- The paper presents a unified post hoc explainability framework that integrates eleven attribution methods with concept-based analysis for transformer models.
- The API streamlines model audits by supporting token-level to sequence-level explanations and unsupervised concept discovery using diverse algorithms.
- Quantitative metrics for faithfulness, stability, and complexity benchmark the reliability of explanations, advancing robust interpretation of deep language models.
Motivation and Positioning
Interpreto (2512.09730) introduces a unified post hoc explainability framework targeting HuggingFace transformer-based NLP models, extending across both classification and generation pipelines. The paper identifies the fragmentation of existing attribution and concept-based methods, many of which are modality-specific or dissociated across distinct libraries. Interpreto centralizes attribution and mechanistic interpretability workflows behind a standardized, reproducible Python API. The core emphasis is on integrating concept-centric analysis with attribution-based explanations, moving beyond conventional feature importance toward interpretable computational abstractions within deep models.
Attribution Methods and Implementation
Interpreto’s attribution module supports eleven established explainability techniques, spanning four perturbation-based and seven gradient-based algorithms. This suite includes KernelSHAP, LIME, Integrated Gradients, Saliency, SmoothGrad, and others, providing fine-grained attribution maps for both token- and sequence-level outputs. The library implements four model-agnostic evaluation metrics for faithfulness and comprehensiveness, thereby facilitating quantitative justification for explanation reliability. Users can select the explanation granularity (token/word/sentence), output space (logits/softmax/log-softmax), and input×gradient variants. Interpreto abstracts away most engineering overhead, allowing researchers to extend or adapt methods with minimal procedural complexity.
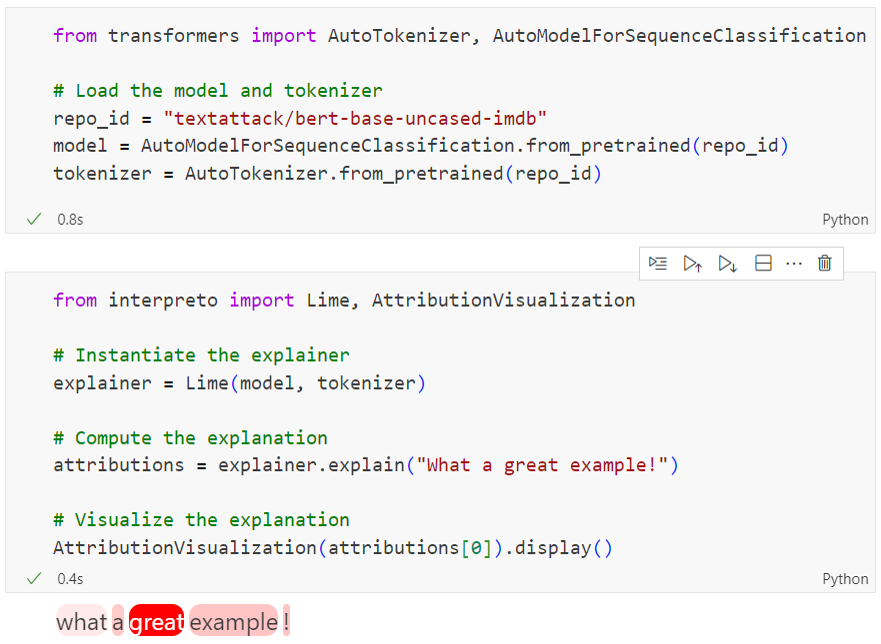
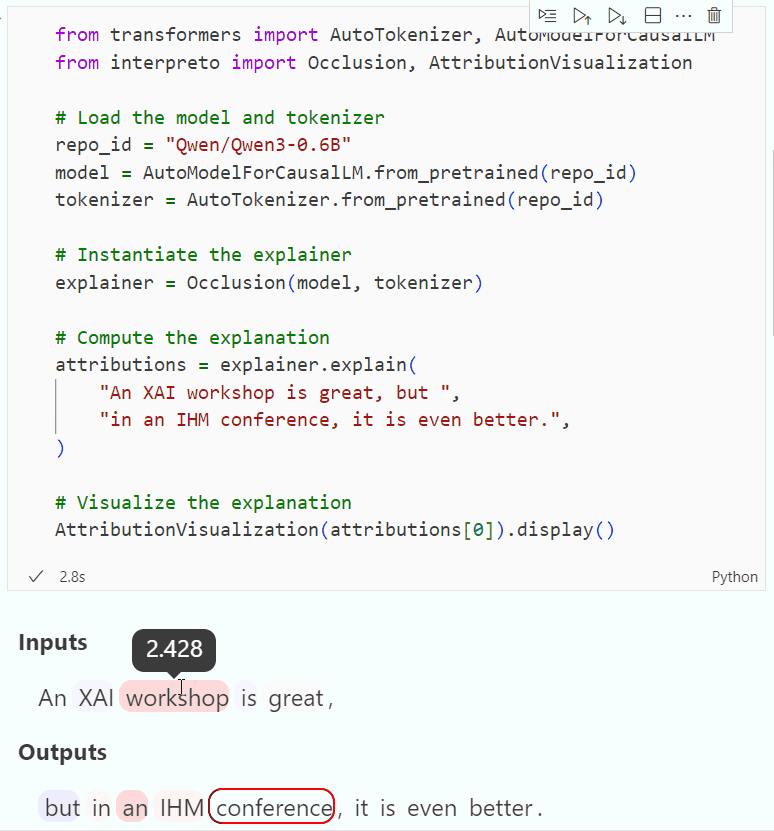
Figure 1: An attribution visualization for a classification model, showing token-level explanations for a sentiment prediction.
Concept-Based Interpretability
The concept-based module operationalizes mechanistic interpretability through post hoc unsupervised concept discovery. Leveraging the NNsight framework for model partitioning, Interpreto applies dictionary learning to extract interpretable concepts from transformer activations. Supported methods include KMeans, PCA, NMF, SVD, ICA, convex NMF, as well as multiple variants of sparse autoencoders (SAEs), such as vanilla SAEs, Jump-ReLU SAEs, and Matching Pursuit SAEs. These approaches produce low-dimensional concept spaces, aligning model features with human-interpretable abstractions or data-derived labels.

Figure 2: Post-hoc, unsupervised pipeline for concept-based interpretability, demonstrating activations extraction, dictionary learning, labeling, and importance quantification.
API and Workflow
Interpreto’s minimal code API guides users through four canonical steps for concept extraction:
- Splitting the HuggingFace model at suitable layers with NNsight.
- Collecting activations and fitting a dictionary-based concept model.
- Interpreting concept dimensions using data-driven labeling strategies.
- Quantifying concept-to-output gradients for importance analysis.
The system supports both global concept analyses—such as class-relevant features—and local analyses on specific samples. The API accommodates classifiers (using [CLS] tokens) and generative models (on non-special tokens), with tutorials for both.


Figure 3: Minimal Python code for the concept-based pipeline, illustrating a complete workflow for Qwen3-0.6B on AG News.
Concept Space Metrics and Evaluation
Interpreto incorporates seven quantitative metrics for evaluating concept faithfulness, stability, complexity, and usefulness. These include MSE, FID, sparsity, stability, and ConSim measures. Concept interpretation strategies implemented range from inspecting top-k vocabulary elements, MaxAct sample selection, to LLM-based automated labeling. The concept-to-output importance estimation supports gradient-based attribution in the concept space, with input-to-concept methods planned for future releases.

Figure 4: Global concept-based explanations for a DistilBERT classifier, demonstrating the identification and interpretation of salient concepts for each class.
Limitations and Development Trajectory
While Interpreto covers a broad set of attribution and concept-based methods, its scope does not include circuit-level mechanistic interpretability, multimodal models, or advanced feature visualization techniques. Planned extensions include integration of supervised post hoc concept discovery (probes, CAVs), additional interpretation metrics (Clarity, Purity), and enhanced GPU utilization. Multimodal capability, example-based explanations, and expanded inter-module connectivity (input-to-concept attributions) are stated as future objectives.
Practical and Theoretical Implications
Interpreto’s modular framework promotes reproducible, scalable explainability research by standardizing the interface between attribution and mechanistic interpretability pipelines in transformer models. The ability to flexibly combine attribution-level and concept-level analyses enables fine-grained model audits, robust error analysis, and systematic evaluation of model internal representations. The explicit focus on quantitative metrics for faithfulness and stability sets a benchmark for explainability best practices. The open-source nature, lightweight extensibility, and interoperability with HuggingFace and PyTorch position Interpreto as an asset for practical deployment and academic research.
The theoretical implications are notable: by facilitating large-scale, post hoc concept extraction and interpretation, Interpreto potentially accelerates analysis of feature entanglement and abstraction in deep LLMs. The tool can support empirical investigation of alignment, simulatability, and intervention, contributing foundational infrastructure to advancing safe and interpretable AI.
Conclusion
Interpreto establishes a comprehensive, extensible explainability toolkit for transformers, unifying attribution methods and concept-based pipelines for LLMs. By bridging practical usability with state-of-the-art mechanistic interpretability, it empowers data scientists and researchers to conduct robust, reproducible analysis of both classification and generation tasks. Ongoing development aims to expand the methodological depth and address emergent challenges in interpretable machine learning.





