- The paper presents an answer-first strategy that inverts conventional DFS methods to efficiently generate complex tool-use datasets.
- It employs a four-module framework—API proposal, execution, selection, and workflow update—to optimize data generation and improve model performance.
- Experimental results demonstrate that models trained on the ToolGrad-5K dataset exhibit superior tool recall, success rates, and quality over baseline methods.
2ToolGrad: Efficient Tool-use Dataset Generation with Textual 2"
Introduction
The paper "2ToolGrad: Efficient Tool-use Dataset Generation with Textual 2" introduces a novel framework, ToolGrad, aimed at optimizing the generation of tool-use datasets for LLMs by inverting conventional data generation paradigms. Unlike prior methodologies that begin with speculative user queries and rely on extensive, often inefficient tool-search processes like DFS, ToolGrad adopts an "answer-first" approach. This involves constructing valid tool-use chains based on textual "gradients," followed by the synthesis of user queries. This innovation results in the creation of the ToolGrad-5K dataset, characterized by complex tool-use chains, reduced cost, and a perfect pass rate of completed annotations.
The ToolGrad framework is designed to efficiently generate datasets by iterating through mini-batches from a large API database, inspired by machine learning optimization loops. The framework involves four core modules: API proposal, execution, selection, and workflow update. These steps parallel the concept of forward inference and backward propagation seen in conventional ML. The generated dataset, ToolGrad-5K, contains detailed examples of user prompts linked to tools and AI responses. This approach significantly outperforms traditional methods in terms of both efficiency and output quality.
Experimental Results
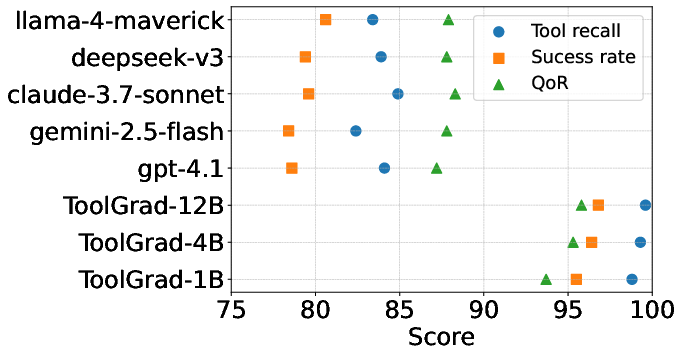
Figure 1: ToolGrad-5K benchmark on non-reasoning models. Raw data in the figure is available.
The experiments demonstrate ToolGrad's superior efficiency in dataset generation compared to traditional methods. The ToolGrad-5K dataset offers a higher pass rate and consists of more complex tool-use sequences, as opposed to the baseline dataset ToolBench, which suffered from lower completion and higher generation costs. Moreover, models trained on ToolGrad-5K exhibited remarkable improvement over proprietary systems in handling out-of-distribution (OOD) tasks, indicating effective generalization capabilities.
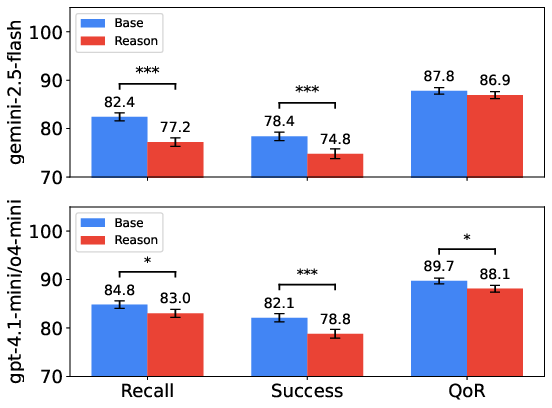
Figure 2: Comparison of base and reasoning Gemini / GPT models on ToolGrad-5K. The error bar represents the standard error. %%%%2Gradients2%%%% and %%%%2ToolGrad: Efficient Tool-use Dataset Generation with Textual 2%%%% denote as p<.05, p<.001 in the paired t-test, respectively.
ToolGrad shows improved performance metrics across tool recall, success rates, and response quality (QoR). Fine-tuned models on ToolGrad-5K outperform equivalent and proprietary models, including those with reasoning capabilities. Interestingly, base models consistently surpassed their reasoning counterparts, highlighting ToolGrad's capability to instruct simpler model architectures without the need for reasoning complexity, which typically increases computational overhead.
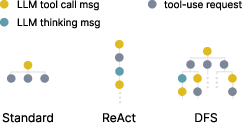
Figure 3: A visualized comparison among standard, ReAct, DFS inference frameworks.
Implications and Future Work
This research suggests potential enhancements in synthetic dataset generation by leveraging a novel answer-first strategy. Beyond efficiency improvements in data generation and model performance, ToolGrad may influence future methodologies in interactive systems and human-AI query frameworks. The possibility of integrating ToolGrad with real-world task agents and post-processing modules for aligning synthetic outputs with human-like queries presents exciting avenues for advancing LLM interactivity.
Conclusion
ToolGrad represents a significant shift in tool-use dataset generation for LLMs, merging efficiency with stability and performance. By employing textual "gradients" early in the dataset creation process, the framework effectively generates comprehensive datasets that enhance model capabilities. Future explorations could exploit its potential in collaborative scenarios and real-world applications, further enriching AI's tool-use adaptability.




