- The paper presents a novel method that compresses Transformer KV caches using 'breadcrumb' tokens, reducing memory use while preserving reasoning performance.
- It employs a joint RL-distillation framework to compress token sequences, achieving memory reductions of 2x to 32x while retaining 65.1% to 89.8% of performance.
- Results demonstrate a superior memory-accuracy trade-off compared to traditional methods, offering scalable solutions for long-context reasoning.
Memory-Efficient Reasoning with Breadcrumbs Reasoning
Breadcrumbs Reasoning proposes a novel approach to address the scalability issue of LLMs constrained by the linear growth of Transformer key-value (KV) caches. By introducing a technique to periodically compress this cache using special-purpose tokens, this research demonstrates significant memory savings while maintaining or even enhancing performance in long-context reasoning tasks.
Introduction
The paper introduces the challenge faced by transformers as they generate tokens, increasing computation and memory costs due to the self-attention mechanism. It posits that not all past token representations hold equal informational value. Consequently, there is an opportunity to compress the KV cache without compromising the model's reasoning capabilities. The proposed solution involves substituting detailed token representations with compact 'breadcrumb' tokens, using a joint reinforcement learning (RL) and distillation framework to train these representations effectively.

Figure 1: Breadcrumbs Reasoning, with a compression ratio c=16. To save memory during inference, a window of c tokens is periodically compressed into a single beacon token.
This method showcases a superior memory-accuracy trade-off, significantly reducing memory usage while maintaining high accuracy levels, thereby offering a scalable solution to long-context reasoning.
Methodology
Breadcrumbs Reasoning leverages the inherent architecture of transformers for compression. The core idea is to replace sequences of tokens with a single compressed "beacon" token, which summarizes prior information without needing the entire sequence of token representations.
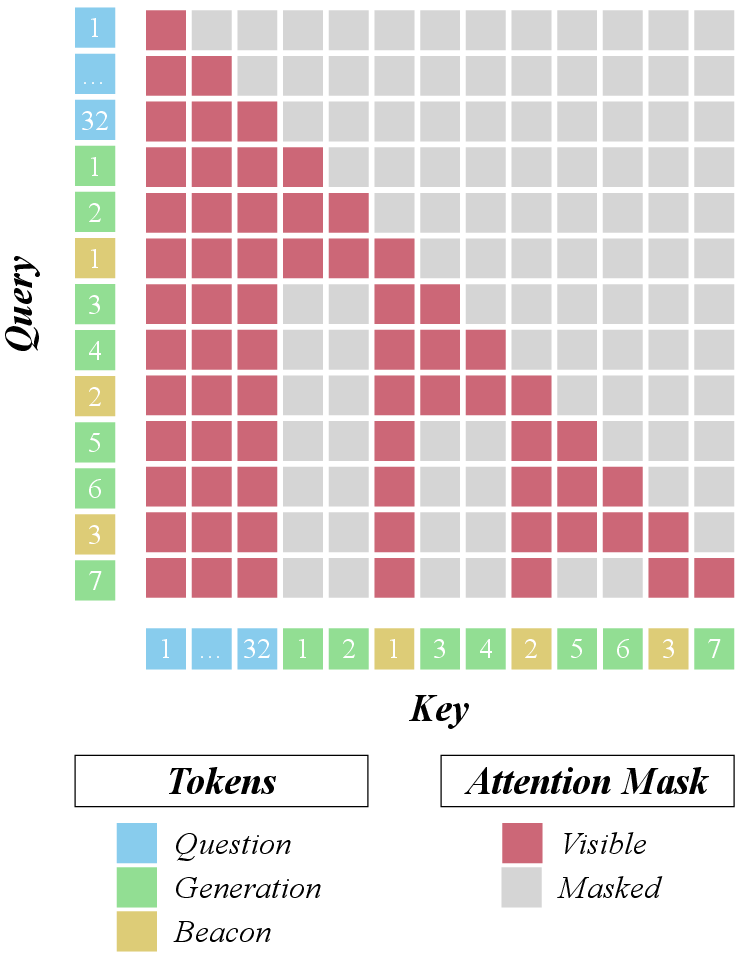
Figure 2: Attention mask used to enforce compression during training, encouraging the model to compress past context efficiently.
The methodology involves implementing a joint RL-distillation training process that aligns the compression strategy with the reasoning task, minimizing training overhead while enhancing performance.
Results
Empirical evaluation demonstrates that Breadcrumbs Reasoning achieves a Pareto improvement in memory efficiency. The method retains between 65.1% to 89.8% of the original performance while using 2 to 32 times less memory for a fixed generation length. Furthermore, it achieves remarkable accuracy when the memory budget is fixed, outperforming training-free baselines like TOVA and StreamingLLM:
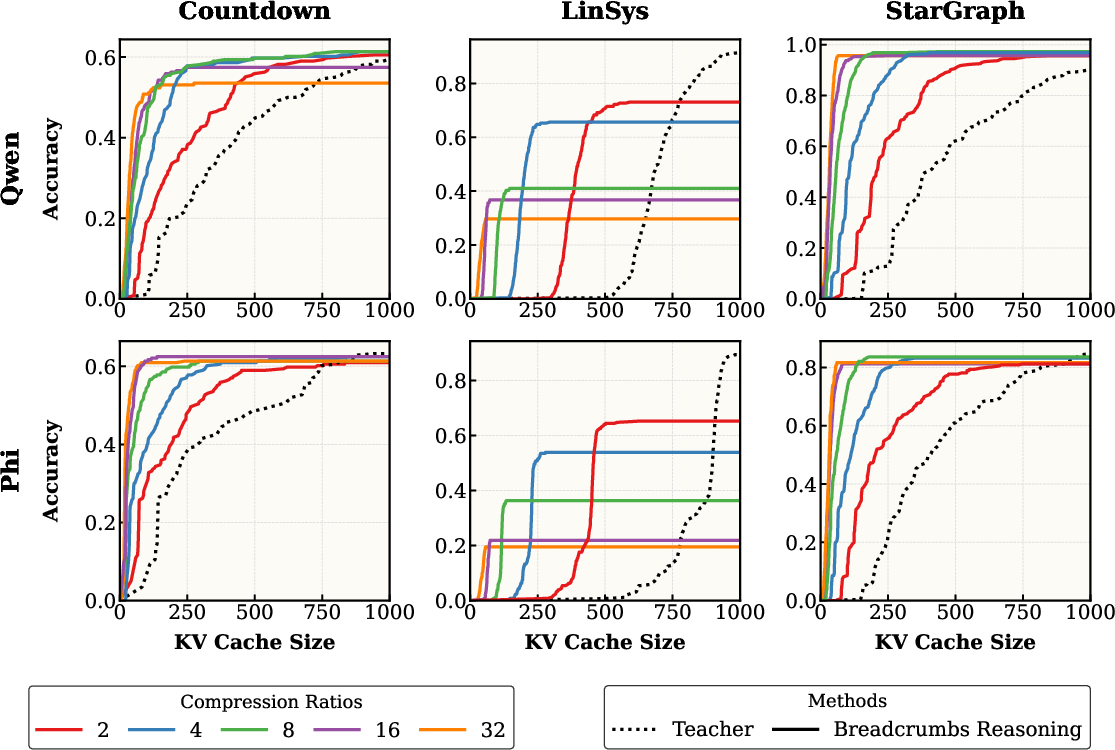
Figure 3: Breadcrumbs Reasoning retains much of the teacher's performance while using significantly fewer KV cache entries.
Additionally, the unique joint RL-distillation approach proves superior to traditional two-step training processes, showcasing the efficacy of learning compression online during the RL process.

Figure 4: Joint RL-distillation vs. Two-step Training on Qwen, where joint training reliably outperforms the more complex two-stage approach.
Implications and Future Directions
The implications of Breadcrumbs Reasoning are twofold. Practically, it presents an efficient solution for deploying LLMs in memory-constrained environments while maintaining performance levels. Theoretically, it opens avenues for developing dynamic compression strategies tailored to varied contexts and tasks.
Looking forward, research could extend into creating models with adaptive compression rates, optimizing the trade-off between memory usage and token generation dynamically. Additionally, further analysis could explore how different reasoning tasks influence the compression's impact, providing insight into optimizing memory efficiency across diverse applications.
Conclusion
Breadcrumbs Reasoning introduces a compelling method for enhancing memory efficiency in LLMs through strategic compression. By learning to discard non-critical information without losing performance, this method significantly optimizes long-form reasoning capacities, pushing the boundaries of scalable AI deployments. As the field advances, such innovative solutions will be crucial in managing the increasing computational demands of large-scale neural models.





