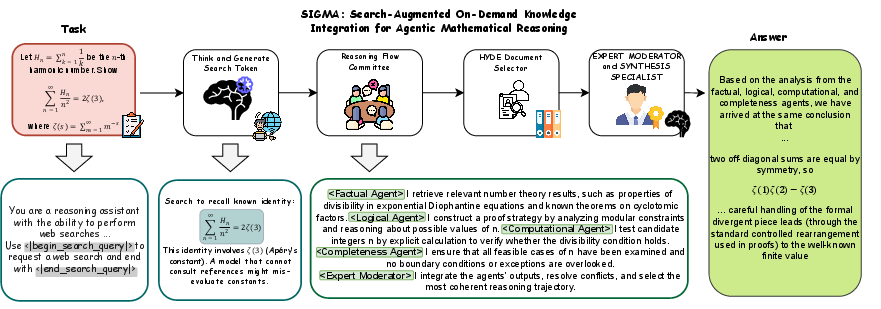
- The paper introduces the SIGMA framework that integrates four specialized agents to perform targeted searches and enhance mathematical reasoning.
- The methodology uses independent reasoning-search cycles and a lightweight moderator to synthesize coherent, multi-perspective solutions.
- Experimental results demonstrate a 7.4% performance gain on benchmarks, with competitive results using only 7B parameters compared to larger models.
SIGMA: Search-Augmented On-Demand Knowledge Integration for Agentic Mathematical Reasoning
Introduction
The paper introduces the SIGMA framework, a novel approach to enhance mathematical reasoning in LLMs by coordinating multiple specialized agents to perform reasoned and targeted searches. The SIGMA framework is designed to overcome the limitations of current retrieval-augmented models, which typically rely on a single perspective and struggle with inflexible search strategies and integration of information from multiple sources.
Framework Components and Methodology
SIGMA orchestrates four specialized agents—Factual, Logical, Computational, and Completeness—that independently generate perspective-specific retrieval queries and only conduct searches under uncertainty. Each agent operates via targeted reasoning-search cycles and contributes to a unified solution synthesis through a lightweight moderator. This architecture ensures efficient knowledge integration and improves computation efficiency without the overhead typical of traditional multi-agent systems.
Hypothetical Document Enhancement: Agents use this technique to generate ideal answer content from their specific perspective, guiding targeted retrieval and ensuring coherence in the reasoning process.
Moderator Role: The moderator synthesizes outputs from specialized agents into a coherent solution. It ensures consistency by collating and deduplicating outputs based on predefined protocols to resolve conflicting reasoning.
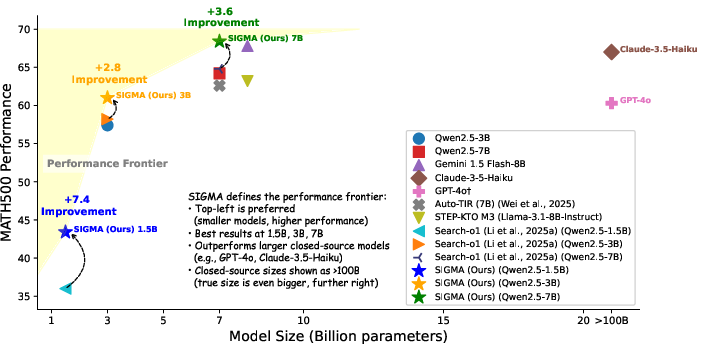
Figure 1: Overview of the SIGMA framework.
Experimental Results
Across mathematical benchmarks such as MATH500, AMC2023, AIME2024, and the scientific PhD-level GPQA dataset, SIGMA demonstrates significant improvements over both open- and closed-source systems. Notably, SIGMA achieves an absolute performance gain of 7.4% compared to the best-performing baselines, with superior generalization to diverse domains beyond mathematics.
Computational Efficiency
Despite the additional overhead of multi-agent collaboration, SIGMA maintains computational efficiency through parallel reasoning and targeted retrieval, making its performance gains particularly noteworthy given the resource constraints.
Conclusion
The SIGMA framework advances the field of mathematical reasoning within LLMs by integrating multiple agent perspectives to enhance problem-solving accuracy and efficiency. The strategic use of on-demand knowledge integration and effective multi-agent collaboration enables SIGMA to push performance boundaries across various knowledge-intensive tasks. Future work may extend this approach to other domains requiring complex reasoning and further optimize its computational efficiency.
In summary, SIGMA's development represents a significant contribution to enhancing the reasoning capabilities of LLMs, demonstrating the power of multi-agent frameworks in large-scale knowledge processing and integration.