- The paper introduces two novel black-box metrics, Semantic Faithfulness (SF) and Semantic Entropy Production (SEP), to quantify LLM alignment and hallucination risk.
- It employs a framework grounded in information theory and thermodynamics, using convex optimization over sentence embedding clusters to derive interpretable topic transitions.
- Empirical analyses reveal significant correlations between question entropy, SF, and SEP, offering actionable insights for robust LLM evaluation and prompt engineering.
Semantic Faithfulness and Entropy Production for LLM Evaluation
Introduction
This work introduces a principled framework for quantitative, reference-free evaluation of LLM faithfulness and hallucination detection, based on information-theoretic and thermodynamic foundations. The central contribution is two novel black-box metrics: Semantic Faithfulness (SF), which quantifies alignment between the question-induced and answer-induced transformations of context, and Semantic Entropy Production (SEP), which characterizes the thermodynamic irreversibility of the answer generation channel.
The paper conceptualizes LLMs as bipartite information engines, invoking the Maxwell's demon paradigm: a hidden controller mediates the transformation of input context C into answer A under the specification of a question Q. Topical representations are employed to construct marginal distributions over latent clusters for each element in the triplet, leading to the inference of optimal topic transition matrices via convex optimization. The resulting framework is both theoretically principled and practically feasible, requiring only sentence embeddings and standard optimization.
The approach formalizes each QCA triplet (Q,C,A) as a set of marginal distributions (p(q),p(c),p(a)) over semantic topics identified via clustering in embedding space. Two key row-stochastic transition matrices, Q and A, encode the mapping of context topics to question and answer topics, respectively. The Semantic Faithfulness score is then defined as
FS=1+Dmin1,
where Dmin is the minimum Kullback-Leibler divergence D(A∣∣Q) over all pairs of feasible matrices matching the constraints induced by the marginals. This setup exploits information geometry—a key property being joint convexity, ensuring global optimality via alternating minimization. High FS signals strong alignment of the semantic transformation specified by the prompt with that realized in the answer.
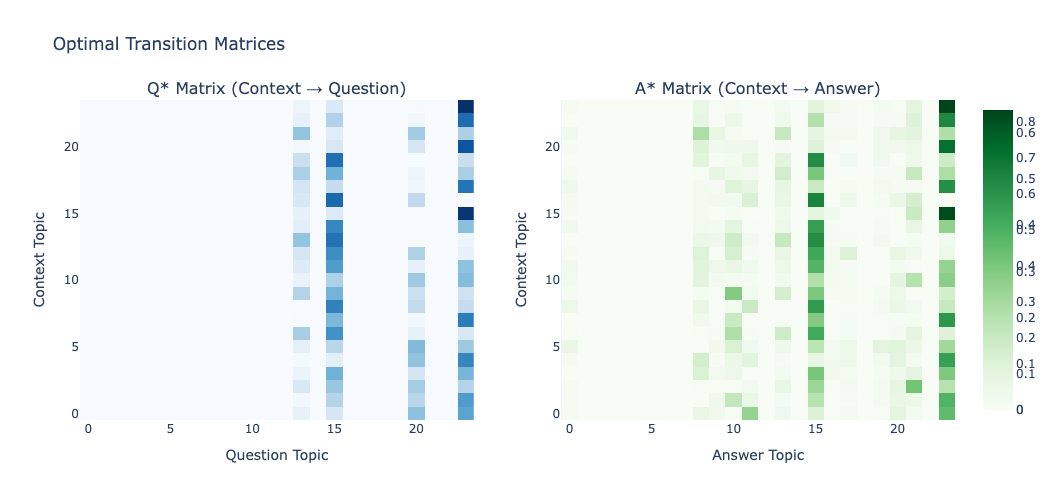
Figure 2: Optimal transition matrices Q⋆ and A⋆, both exhibiting sparse, interpretable alignments between context topics and those in question/answer.
The transition matrices themselves serve as interpretable artifacts that reveal how context is projected semantically into both question and answer spaces.
Thermodynamic Interpretation: Semantic Entropy Production
LLM answer generation is further analyzed through the lens of stochastic thermodynamics. The transition from C to A is treated as an out-of-equilibrium process, and SEP is derived as the minimal KL divergence between the forward (optimal) and a class of reverse transition matrices. The total entropy production S˙tot decomposes into:
S˙tot=H(p(a))−H(p(c))+S˙m
where S˙m is the dissipated "heat"—which, when negative, indicates the LLM draws on its internal knowledge base to produce more informative (higher entropy) answers than available in context alone.
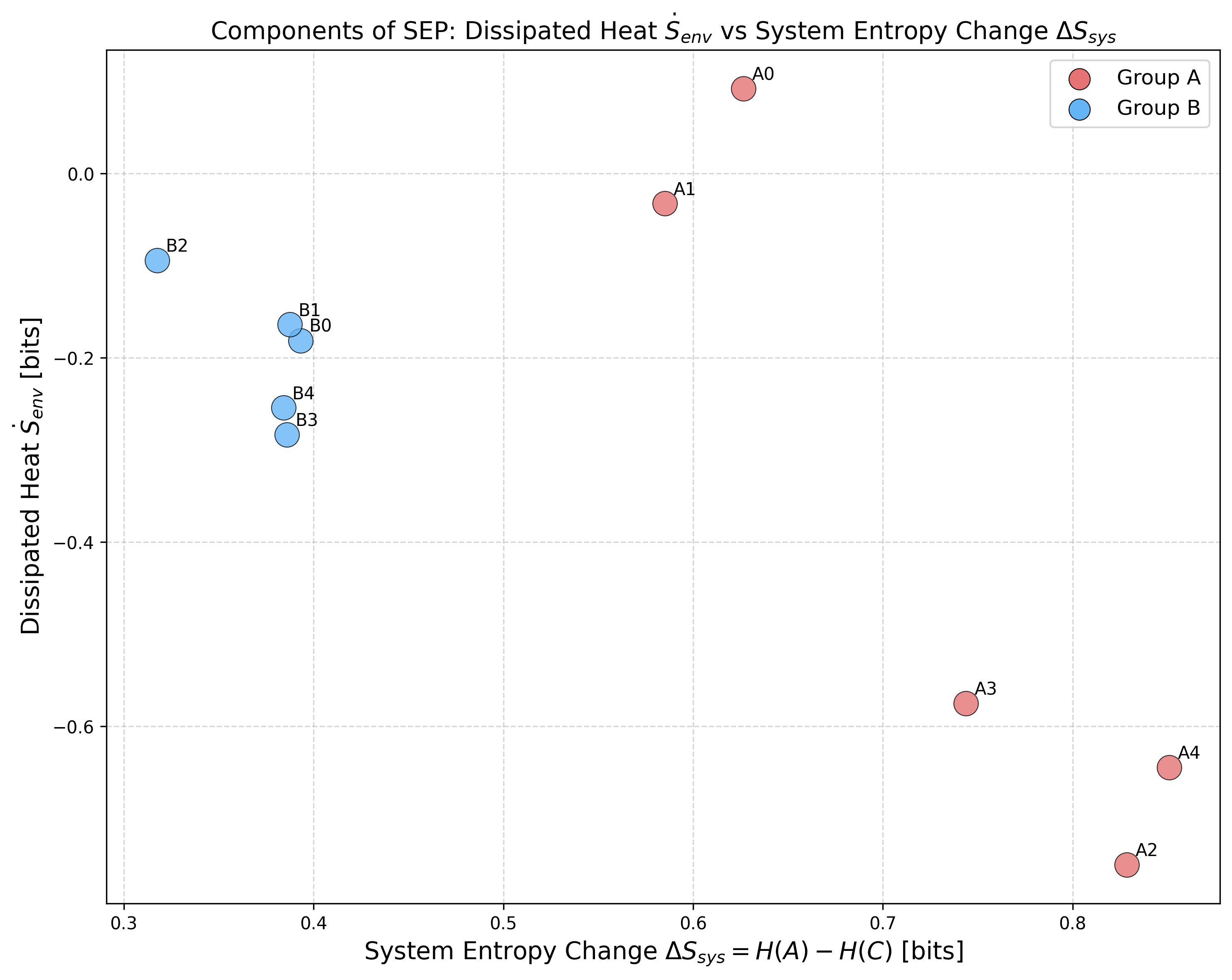
Figure 4: SEP decomposition shows negative S˙m for many QCA triplets, supporting the interpretation of knowledge injection from the model.
The SEP provides a theoretically motivated alternative to the recently proposed semantic entropy metric [farquhar2024semantic], incorporating context complexity inherently and capturing process irreversibility.
Empirical Evaluation
The framework was validated on 10 QCA triplets constructed from NVIDIA's 2024 10-K risk factor disclosures, probing both comprehensive and competitive-risk-focused questions.
- Semantic distributions: Sentence embeddings (Qwen3-Embedding-0.6B) are clustered into 23 topics (UDIB). Probabilities are derived via cluster assignments of sentences.
- Algorithm: Convex alternating minimization for A and Q (SF). Dual Lagrangian maximization for reverse-channel SEP lower bound.
- Primary findings:
- Both question structure and entropy affect faithfulness. A positive Pearson’s r=0.695 is observed between question entropy H(Q) and FS.
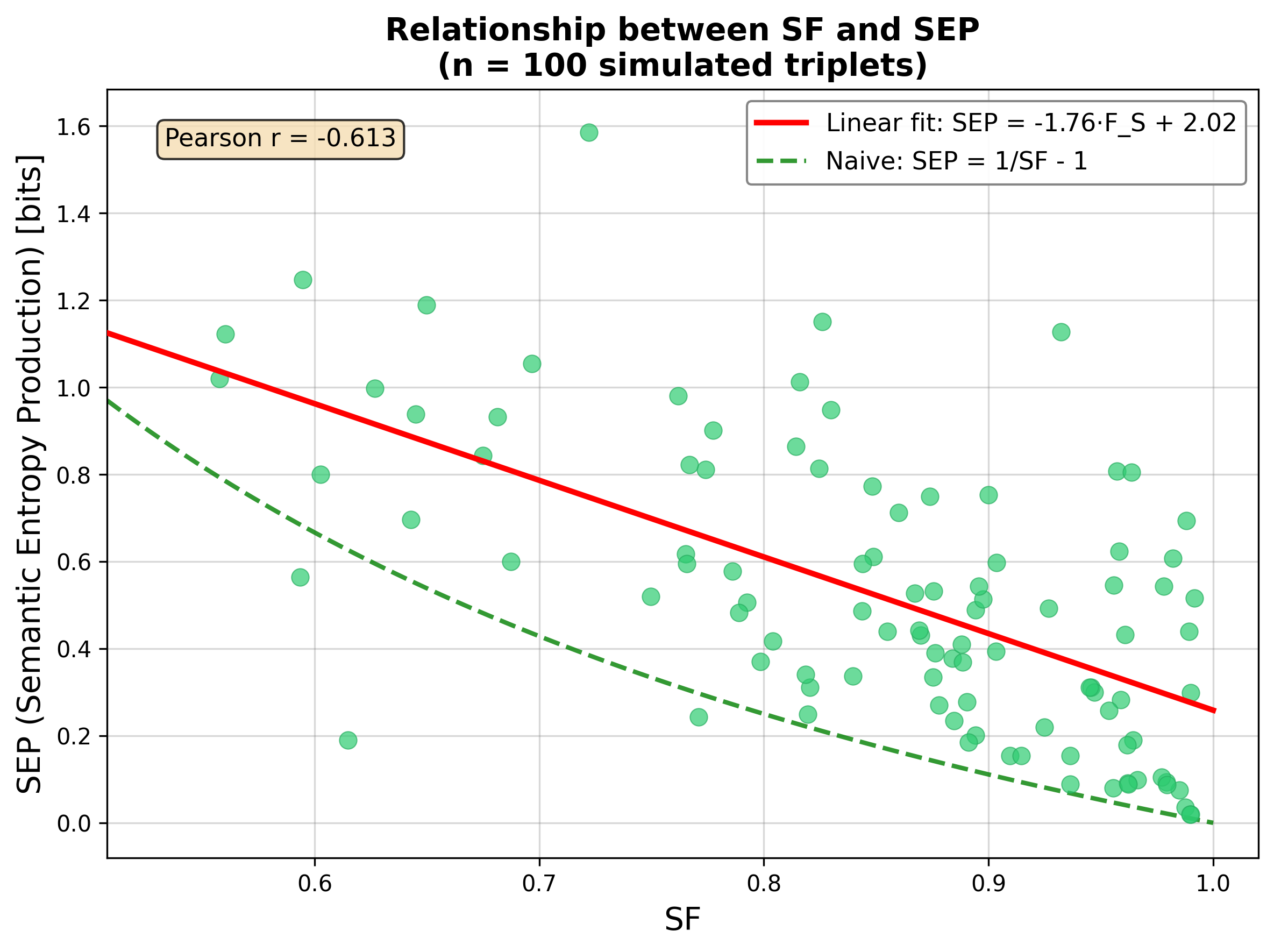
- SEP and SF are negatively correlated (r=−0.612), but the linear relationship deviates from the naive 1/FS−1 approximation, supporting their complementarity.
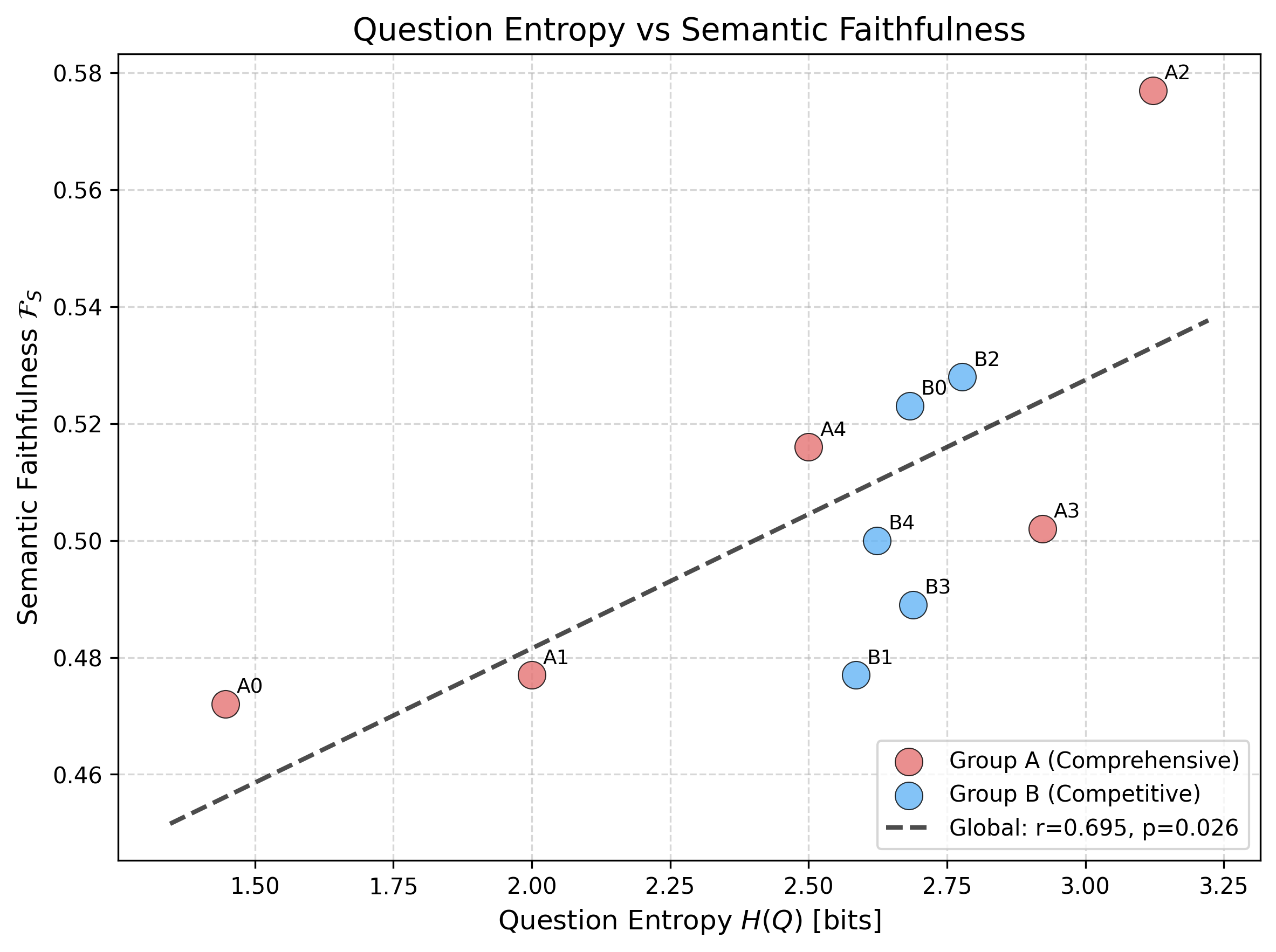
Figure 5: Higher question entropy is associated with increased semantic faithfulness. Group A (multi-topic) shows broader variation.
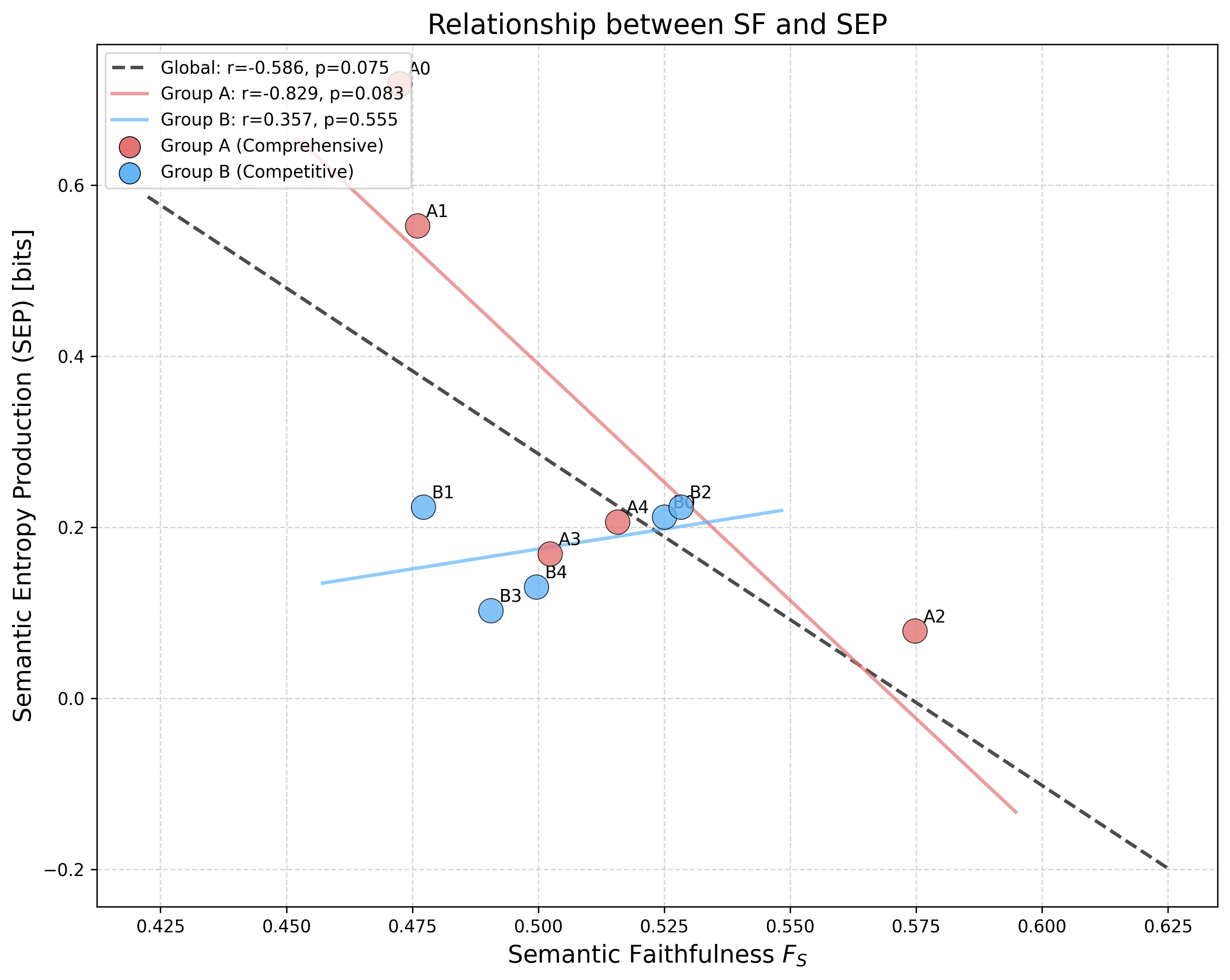
Figure 3: Negative association between FS and SEP (more faithful answers are thermodynamically less irreversible), with different regimes for question types.
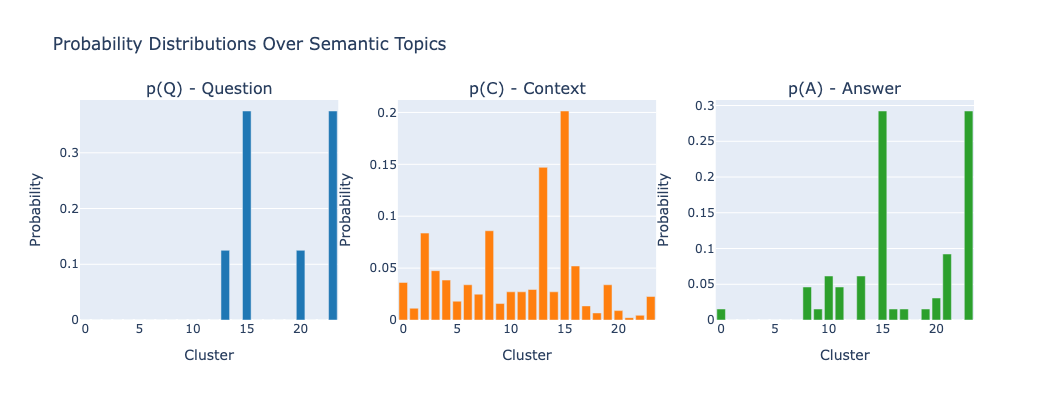
Figure 6: Marginal topic distributions in triplet A0, illustrating how sparse question demands induce focused answer topics from a diffuse context.
Comprehensive questions evoke greater semantic expansion (higher H(A)−H(C)) and SEP, while focused competitive questions manifest low-dispersion, low entropy changes.
Qualitative and LLM-as-a-Judge Analysis
LLM-based evaluation (Claude Sonnet 4.5) was used to adjudicate SF-guided answer selection. While high and low FS answers exhibited equivalent human-perceived quality by standard criteria (faithfulness, completeness, coherence, relevance), additional experiments revealed SF can sometimes expose semantic drift or hallucination undetected by surface-level metrics. Thus, FS provides a distinct axis of evaluative insight, emphasizing alignment in information flow rather than stylistic or surface coverage.
Theoretical and Practical Implications
This framework addresses several key limitations of existing evaluation protocols:
Future Directions
- Scaling and domain transfer: Application to larger, more diverse datasets and different domains.
- RAG and multi-turn: Adaptation to retrieval-augmented architectures and multi-step dialogues.
- Robust uncertainty quantification: Integration with Bayesian uncertainty and epistemic risk monitors.
- Prompt and answer optimization: Using metrics for systematic prompt engineering and answer curation.
Conclusion
This work establishes an information-theoretic and thermodynamic foundation for evaluating LLM semantic faithfulness and hallucination risk, operationalized through the black-box metrics of SF and SEP (2512.05156). These advances extend the semantic divergence framework [halperin2025sdm, halperin2025dib], providing practical, theoretically justified tools for answer selection, algorithmic governance, and empirical audit in high-stakes LLM deployement. The joint use of SF and SEP yields richer diagnostics than either metric alone, with broad implications for both foundational LLM analysis and downstream applications.