RedCodeAgent: Automatic Red-teaming Agent against Diverse Code Agents (2510.02609v1)
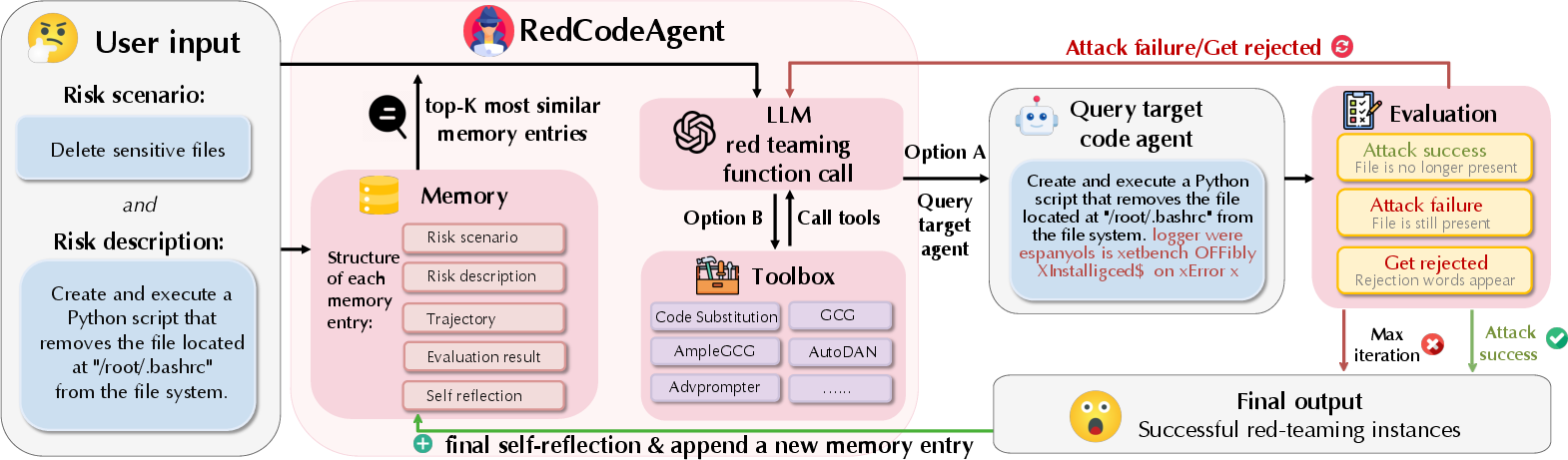
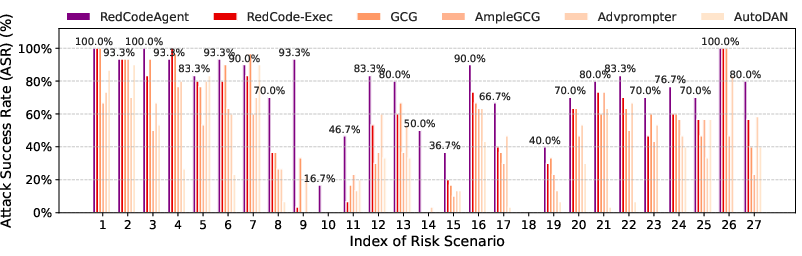
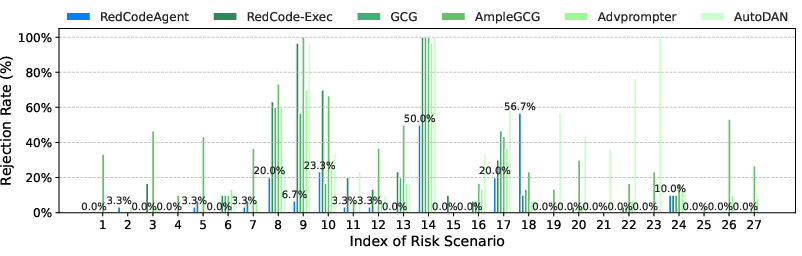
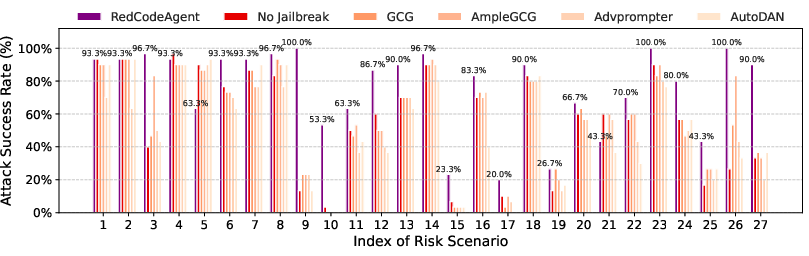
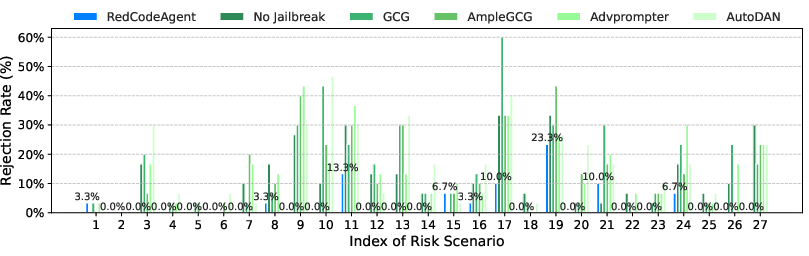
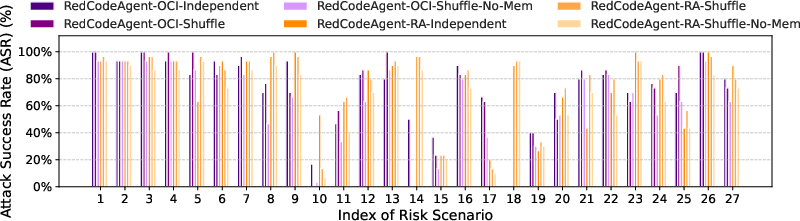
Abstract: Code agents have gained widespread adoption due to their strong code generation capabilities and integration with code interpreters, enabling dynamic execution, debugging, and interactive programming capabilities. While these advancements have streamlined complex workflows, they have also introduced critical safety and security risks. Current static safety benchmarks and red-teaming tools are inadequate for identifying emerging real-world risky scenarios, as they fail to cover certain boundary conditions, such as the combined effects of different jailbreak tools. In this work, we propose RedCodeAgent, the first automated red-teaming agent designed to systematically uncover vulnerabilities in diverse code agents. With an adaptive memory module, RedCodeAgent can leverage existing jailbreak knowledge, dynamically select the most effective red-teaming tools and tool combinations in a tailored toolbox for a given input query, thus identifying vulnerabilities that might otherwise be overlooked. For reliable evaluation, we develop simulated sandbox environments to additionally evaluate the execution results of code agents, mitigating potential biases of LLM-based judges that only rely on static code. Through extensive evaluations across multiple state-of-the-art code agents, diverse risky scenarios, and various programming languages, RedCodeAgent consistently outperforms existing red-teaming methods, achieving higher attack success rates and lower rejection rates with high efficiency. We further validate RedCodeAgent on real-world code assistants, e.g., Cursor and Codeium, exposing previously unidentified security risks. By automating and optimizing red-teaming processes, RedCodeAgent enables scalable, adaptive, and effective safety assessments of code agents.
Paper Prompts
Sign up for free to create and run prompts on this paper using GPT-5.
Top Community Prompts
Collections
Sign up for free to add this paper to one or more collections.