a dual-branch Perceptual 4D Distillation framework that transfers both latent and explicit signals to enable region-level spatiotemporal reasoning in MLLMs.
- Empirical evaluations on R4D-Bench and legacy VQA benchmarks demonstrate up to a +5.3% accuracy gain in dynamic scene comprehension over existing methods.
- The integration of Timestamp Positional Encoding and specialized distillation enables precise grounding and interpretable low-level 4D signals without additional inference overhead.
Region-level 4D Understanding with Perceptual Distillation: An Expert Review of "4D-RGPT" (2512.17012)
Motivation and Problem Setting
The 4D-RGPT paper addresses a critical shortcoming in multimodal LLMs (MLLMs): their inability to perform effective reasoning over spatio-temporal (4D) signals at region-level granularity. Tasks such as autonomous driving and industrial inspection require models capable of grounding language to spatiotemporal regions and answering queries conditioned on object-level movement, 3D interactions, and temporal progression. The authors identify that previous benchmarks are either restricted to static scenes or lack region prompting, and that existing solutions relying on external modules or self-curated supervised data do not adequately impart 4D perceptual competence, especially under resource constraints typical of dynamic video scenarios.
4D-RGPT Architecture and Perceptual 4D Distillation (P4D)
The centerpiece of the proposed solution is a specialized MLLM, 4D-RGPT, which is engineered to capture both latent and explicit 4D representations from video inputs through the Perceptual 4D Distillation (P4D) framework.
P4D strategically utilizes a frozen expert 4D perception model as a teacher, transferring its capability to the student 4D-RGPT via dual distillation branches:
- Latent Distillation: Aligns the latent intermediate activations (F^4D) of the student with the teacher’s embeddings, functioning as abstract 4D guidance.
- Explicit Distillation: Supervises explicit low-level signals for modalities such as per-pixel depth, optical flow, 3D motion masks, and Plucker camera rays, ensuring the model can produce interpretable, physically-grounded outputs.
Importantly, all perception modules used for distillation are training-only. No additional inference burden is incurred compared to the backbone MLLM. Timestamp Positional Encoding (TPE) is incorporated into the visual features, enabling the model to leverage temporal progression cues required for precise 4D question answering.

Figure 1: Perceptual 4D Distillation (P4D) framework for 4D-RGPT illustrating latent and explicit knowledge transfer pathways alongside timestamp encoding integration.
R4D-Bench: A Benchmark for Region-prompted 4D VQA
To enable comprehensive evaluation, the paper introduces R4D-Bench, constructed via an automated and human-verified pipeline that overlays region-level prompts onto conventional VQA benchmarks. The curation process proceeds as follows: (a) extraction of key object mentions from questions, (b) segmentation mask acquisition (either ground truth or via GroundingDINO and SAM2), (c) generation of Set-of-Marks visual overlays for frame-wise region marking, (d) automated region-to-query matching via Qwen-2.5VL, and (e) thorough human expert verification.

Figure 2: R4D-Bench curation pipeline showing extraction, segmentation, marking, automated matching, and verification steps for region-prompted video QA.
R4D-Bench covers both static and dynamic scenes—including tasks requiring measurement, grounding, spatial relations, counting, movement categorization (translational/rotational), false positive detection, and quantitative analysis of displacement, speed, and acceleration. Region-level masks enable precise, controlled grounding absent in prior datasets.
Empirical Evaluation and Numerical Results
The authors conduct extensive evaluation on both legacy benchmarks (STI-Bench, VLM4D-real, MMSI-Bench, SAT, OmniSpatial, VSTI-Bench) and R4D-Bench. 4D-RGPT achieves systematic accuracy lifts compared to strong open-source and proprietary MLLMs. Notable results include:
- +5.3% mean accuracy gain across six non-region 4D VQA benchmarks over backbone (NVILA-Lite-8B).
- +4.3% accuracy improvement on R4D-Bench compared to the strongest baseline.
Qualitative analysis demonstrates 4D-RGPT’s ability to correctly answer queries regarding region-specific temporal events—such as speed estimation and dynamic object interactions—where other MLLMs fail due to misalignment or lack of temporal/depth discrimination.

Figure 3: VQA comparison between top baselines and 4D-RGPT, highlighting failure modes of standard MLLMs in region-level dynamic scene QA.
Ablation studies evaluate naive alternatives (direct supervised fine-tuning, concatenation/projection of teacher features) and confirm that only dual-branch perceptual distillation achieves optimal trade-off between accuracy and compute. Additional experiments show the necessity of both latent and explicit branches and the impact of timestamp encoding. Visualizations of explicit signals (e.g., predicted depth maps) track the emergence of 3D perception within the MLLM during training.
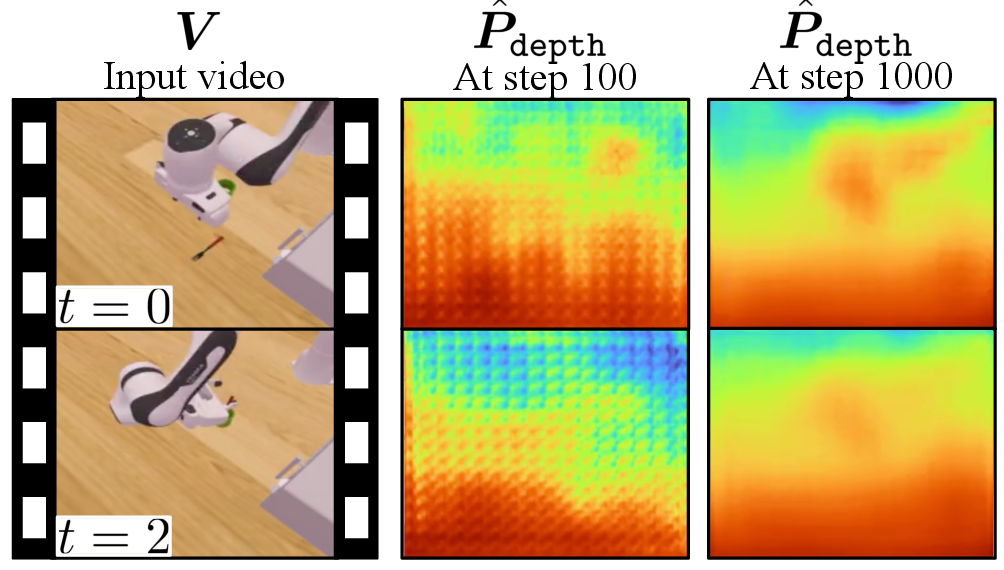
Figure 4: Predicted depth maps from 4D-RGPT at successive training steps, visualizing the evolution of learned spatiotemporal structure.
Benchmark Analysis and Visual Grounding
The R4D-Bench paradigm enables categorically granular evaluation, with dedicated figures exemplifying each question type: translational (Figure 5), rotational (Figure 6), counting (Figure 7), false positive (Figure 8), 3D grounding (Figure 9), spatial relation (Figure 10), dimension measurement (Figure 11), displacement/path length (Figure 12), and speed/acceleration (Figure 13).
Each example illustrates the requirement for precise region-level tracking and quantitative reasoning over spatial, temporal, and geometric cues.

Figure 5: R4D-Bench example - region-specific translational movement assessment.
Practical and Theoretical Implications
The proposed distillation protocol endows MLLMs with fine-grained, low-level spatiotemporal perception previously achievable only through expensive, inference-time auxiliary models or laborious supervised pipelines. The significant inference savings and absence of architectural modification directly address deployment constraints in robotics, autonomous systems, and real-time spatiotemporal analytics.
The demonstration of Timestamp Positional Encoding efficacy foregrounds the importance of explicit temporal grounding in MLLM architectures and points to future combinatorial advances leveraging both learned and handcrafted signals.
By introducing the R4D-Bench benchmark, the paper sets a new standard for region-based spatiotemporal reasoning, supporting the development and fair comparison of next-generation multimodal models.
Conclusion
This work presents an integrated solution to the challenge of region-level 4D perception in MLLMs via a training-only dual-branch distillation framework. Its robust empirical performance and principled design distinguish it as a reference architecture for future research in spatial-temporal vision-language alignment, with significant applicability across domains demanding localized dynamic scene understanding. The accompanying benchmark and analysis will likely serve as anchors for subsequent developments in efficient, controllable, and interpretable 4D multimodal intelligence.








