- The paper introduces a two-stage relevance process that decomposes search into path construction and path following using domain knowledge and multimodal evidence.
- It employs a progressive chain-of-thought synthesis integrating knowledge injection, caption-mediated multimodal comprehension, and rule awareness optimized via reinforcement learning.
- Empirical results show notable improvements, including +2.4% pass@1 and enhanced macro-F1 scores, demonstrating robust performance in e-commerce search applications.
LORE: A Large Generative Model for Search Relevance
Theoretical Foundation and Framework
LORE (Large Generative Model for Relevance) presents a principled, end-to-end paradigm for optimizing LLMs for e-commerce search relevance tasks. The authors establish that relevance judgment in search is not a singular classification problem but a composite reasoning process requiring domain knowledge integration, chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning, multi-modal matching, and rule adherence. They introduce a formal decomposition of relevance discrimination into a two-stage process: Path Construction—mapping query requirements to item attributes using semantic and domain knowledge—and Path Following—executing differentiation via multimodal evidence and business rules.
This analytical structure allows for explicit modeling of distinct capabilities mapped to the computational stages of relevance analysis:
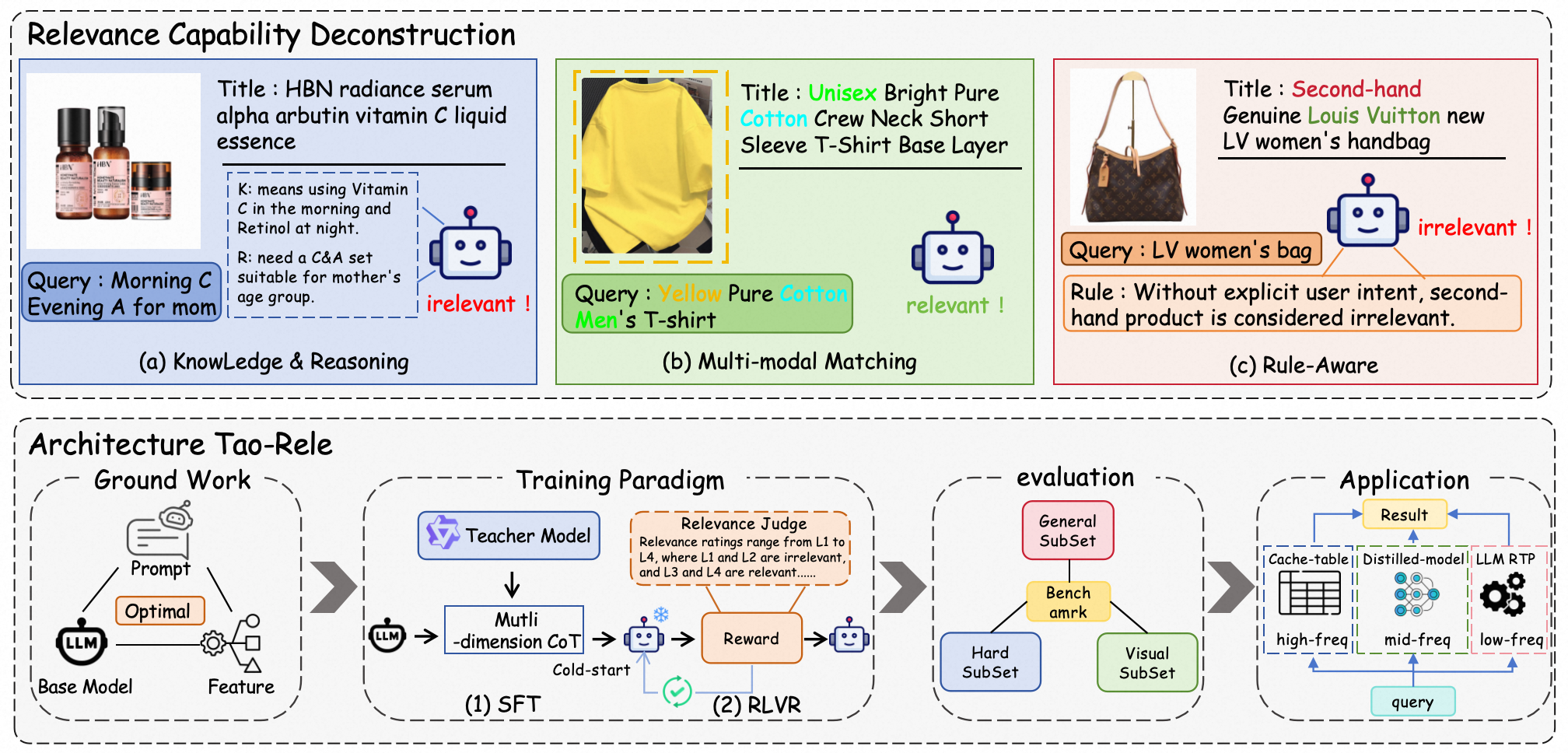
Figure 1: Overview of the LORE theoretical framework and architecture, highlighting the decomposition of relevance into knowledge-driven, multimodal, and rule-aware stages.
The task definition is enriched beyond binary relevance by introducing a four-level grading and an 18-dimensional schema for attributes, enabling nuanced discrimination and explainable scoring. The framework directly motivates the modeling of advanced item understanding (inherent and derived attributes, text and image modalities), sophisticated query understanding (entity/intent recognition, knowledge dependency), and the construction of robust reasoning paths.
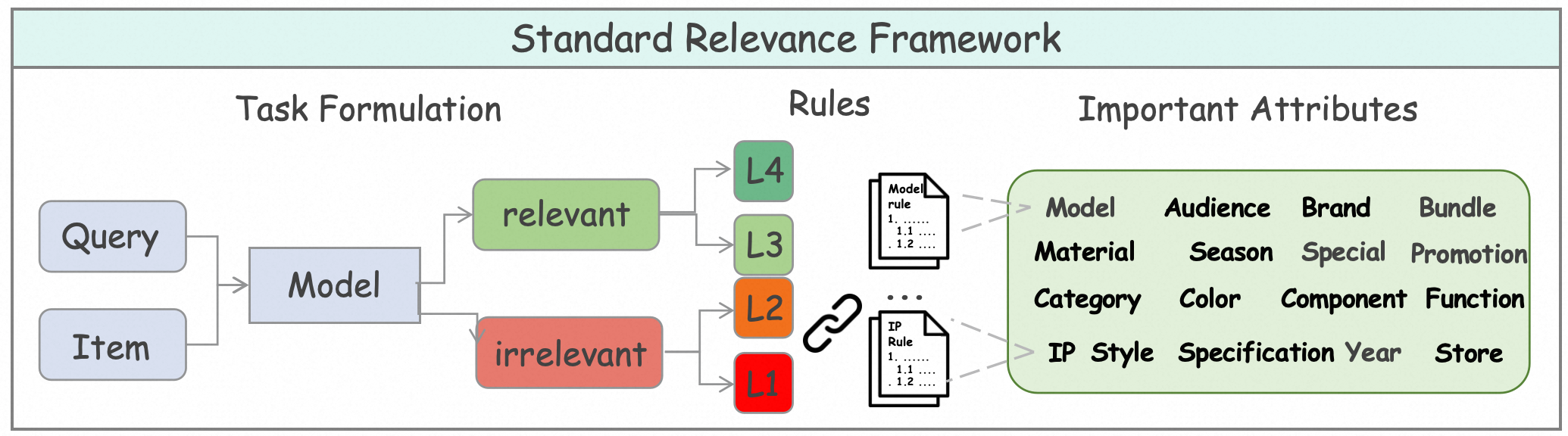
Figure 2: A standard definition of the relevance task, indicating the multi-level and multi-attribute granularity of query-item matching.
Methodological Innovations: Data, Features, and Training Paradigm
Preliminary Exploration
The authors design a rigorous data and feature pipeline, emphasizing comprehensive attribute coverage across modalities. Statistical filtering and LLM-based relevance validation are used to select high-frequency and stable CPV/SKU attributes and main images, achieving +2.4% absolute pass@1 improvement from feature enhancement.
Model Selection and Prompt Optimization
Empirical benchmarks on scalable open-source base models (Qwen2.5-7B) balance reasoning capacity and deployability. Distinct prompt variants are compared, revealing that concise prompts maximize discriminative power, with excessive verbosity degrading attention focus—a critical observation for SFT protocol design.
Progressive Chain-of-Thought Synthesis
The central innovation is a three-stage CoT synthesis pipeline:
- Knowledge Injection: Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and context enrichment inject world and e-commerce domain knowledge, augmenting both query-side and item-side information.
- Multimodal Comprehension: Rather than direct VLM fine-tuning, a caption-mediated approach combines VLM-generated image-to-text descriptions aligned with reasoning context, enhancing cross-modal interpretability.
- Rule Awareness: Rule sets are integrated into CoT generations, enabling downstream model compliance and increased generalization.
This synthesized reasoning chain (CoTstep3) is distilled via SFT, using structured targets for explicit separation of reasoning and output, yielding a cold-start model that improves pass@8 by 2.7% over vanilla SFT baselines.
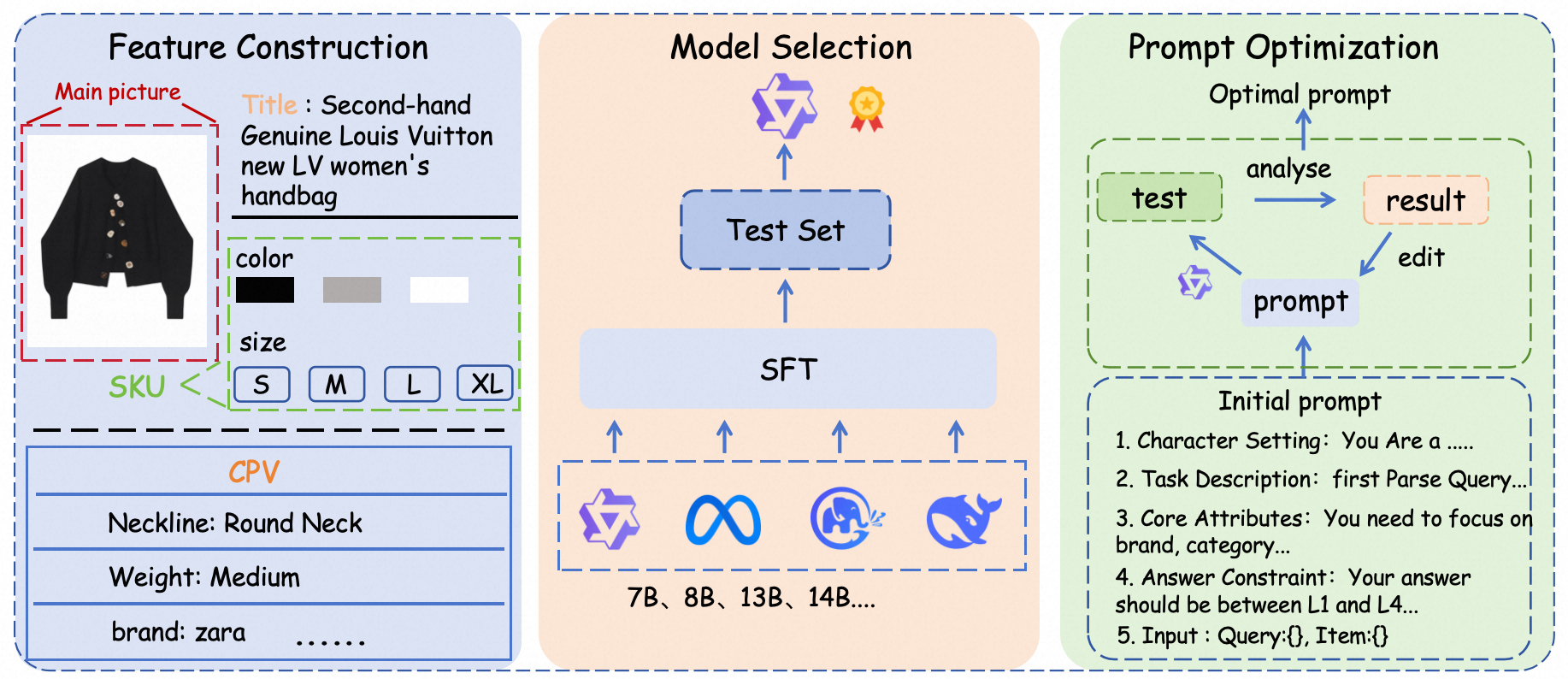
Figure 3: Preliminary exploration prior to training, encompassing feature selection, base model benchmarking, and prompt engineering for robust discriminatory power.
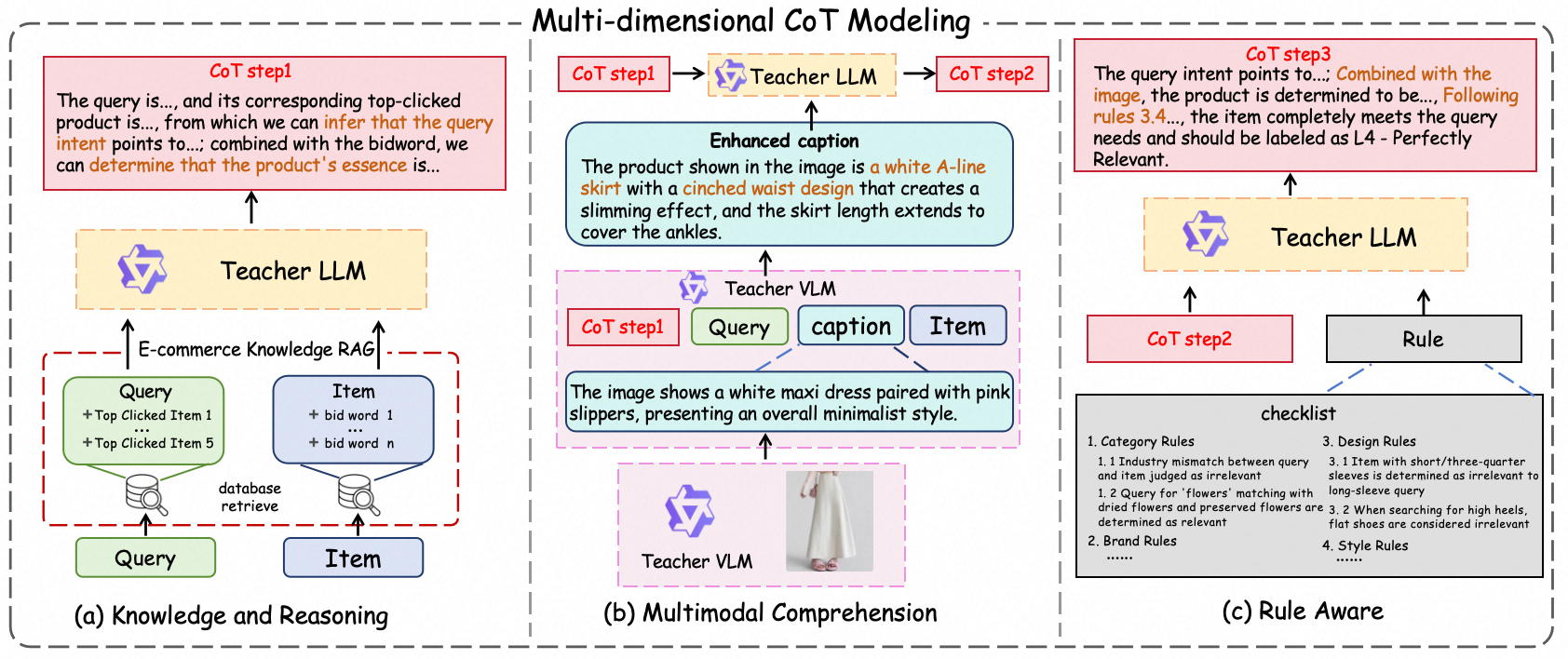
Figure 4: Progressive multi-dimensional CoT synthesis framework capturing knowledge, multimodal, and rule-aware reasoning steps.
Reinforcement Learning for Preference Alignment
To address performance upper bound and single-shot precision (pass@1), LORE introduces RLVR, utilizing GRPO-style RL (without KL regularization for greater exploration). Rewards encode not only prediction correctness but compliance with output format and constrained error types (attribute-level mismatches), yielding stability and progressive capability improvements.
Hard-sample mining and curriculum learning optimize the sample pool for RL, moving beyond saturated/easy cases and maximizing challenging supervision signals. Entropy collapse mitigation via "clip-higher" strategy is shown to slow premature convergence and maintain policy diversity with superior stability compared to on-policy or explicit entropy regularization alternatives.
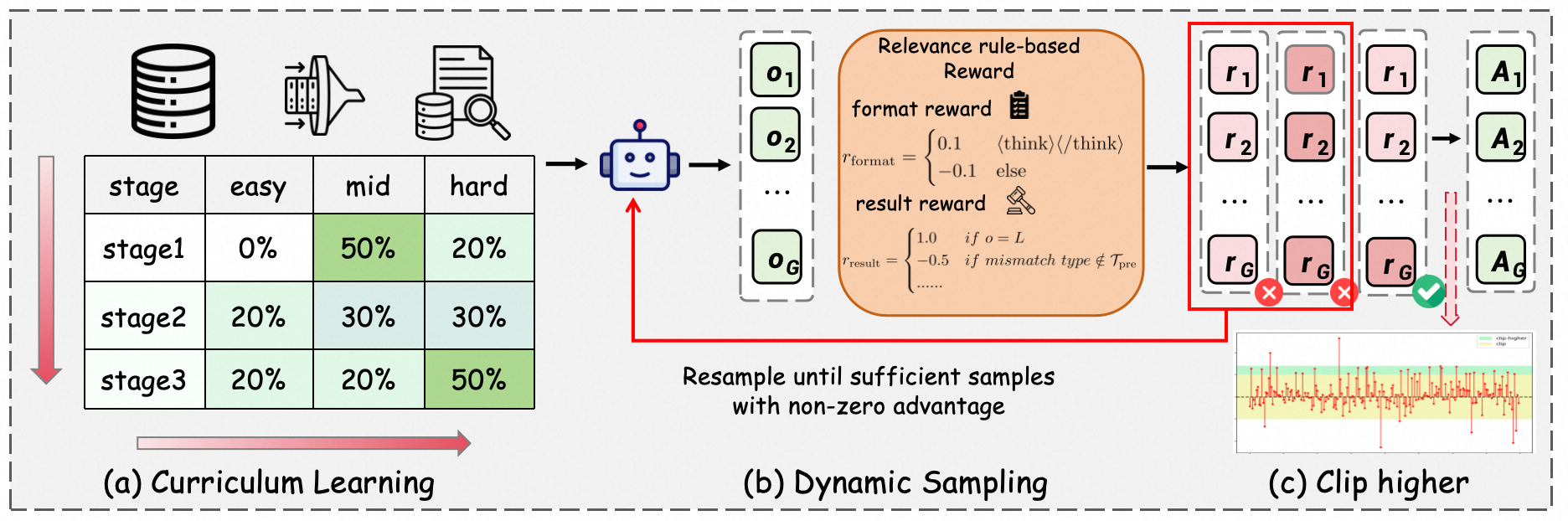
Figure 5: Overview of RLVR, demonstrating the curriculum learning regime and entropy-controlled optimization.
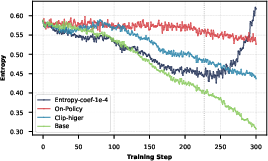
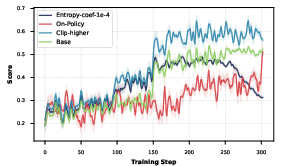
Figure 6: Experimental comparison of entropy collapse mitigation strategies, confirming "clip-higher" as optimal for relevance tasks.
Token vs. Sequence-Level Importance Sampling
Extensive experiments reveal that while sentence-level importance sampling yields smoother convergence, it also accelerates entropy collapse and restricts exploration, making token-level granularity preferable for modeling complex reasoning diversity.
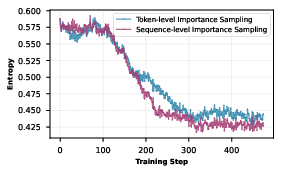
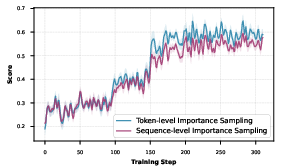
Figure 7: Comparative analysis of token- vs. sequence-level importance sampling strategies and their effect on policy convergence.
Rigorous Evaluation: Benchmark Design and Empirical Validation
LORE introduces RAIR—a comprehensive benchmark explicitly measuring knowledge-driven reasoning, multimodal comprehension, and rule adherence across 63,601 samples and 14 verticals. The inclusion of hard long-tail queries and visually salient cases allows for discriminability far beyond existing datasets.
Quantitatively, LORE achieves superior results, with acc@2 gains of +8.8% (vs. GPT-5) and macro-F1 improvements exceeding +28% on general subsets. On long-tail hard subsets, the model is +4.4% and +5.3% ahead in acc@2 and macro-F1, respectively, compared to the strongest baselines. The multimodal caption-guided CoT enhancement increases macro-F1 by +4.8% on visually complex queries.
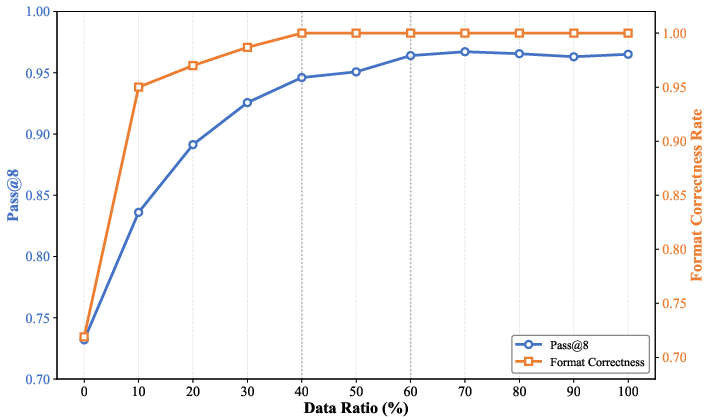
Figure 8: Evolution of pass@8 and format correctness rate with varying data proportions in the SFT process, demonstrating rapid saturation and diminishing returns.
Qualitative Capability Analysis
Case studies illustrate the successful incorporation of external knowledge, compositional reasoning, robust multimodal understanding, and strict rule adherence, with detailed error attribution enabled by RAIR’s rule checklists.
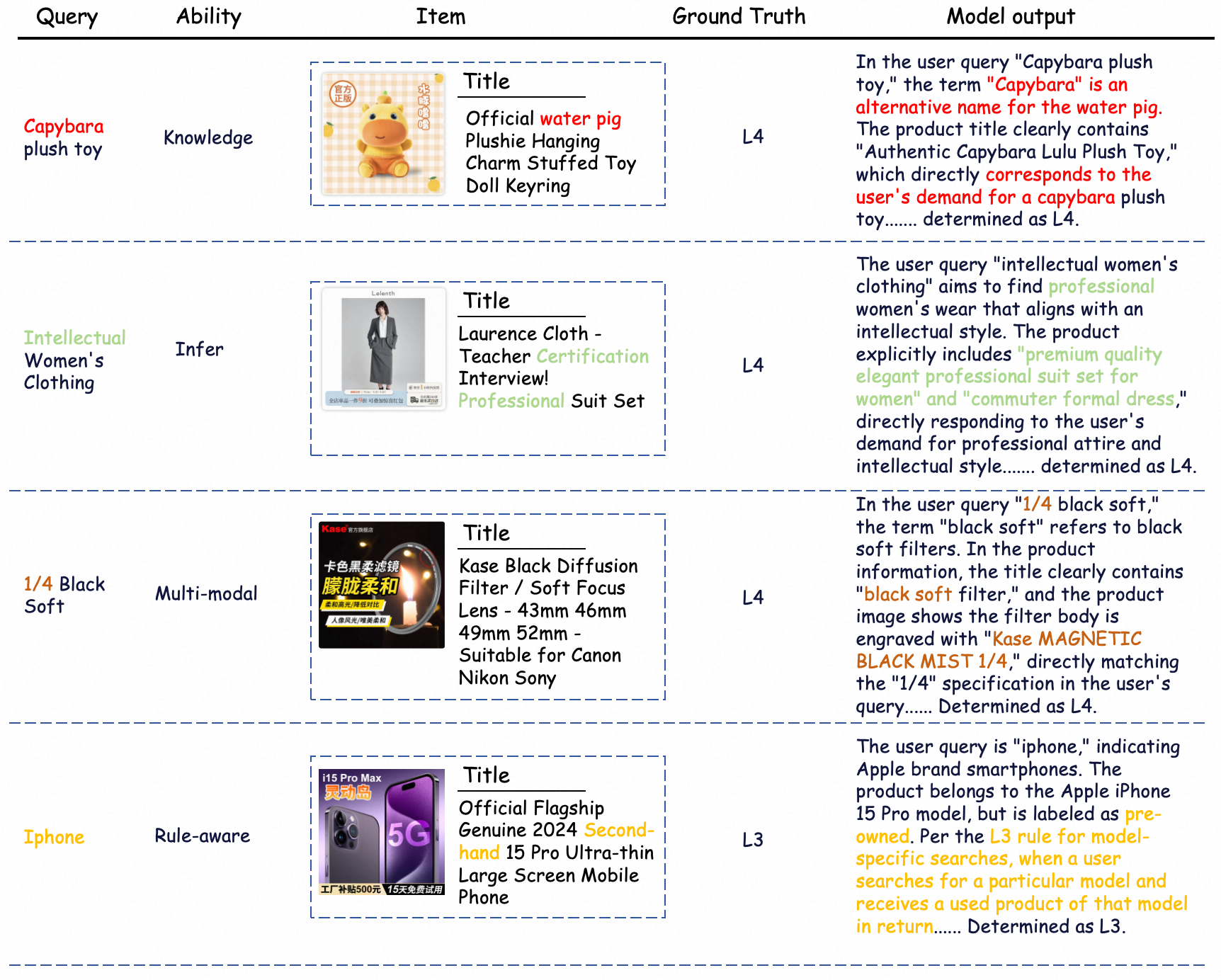
Figure 9: Example analysis of capabilities required for relevance evaluation with detailed reasoning and attribute-path following.
Online Application and System Integration
LORE is deployed using a stratified serving strategy based on query frequency—combining high-frequency caching, knowledge distillation for mid-frequency traffic, and direct RL-empowered real-time inference for hard queries. This regime, alongside optimized system infrastructure, produces a cumulative online GoodRate improvement of +27%.
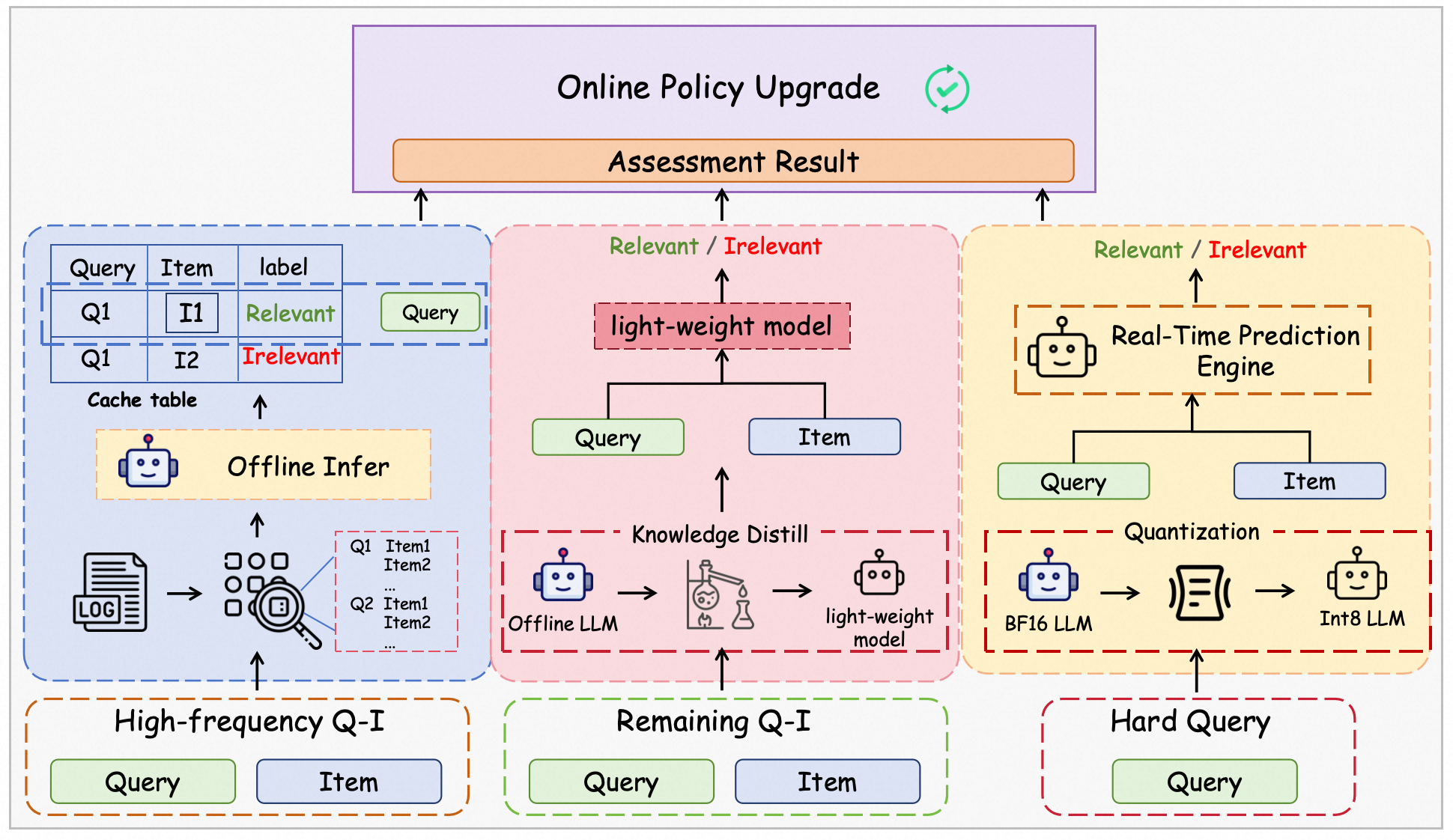
Figure 10: Online application approach of LORE with query frequency segmentation for targeted model/application policy deployment.
Evolutionary Trajectory: Iterative Advancement Across Three Phases
LORE’s advancement is charted through three systematic iterations: foundational e-commerce semantic understanding, CoT-driven deep reasoning and hard case mining, and fully integrated rule-aware multimodal reasoning with scalable RL optimization.
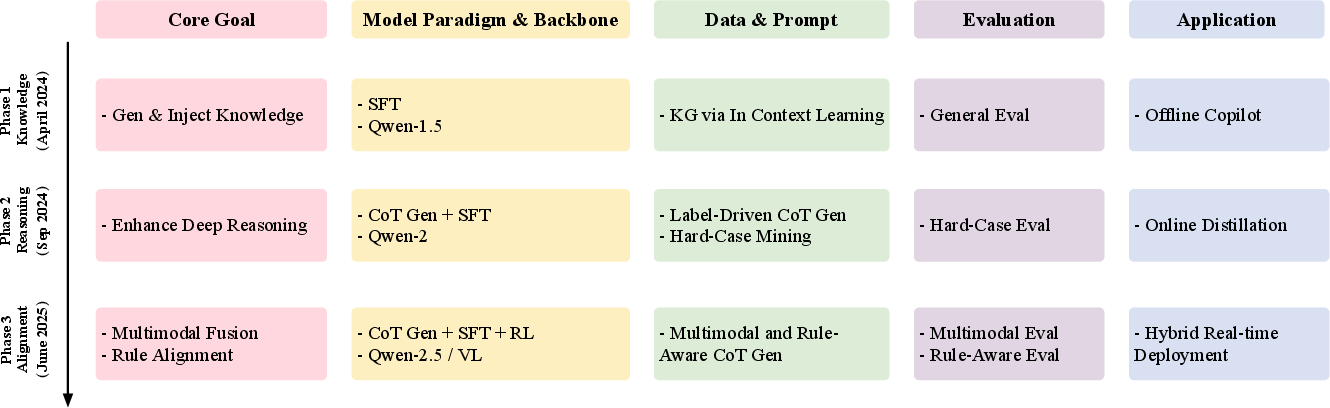
Figure 11: Three-phase evolution of LORE system across five dimensions: goals, backbone, data, evaluation, and application.
Implications, Contradictory Claims, and Future Directions
A bold finding is that naive teacher CoT distillation degrades single-pass accuracy versus vanilla SFT due to distribution shift; only CoT distillation combined with RL optimization achieves both diversity and precision. Additionally, long CoT chains are not indicative of improved performance, with output length decreasing and stabilizing as the model matures in relevance tasks—contradicting assumptions from mathematical or code domains.
Empirical analysis shows that multimodal modeling via caption-enhanced LLM outperforms direct VLM fine-tuning in reasoning-rich scenarios, although VLMs are stronger on purely visual salience cases. This supports a hybrid paradigm for relevance tasks.
LORE provides a robust blueprint for domain-adapted LLM relevance modeling with systematic capability injection and entropy management. Future directions involve further scaling of multimodal integration, automated rule system evolution, and model quantization for darker real-time inference in latency-constrained production systems. Extension to other vertical domains—where fine-grained reasoning and compliance require explicit domain adaptation, knowledge augmentation, and hybrid multimodal architectures—is an actionable trajectory.
Conclusion
LORE delivers a comprehensive, replicable, and methodologically sound framework for LLM-based relevance assessment in e-commerce. Through a principled combination of problem decomposition, feature enrichment, progressive CoT synthesis, reward-driven RL alignment, and stratified deployment, LORE achieves both state-of-the-art offline results and significant online application impact. The insights and technical regimes reported set a precedent for post-training adaptation, capability auditing, and deployment of vertical-domain LLMs, warranting further investigation in domains demanding high-fidelity alignment of LLM output with structured, multimodal, and rule-constrained reasoning objectives.














