- The paper presents an iterative framework that integrates data synthesis and model training for enhanced LLM tool usage.
- It introduces Greedy Capability Probing, Judgement-Guided Label Verification, and Error-Driven Data Expansion to refine training data.
- Experiments on BFCL-v3 and ACEBench show improved tool-call accuracy, setting state-of-the-art records at the 8B model scale.
LLMs augmented with tool-use capabilities are at the forefront of enabling complex, multi-step task execution beyond traditional text generation. This essay explores "LoopTool: Closing the Data-Training Loop for Robust LLM Tool Calls" (2511.09148), a framework designed to advance tool-use in LLMs through a closed-loop data and training pipeline.
LoopTool addresses the deficiencies of traditional static data pipelines used in training tool-augmented LLMs, where data generation and model training occur as isolated processes. These conventional methods fail to dynamically adapt to a model's evolving capabilities and perpetuate inefficient training with noisy, unpurified data. In response, LoopTool introduces an automated, iterative framework integrating data synthesis and model training to enhance robustness in tool-use.
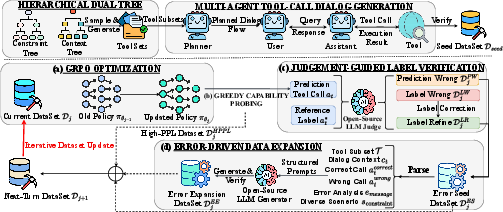
Figure 1: The overall closed-loop automatic pipeline of LoopTool, which couples (a) GRPO optimization, (b) Greedy Capacity Probing, (c) Judgement-Guided Label Verification, and (d) Error-Driven Data Expansion for iterative tool-use enhancement.
Architecture and Methodology
LoopTool encompasses several key components that together form a closed-loop system:
- Greedy Capability Probing (GCP): This module assesses the model's tool-using abilities by monitoring performance on synthesized tasks, identifying both strengths and areas requiring improvement.
- Judgement-Guided Label Verification (JGLV): Utilizing an open-source judge model, this component cleanses the dataset by correcting mislabeled data, thus progressively refining the learning signals.
- Error-Driven Data Expansion (EDDE): By transforming errors into new, challenging samples, this builds a diverse set of training instances, driving the model to adapt to a wide variety of scenarios.
The framework is adept at combining these modules to iteratively refine both the data and the model, providing better-aligned training examples that dynamically respond to the model's learning state. This iterative process significantly improves learning efficacy by concentrating on unresolved, complex cases while eliminating noise-induced learning failures.
Experimental Results
The efficacy of LoopTool is validated against BFCL-v3 and ACEBench benchmarks, where it outperformed the generating model (32B Qwen), setting state-of-the-art records at its 8B model scale. The LoopTool-8B model achieved substantial improvements in tool-call accuracy, underscoring the advantages of applying an adaptive, model-aware data refinement strategy.
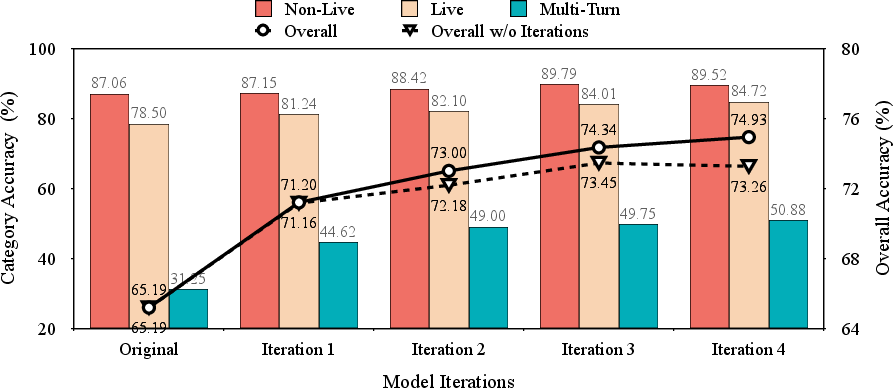
Figure 2: The Iterative Performance across four iterations evaluated in BFCL-v3. The left y-axis represents Category Acc (bar chart), while the right y-axis denotes Overall Acc (line chart). "Overall w/o Iterations" refers to the result obtained under the same number of iteration steps, where we train solely on the initial seed dataset.
Implications and Future Directions
The implications of LoopTool are multifaceted. Practically, it provides a cost-effective approach to tool-augmented LLM training by reducing dependency on expensive closed-source data generation models while enhancing training data quality through iterative refinement. Theoretically, it exemplifies a paradigm shift towards more integrated learning approaches where data and model co-evolve, suggesting a path forward for creating models that are more contextually aware and capable of complex tool use.
Future research may explore extending these methodologies to support online or streaming variants, further reducing latency in data-model adaptation, and incorporating parallelized iteration schemes to hasten convergence.
Conclusion
LoopTool represents a significant step in closing the loop between data generation and model training, creating a more efficient, adaptive, and robust framework for developing tool-augmented LLMs. By iteratively enhancing data quality and aligning it with model learning stages, LoopTool not only demonstrates superior performance on benchmarks but also sets a precedent for the next generation of AI systems capable of sophisticated tool use in dynamic environments.



