- The paper presents a training-free plug-in that exploits attention-derived motion cues to suppress dynamic-region artifacts and stabilize geometric estimates.
- It integrates three gating strategies—image self, cross, and reverse cross-attention—to effectively mitigate non-rigid motion interference in early transformer layers.
- Quantitative tests on datasets like Sintel, KITTI, and DyCheck demonstrate significant improvements in depth, camera pose, and 4D reconstruction accuracy.
Dynamic scene 3D reconstruction remains a fundamental yet unsolved problem, especially under real-world non-rigid motion. Recent vision transformer-based architectures, such as CUT3R and related streaming models, have established a new paradigm by directly regressing camera pose and dense geometry from sequences of images, leveraging recurrent state tokens to incorporate temporal context. However, these architectures—despite being trained on dynamic data—exhibit susceptibility to motion artifacts: dynamic regions are often inappropriately propagated through the state, destabilizing static-region geometry and camera pose estimation.
The MUT3R framework critically observes that pretrained transformer models encode motion saliency implicitly in their attention maps. However, these internal motion cues are not actively exploited during inference, nor are dynamic interferences explicitly suppressed. This motivates a training-free, inference-time approach to enhancing the robustness of streaming 3D transformers in dynamic scenarios.
Methodology
MUT3R operates as a plug-in module to the frozen CUT3R backbone, maintaining architectural and parameter integrity without any finetuning. The key steps include:
- Attention-Based Motion Cue Extraction: MUT3R analyzes multi-layer self-attention activations of the frozen decoder, aggregating them into per-patch motion scores. These scores reflect motion-induced instability in the attention maps, effectively distinguishing dynamic from static regions.
- Early-Layer Motion Suppression: The aggregated dynamic score map is injected as a soft bias via an attention-gating module, targeting the early decoder layers. Three gating configurations are integrated:
- Image self-attention gating suppresses static-to-dynamic key interactions.
- Cross-attention gating from image to state penalizes dynamic image regions.
- Reverse cross-attention (state-to-image) suppresses updates into dynamic query regions.
This gating utilizes a unified soft-mask approach, governed by a sharpness parameter, which smoothly suppresses or attenuates dynamic-region contributions without hard masking, thus preserving differentiable signal flow and geometric reasoning.
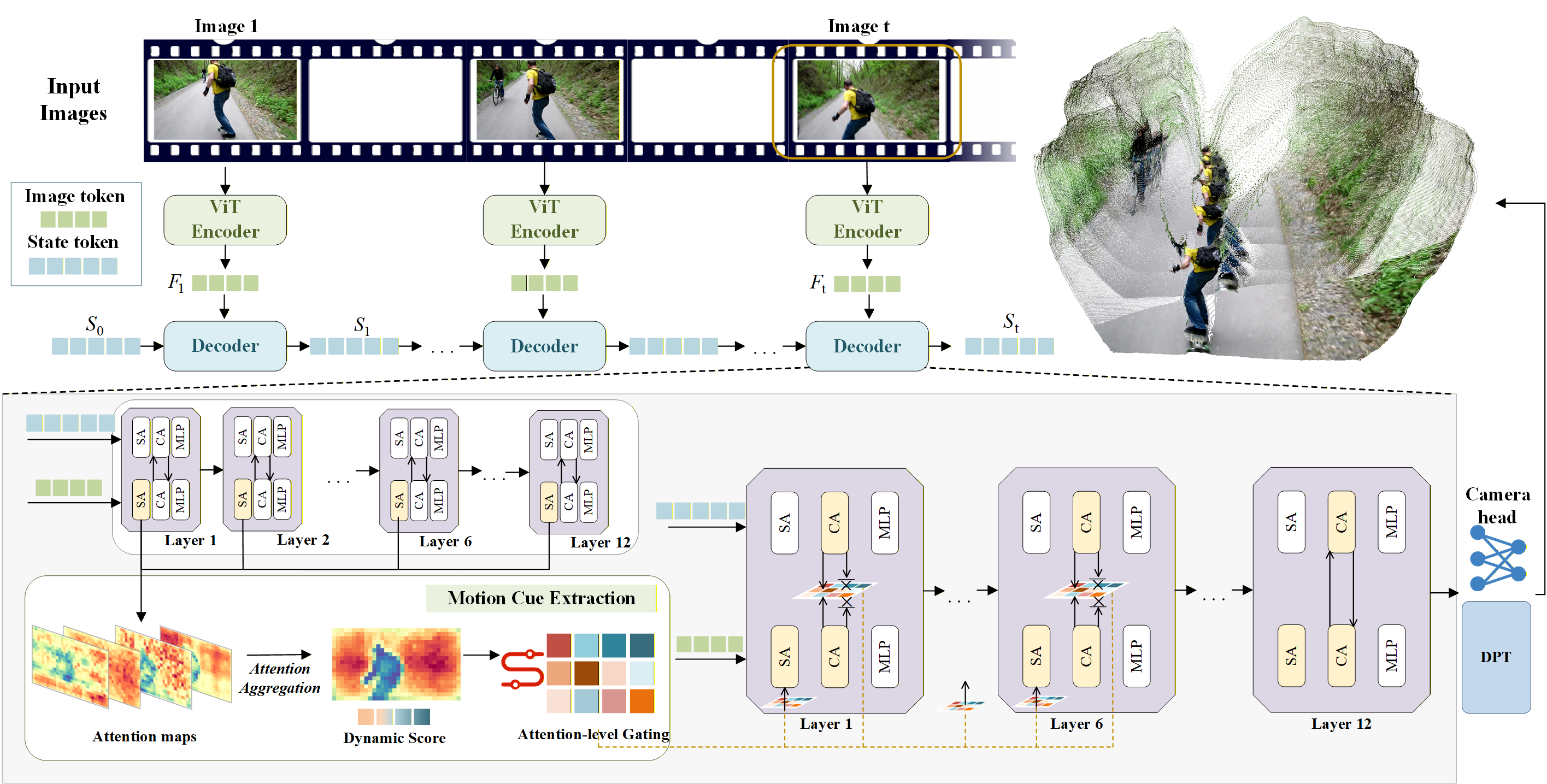
Figure 1: The MUT3R pipeline: per-frame visual tokens are processed by a persistent-state CUT3R decoder; multi-layer attention maps yield patch-level dynamicity scores, which guide early attention gating to suppress motion-dense areas.
Visualization and Internal Analysis
MUT3R provides insight into transformer internal dynamics by visualizing aggregated self-attention across layers:
- Shallow attention layers are highly localized and sensitive to appearance and dynamics, with fragmented activations.
- Deeper layers, after repeated state-image interactions, induce more spatially and temporally coherent patterns aligned with rigid scene elements.
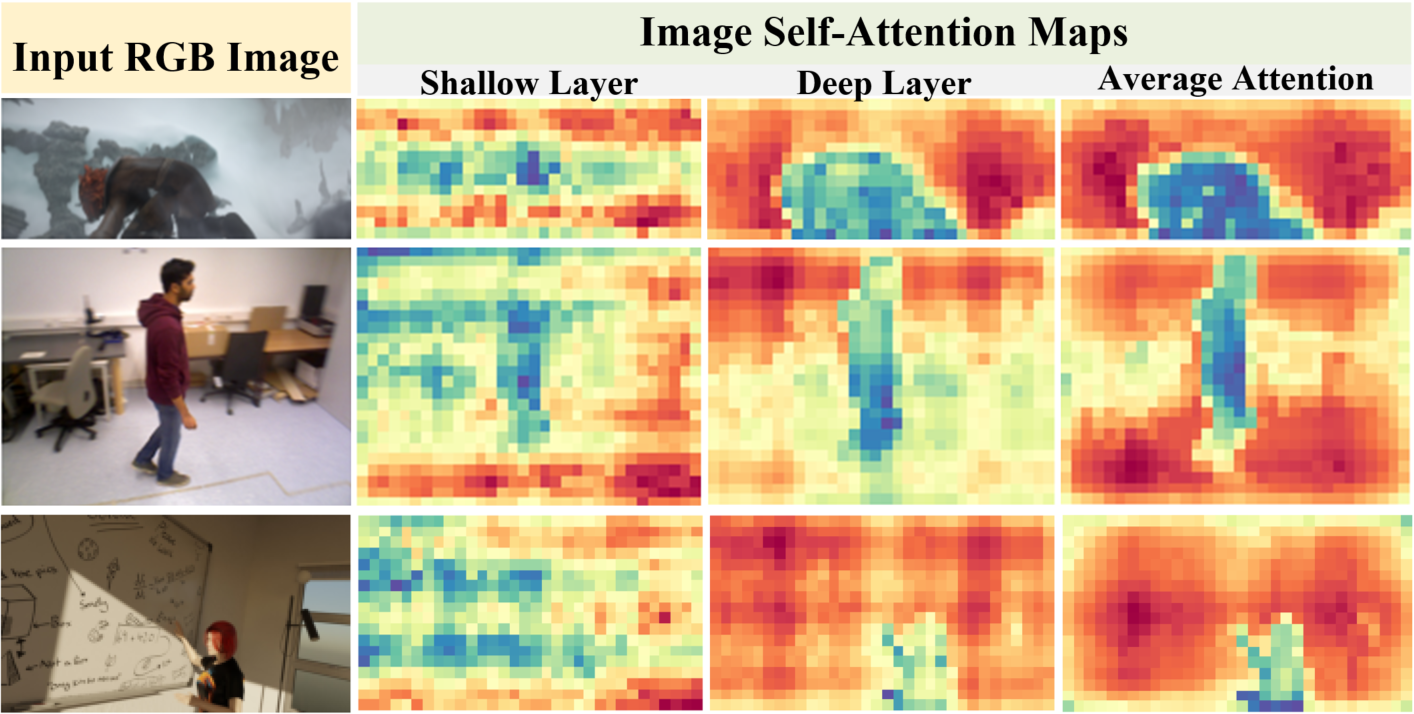
Figure 2: Left to right — input RGB, shallow-layer attention, deep-layer attention, and mean attention maps; dynamic regions exhibit weaker (blue) response.
Early-layer gating by MUT3R accelerates convergence towards stable representations, minimizing propagation of motion-corrupted activations deeper into the model and resulting in improved geometric consistency.
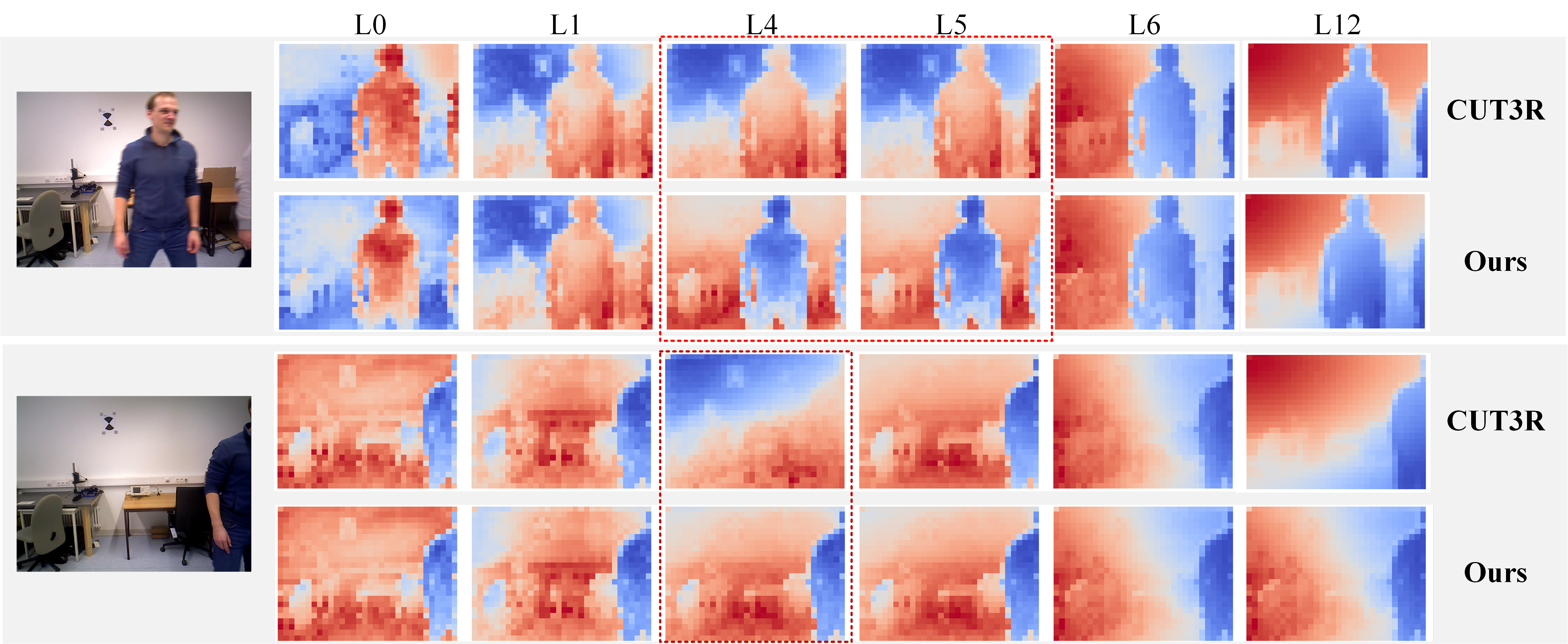
Figure 3: PCA visualization shows the evolution of image-token embeddings across decoder layers: MUT3R achieves faster and more orderly stabilization compared to vanilla CUT3R.
Quantitative and Qualitative Results
Depth Prediction: On challenging dynamic-scene video datasets (Sintel, Bonn, KITTI), MUT3R achieves improved absolute relative error and inlier metrics over streaming baselines, particularly CUT3R, indicating better temporal coherence and per-frame accuracy. The improvements are consistent both in alignment-free (metric scale) and alignment-based protocols.
Camera Pose Estimation: MUT3R outperforms or matches state-of-the-art methods in ATE and RPE (translation and rotation) across dynamic benchmarks (Sintel, TUM-dynamics, ADT), demonstrating increased temporal stability and resilience to motion-induced outliers.
4D Reconstruction: On DyCheck, MUT3R yields superior accuracy, completeness, and overall distance in reconstructed point clouds. Qualitative evaluations reveal that dynamic-region artifacts and temporal drift, prevalent in CUT3R, are largely mitigated in MUT3R outputs.
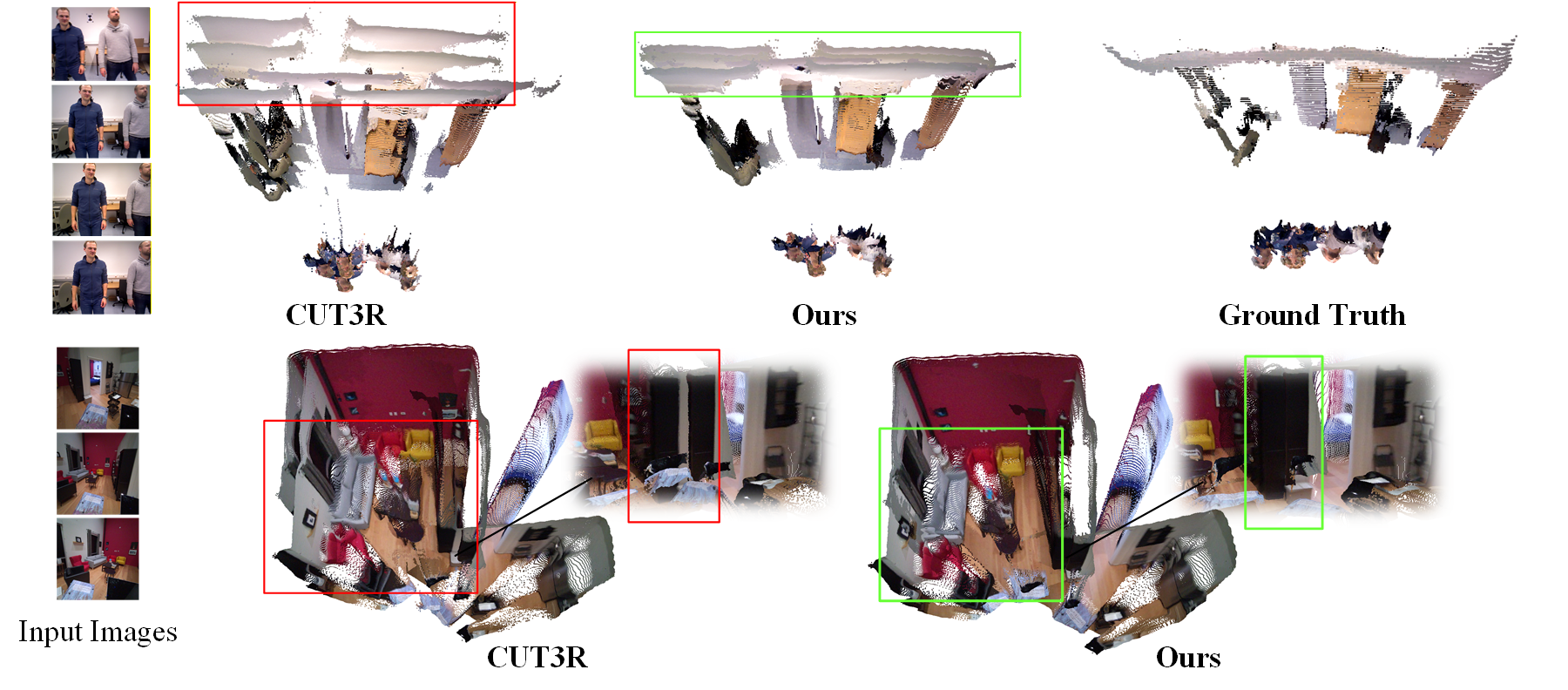
Figure 4: Comparison of four-dimensional reconstruction on Bonn and ADT datasets, with green marking improved areas under MUT3R and red highlighting unstable predictions.
Ablation and Analysis
Extensive ablation studies demonstrate:
- Optimal gating is achieved with early-to-middle decoder layer suppression; over-suppressing in later layers degrades accuracy, indicating that motion interference is predominantly introduced early in the attention hierarchy.
- All three gating types (image self, image-to-state, state-to-image) are necessary for maximal suppression of dynamic noise; removing any reduces overall performance.
- The attention-derived motion cues are robust and discriminative, validating the efficacy of entirely unsupervised, training-free dynamic saliency estimation.
Implications and Future Work
MUT3R illustrates that pretrained streaming 3D transformers intrinsically encode rich dynamic cues within multi-layer attention maps, which can be surfaced and re-injected to suppress non-rigid scene artifacts—without retraining or architecture change. This paradigm provides a succinct, modular approach to robustness under motion, applicable to any transformer-based causal 3D perception framework with persistent state representations.
In terms of broader implications, MUT3R closes the gap between static-scene and dynamic-scene 3D reconstruction in an online processing regime. This raises further research opportunities:
- Application to variant architectures, including pointer-based or spatial-memory models for ultra-long sequence fusion.
- Real-time dynamic SLAM and AR scenarios, where temporal stability and low-latency updating are mission-critical.
- Joint motion segmentation and geometry estimation via unsupervised, attention-guided disentanglement.
Conclusion
MUT3R presents a robust, non-intrusive strategy for fortifying streaming 3D transformer models against motion-driven artifacts. By explicitly harnessing and gating implicit dynamic cues in pretrained attention maps, it achieves strong improvements in depth, pose, and 4D consistency in dynamic scenes—all with zero retraining. This points to a promising research direction of self-regularization and self-introspection in foundation geometric models, potentially leading to more generalizable and resilient perception systems for dynamic and real-world scenarios.





