- The paper introduces an innovative ARBB framework that achieves flicker-free long-range 4D motion modeling through bidirectional blending and on-demand key-frame anchoring.
- The paper employs Feature-variance-guided Hierarchical Densification to adaptively refine anchor points based on feature complexity, optimizing both reconstruction detail and memory usage.
- The paper validates MoRel on high-motion dynamic scenes, demonstrating superior reconstruction fidelity, reduced temporal inconsistencies, and enhanced scalability compared to prior methods.
MoRel: Anchor Relay-based Bidirectional Blending and Hierarchical Densification for Scalable Flicker-Free Long-Range 4D Gaussian Splatting
Problem Statement and Motivation
Modeling dynamic scenes for novel view synthesis requires handling both high visual fidelity and temporal consistency, especially over extended video sequences. While 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has enabled efficient real-time photorealistic rendering in static scenes, extending these methods to the temporal domain presents new challenges: naive all-at-once 4DGS approaches incur exponential memory usage and fail to handle occlusions and disocclusions robustly, while chunk-based methods optimize smaller temporal windows at the cost of temporal discontinuities and boundary artifacts. Prior methods employing sliding windows or hierarchical temporal structures have struggled to generalize, especially under practical constraints such as random frame access and system memory budgets (Figure 1).

Figure 1: Conceptual comparison of existing 4DGS methods, highlighting the fundamental trade-offs and system challenges in modeling long-range 4D motion.
MoRel Architectural Innovations
To address the limitations of prior methods, MoRel introduces an Anchor Relay-based Bidirectional Blending (ARBB) mechanism. The ARBB framework leverages periodically inserted Key-frame Anchors (KfAs) to define local canonical spaces, each optimized to represent temporally localized scene features. Bidirectional deformation fields between adjacent KfAs dynamically model complex motions, with a learnable temporal blending (opacity control) that ensures smooth transitions and effective handling of occlusion/disocclusion events. MoRel’s on-demand KfA loading maintains scalable memory usage and enables temporal random access. The four-stage training pipeline—global canonical anchor initialization, KfA optimization, progressive windowed bidirectional deformation (PWD), and intermediate frame blending (IFB)—systematically refines the representation without compromising temporal coherence (Figure 2, Figure 3).

Figure 2: MoRel framework overview—a multistage pipeline adapting ARBB and hierarchical densification for bounded memory and consistent long-range motion modeling.

Figure 3: Comparison of training strategies, illustrating the superior bounded memory and coherence of MoRel bidirectional blending relative to all-at-once and chunk-wise alternatives.
Feature-Variance-Guided Hierarchical Densification
MoRel further introduces Feature-variance-guided Hierarchical Densification (FHD), a novel anchor-point refinement strategy. By analyzing feature variance from global anchor training, anchor-points are assigned hierarchical levels that reflect local frequency complexity. Early training iterations prioritize stabilization of low-frequency regions, while later densification adaptively grows anchor-points in high-frequency regions using gradient-based statistics modulated by their level assignment. This frequency-aware protocol suppresses excessive anchor growth, preserves spatial detail, and optimizes memory allocation (Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6).
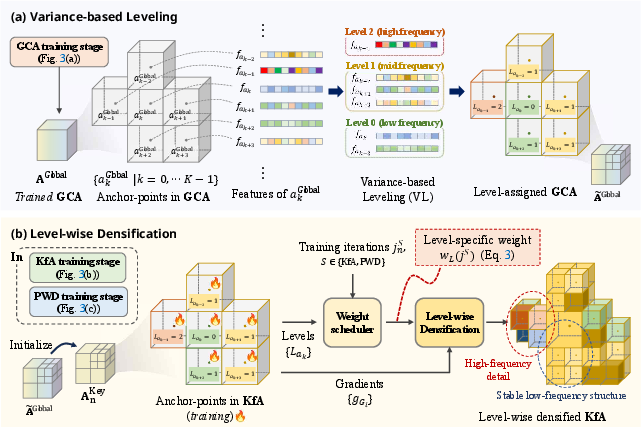
Figure 4: Feature-variance-guided Hierarchical Densification protocol—variance-based leveling and targeted anchor-point growth enable efficient detail refinement.

Figure 5: FHD visualization and frequency analysis, showing progressive high-frequency component emergence at higher anchor-point levels.

Figure 6: Hierarchical level-wise renderings demonstrate efficient static content reconstruction and detail recovery under adaptive densification.
Preventing Inter-Chunk Interference and Temporal Flicker
MoRel’s progressive windowed bidirectional deformation (PWD) and intermediate frame blending (IFB) stages mitigate backward contamination prevalent in naive chunk-wise training. PWD ensures independent temporal optimization windows for each anchor, whereas IFB fuses overlapping anchor regions with learnable temporal offset and decay parameters, eliminating ghosting and appearance shifts (Figure 7, Figure 8).

Figure 7: Visual example of backward contamination and object degradation in naive chunk-wise bidirectional deformation.

Figure 8: Temporal profile analysis—bidirectional deformation eliminates chunk boundaries and ensures flicker-free temporal continuity.
Extensive experiments on the newly proposed SelfCapLR dataset, containing high-motion and wide-spatial-range scenes over thousands of frames, demonstrate that MoRel achieves superior reconstruction fidelity (PSNR, SSIM, LPIPS), lowest temporal consistency error (tOF), and efficient memory utilization versus SOTA all-at-once and chunk-based competitors. Notably, MoRel maintains sharp reconstructions and prevents boundary flickering even under challenging dynamic content (Figure 9). Ablation analyses confirm the individual contributions of ARBB, PWD, IFB, and FHD to the overall system capacity and stability.

Figure 9: Qualitative comparison on SelfCapLR, highlighting sharper, temporally consistent modeling by MoRel in high-magnitude motion.
Practical and Theoretical Impact
MoRel’s architecture is directly applicable to memory-constrained long-range dynamic scene modeling, such as view synthesis in streaming or interactive environments. The ARBB design generalizes across varied motion patterns and spatial scales, and the FHD protocol offers a template for frequency-aware anchor refinement adaptable to large-scale and multi-modal input. The ability to support random-access rendering with bounded memory overhead marks a critical step toward real-time deployment in immersive applications.
On a theoretical level, MoRel advances learnable bidirectional blending in sparse anchor-based representations, connecting frequency analysis with anchor-point management. This opens new research avenues in multi-scale, spatio-temporal modeling, and dynamic resource allocation for neural graphics primitives.
Future Directions
While MoRel addresses many computational bottlenecks, further research is warranted on spatially expansive and rapidly varying scenes, where global anchors may lose representational coherence. Integration of spatial grid-aware scheduling and refined frequency estimation, leveraging recent advances in scalable neural view synthesis and blockwise scene partitioning, could enhance compositionality and further reduce boundary inconsistencies.
Conclusion
MoRel establishes a highly scalable and temporally stable paradigm for long-range 4D Gaussian Splatting via its ARBB mechanism and hierarchical densification. The approach simultaneously achieves flicker-free reconstructions, efficient memory usage, and competitive fidelity in challenging dynamic scenes, reflecting strong applicability to both academic study and real-world system design (2512.09270).










