- The paper introduces NVRC-Lite, a neural video codec that leverages a reconfigured HiNeRV architecture with multi-scale feature grids and an octree-based entropy model to reduce computational complexity.
- It achieves significant improvements with up to 21.03% PSNR gains and 23.06% MS-SSIM BD-rate savings compared to prior methods, while accelerating encoding and decoding speeds.
- The framework’s innovations offer practical benefits for real-time deployment on consumer hardware and edge devices in bandwidth-constrained environments.
Ultra-lightweight Neural Video Representation Compression: Technical Overview and Implications
Introduction
The paper "Ultra-lightweight Neural Video Representation Compression" (2512.04019) presents NVRC-Lite, a novel neural video codec that targets the ultra-lightweight regime, achieving efficient video compression with notably reduced computational complexity. The framework leverages implicit neural representations (INRs), multi-scale feature grid encoding, and a specialized octree-based entropy coding approach to push the limits of neural video compression towards practical, high-speed, low-resource deployment. The methodology and results outlined in the work constitute a significant technical advancement over previous INRs and autoencoder-based codecs, with particular emphasis on encoding and decoding speed, rate-distortion performance, and scalability.
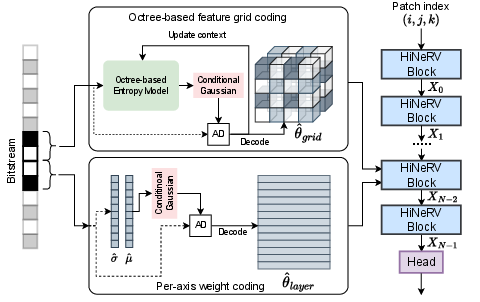
Figure 1: The NVRC-Lite framework, integrating a multi-scale INR (HiNeRV) and octree-based entropy coding for hierarchical parameter compression.
Methodology
Multi-scale Lightweight Neural Representation
NVRC-Lite builds its neural representation atop a reconfigured HiNeRV architecture, which supports multi-resolution feature grids injected into several network stages, instead of restricting grid features to only the initial layer. This design choice enhances expressive capacity at high spatial resolution, maximizing reconstruction fidelity under tight parameter budgets and computational constraints (<10k MACs/pixel). The architectural hybridization bridges strengths of NeRV-style (frame/patch-based) and COOL-CHIC-style (pixel-wise mapping at output resolution) representations, yielding superior rate-distortion performance without sacrificing computation speed.
In practice, NVRC-Lite empirically selects the smallest admissible HiNeRV variant and modifies the convolutional stem (using 2D and 1D convolutions for spatial and temporal axes) to further trim computational requirements. The multi-grid design ensures richer context sharing across resolutions and maintains visual fidelity even at aggressive bitrate reduction.
Octree-based Entropy Coding
Traditional INR-based codecs often rely on high-performing but slow autoregressive entropy models for parameter compression, creating a bottleneck for real-time and resource-constrained applications. NVRC-Lite introduces a novel octree-based context model tailored for feature grid tensors. By partitioning the spatio-temporal grids into 2×2×2 blocks and encoding both odd/even indices per step, the entropy coding process is accelerated, reducing sequential dependencies and enabling efficient parallelization.
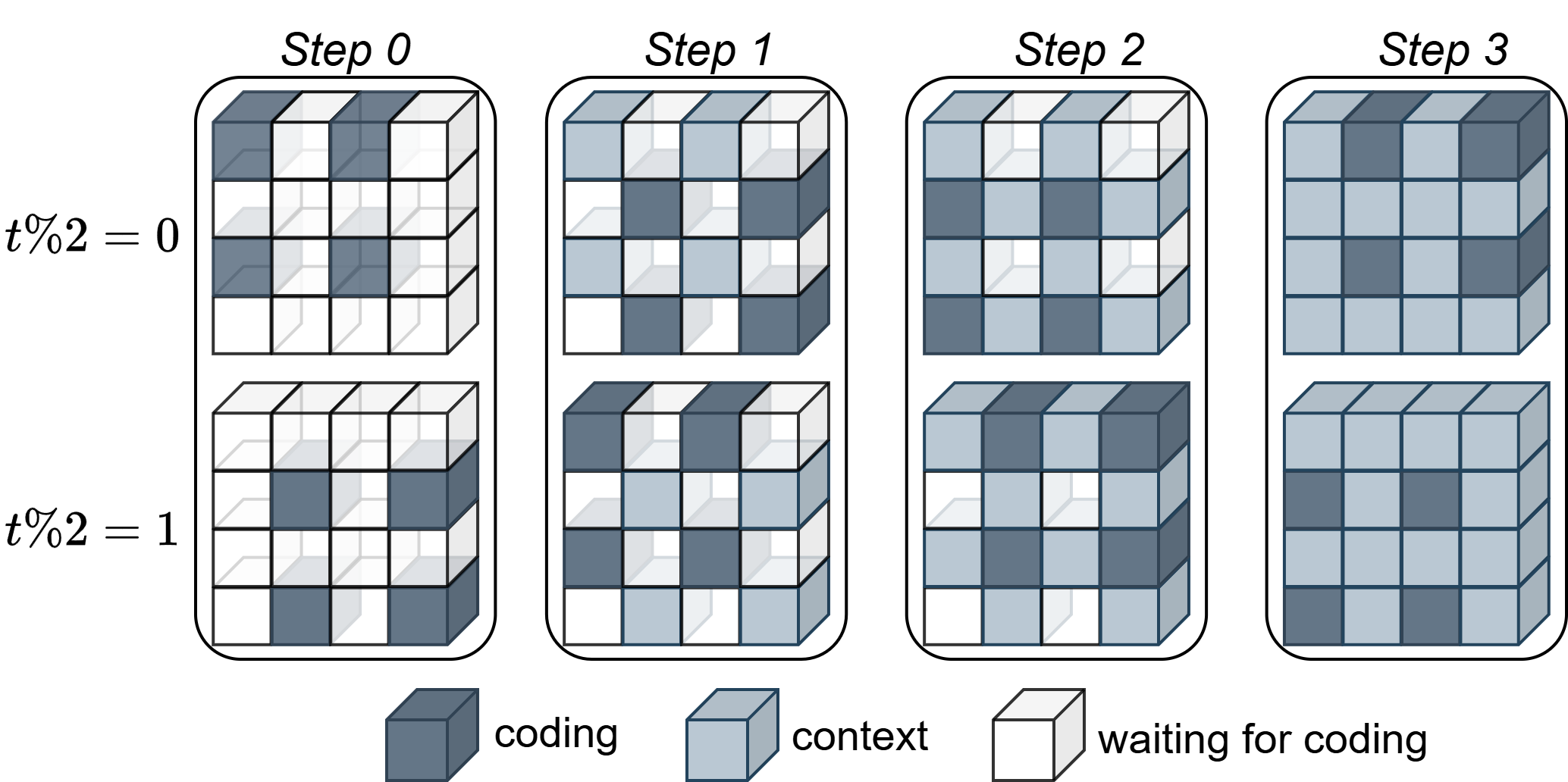
Figure 2: Octree-based entropy coding structure partitions spatio-temporal grids, enabling accelerated context-based compression.
The conditional entropy model exploits a learned auxiliary latent (akin to hyperprior-based models) on block partitions, allowing divergent local statistics to be optimally modeled and compressed. Channel interleaving strategies further augment coding efficiency. Ablation studies confirm that the octree approach delivers up to 4× entropy coding speedup compared to traditional autoregressive methods, with negligible compromise on compression gains.
Experimental Evaluation
NVRC-Lite was evaluated on UVG and HEVC-B datasets, benchmarking against x265 (medium and veryslow presets) and C3, a leading lightweight INR-based codec. Under abbreviated training regimes, NVRC-Lite surpasses C3 with up to 21.03% (PSNR) and 23.06% (MS-SSIM) BD-rate savings, while also outperforming x265-medium in PSNR by 5.27%. The model maintains these advances across challenging HD sequences with diverse content structure.
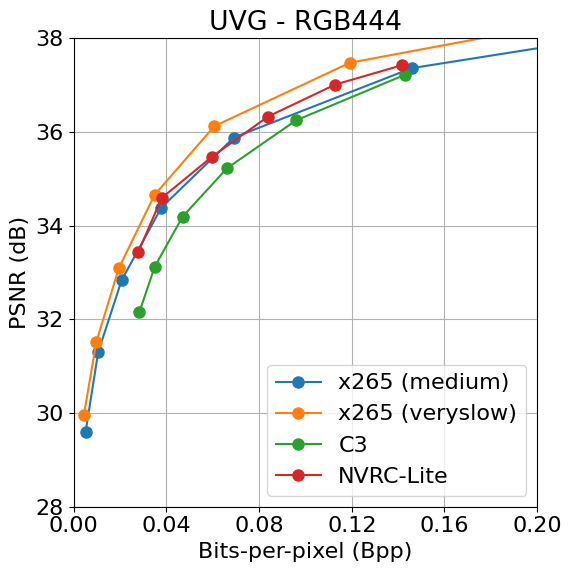
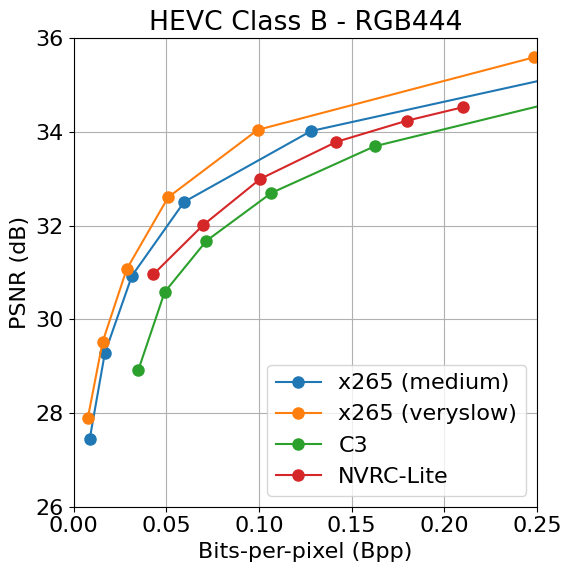
Figure 3: Rate–distortion curves showcasing NVRC-Lite’s superior coding efficiency over C3 and x265 across UVG and HEVC-B datasets.
Visual comparisons further reinforce the quantitative results: NVRC-Lite reconstruction delivers markedly fewer artifacts and better textural detail at equivalent or lower bitrates relative to C3, substantiating its quality improvements.
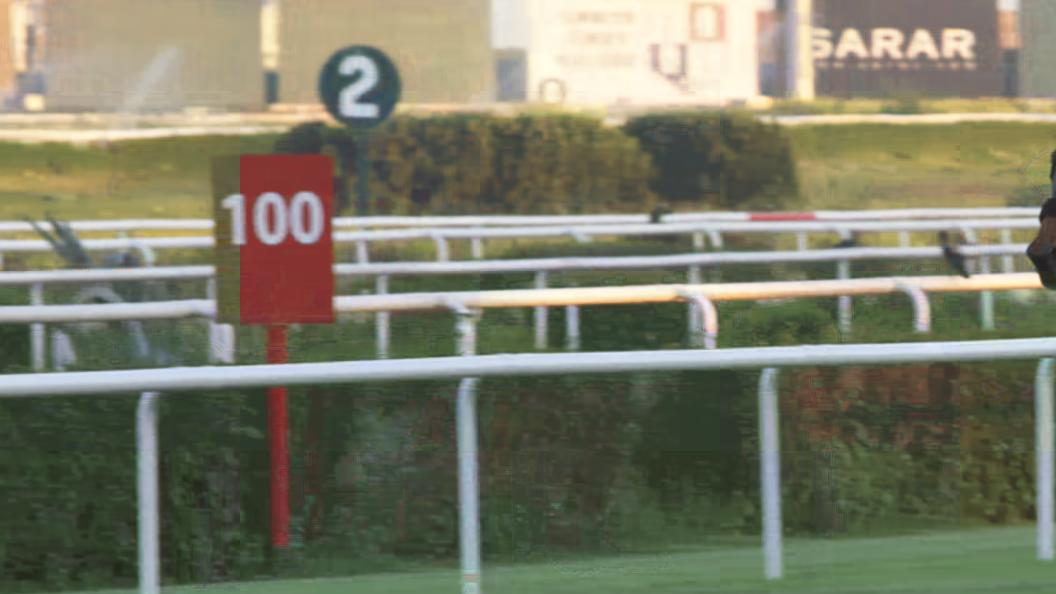
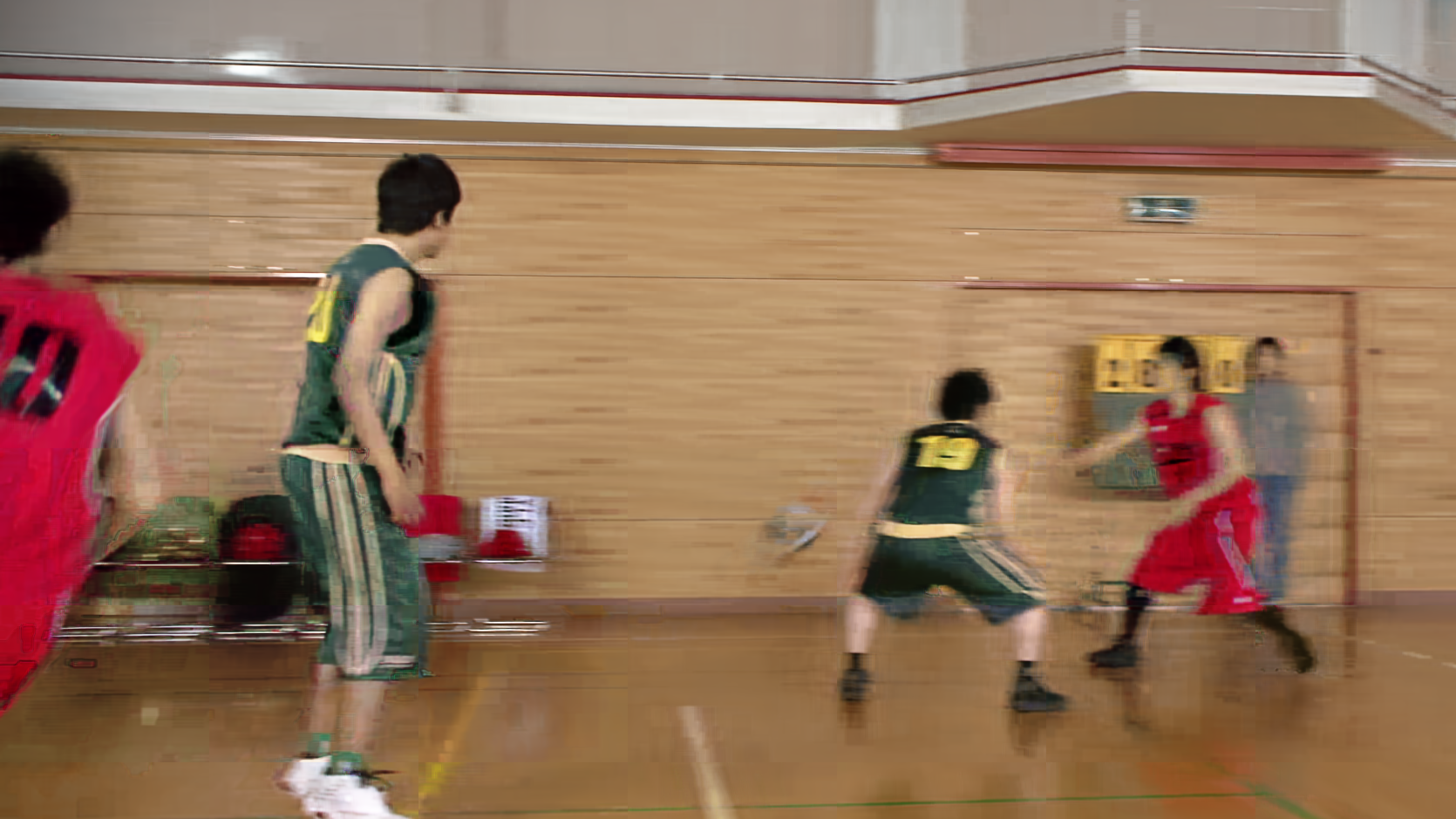
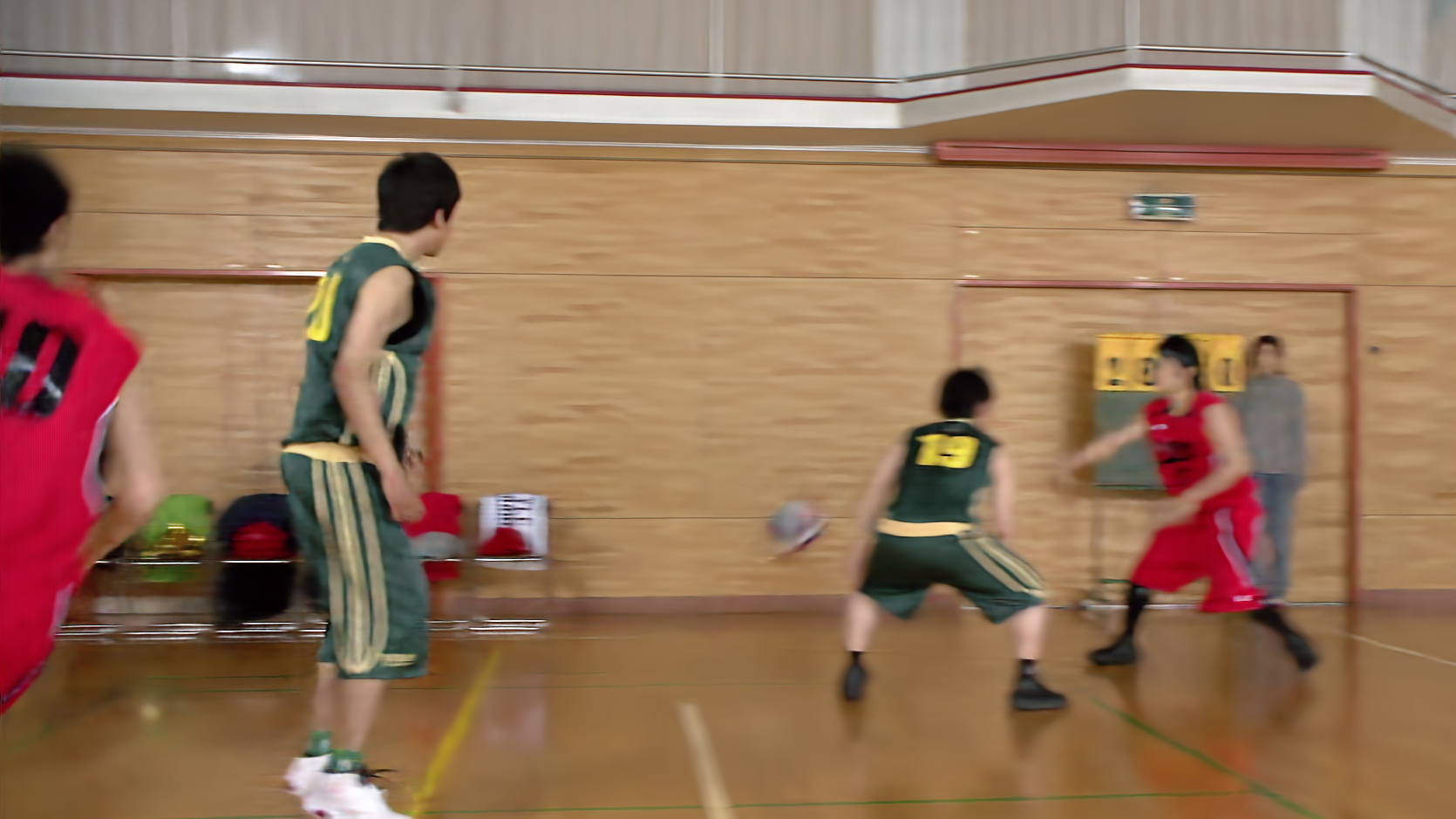




Figure 4: Frame-level visual comparison: NVRC-Lite preserves finer structure and reduces artifacts versus C3 on UVG (top row) and HEVC-B (bottom row) material.
Computational Complexity
Profiling on RTX4090 demonstrates NVRC-Lite's practical efficiency. Despite slightly higher MACs/pixel, encoding throughput increases by 8.4× and decoding by 2.5× compared to C3. This improvement is attributed both to the octree entropy model and scalable hierarchical parameter coding.
Ablation Studies
Empirical studies substantiate two core claims: the multi-scale grid feature design broadens the quality-range coverage and enhances rate-distortion tradeoff; the octree entropy model provides substantial speedup without BD-rate penalty. In contrast, reverting to single-scale features or autoregressive entropy coding curtails both compression efficiency and operational speed.
Implications and Future Directions
The NVRC-Lite framework sets a precedent for practical, real-time neural video codecs suitable for deployment on consumer hardware, edge devices, and bandwidth-constrained infrastructures. The technical innovations—multi-scale grid injection and octree entropy context modeling—can be extended to other INR-based tasks, such as immersive video, low-delay streaming, and adaptive-rate compression.
The hierarchical approach to parameter coding hints at further scalability for variable content mangling, while the elimination of slow autoregressive dependencies is critical for on-device video analytics and resource-sensitive interactive media. The hybrid methodology could catalyze new families of content-specific neural codecs or parameter-efficient transformers for temporal-spatial compression.
Advancements in quantization, context priors, and meta-learning approaches could further enhance NVRC-Lite's robustness across diverse video domains and resolutions. Extension to low-latency, online adaptive scenarios is particularly promising, leveraging instance-optimized subnetworks and cross-model grid sharing.
Conclusion
NVRC-Lite delivers an ultra-lightweight, high-efficiency solution for neural video representation compression, introducing principled architectural and coding innovations that yield substantial gains in rate-distortion performance and operational speed over the previous state-of-the-art. The framework’s methodological choices and empirical validation offer a pathway toward practical, scalable, neural-based video codecs for next-generation multimedia systems and resource-constrained applications. Future work should emphasize further efficiency gains and domain-agnostic adaptability while exploring broader deployment in streaming, cloud, and mobile environments.









