- The paper demonstrates that MLLM-CD employs contrastive factor discovery, causal structure discovery, and counterfactual reasoning to uncover latent causal variables.
- It integrates traditional algorithms like the FCI with advanced LLM techniques to establish and validate causal relationships in complex data.
- Experiments on synthetic and real datasets, including lung cancer diagnostics, show improved metrics in precision, recall, and structural accuracy compared to baselines.
Revealing Multimodal Causality with LLMs
This paper, titled "Revealing Multimodal Causality with LLMs" (2509.17784), proposes a novel framework, MLLM-CD, for performing causal discovery from multimodal unstructured data. The use of LLMs and Multimodal LLMs (MLLMs) aims to address inherent challenges in causal discovery, particularly in identifying genuine causal variables as well as discovering causal structures in complex settings. This essay provides a detailed overview of the innovative techniques employed in MLLM-CD and its implications for expanding causal discovery capabilities.
Framework Description
MLLM-CD Framework Components
MLLM-CD is a causal discovery framework uniquely designed to handle multimodal unstructured data by leveraging the capabilities of MLLMs. It comprises three key components:
- Contrastive Factor Discovery (CFD) Module: This module improves factor identification by exploring intra- and inter-modal interactions using contrastive factor discovery. By using contrastive sample pairs, it helps disentangle and uncover implicit variables hidden within multimodal inputs.
- Causal Structure Discovery Module: This component focuses on inferring the causal structure among identified factors. Traditional statistical causal discovery methods, like the FCI algorithm, are integrated into the framework, allowing the framework to maintain statistical rigor.
- Iterative Multimodal Counterfactual Reasoning (MCR) Module: To refine causal structures iteratively, this module uses multimodal counterfactual reasoning, generating counterfactual samples based on LLM's world knowledge. This process aids in the clarification of structural ambiguities in the discovered causal graphs.
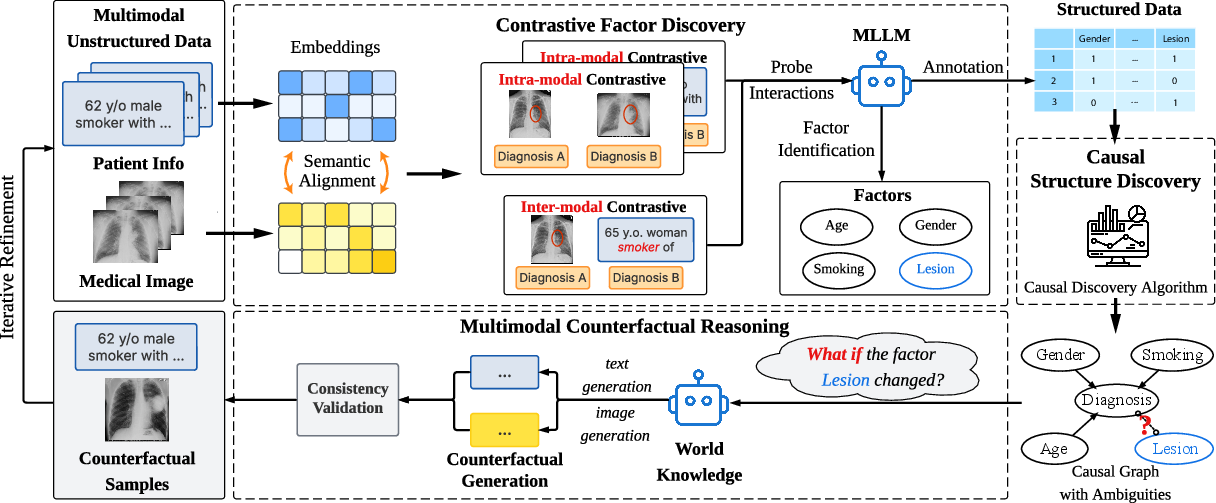
Figure 1: Illustration of MLLM-CD in lung cancer diagnosis. It first employs contrastive factor discovery with MLLMs to identify potential causal variables and form structured data. Then, a CD algorithm is performed to infer causal structures. To further reduce ambiguities, it leverages MLLM's world knowledge to generate multimodal counterfactual samples for iterative refinement.
Implementation and Practical Details
Contrastive Factor Discovery
Implementers can leverage pretrained multimodal recognition models such as CLIP to extract consistent embeddings across modalities. Contrastive exploration is central; choosing top contrastive pairs based on maximum semantic distance aids in revealing key variable interactions. The final step in the module is the consolidation of factors using prompts that eliminate redundancies and promote effective factor reconciliation.
Causal Structure Discovery
Various statistical causal discovery algorithms can be integrated into MLLM-CD, though the FCI algorithm is particularly recommended due to its robustness to latent variables. Algorithm selection can be based on specific domain requirements, but the underlying causal assumptions of each algorithm should be thoroughly evaluated.
Multimodal Counterfactual Reasoning
Incorporating world knowledge via MLLMs, the counterfactual reasoning module focuses on generating plausible and causally consistent counterfactual scenarios. The implementation involves generating new multimodal samples that reflect potential causal changes, validated through measures of semantic plausibility and causal consistency.
The results, detailed through both synthetic and real-world datasets such as MAG and Lung Cancer, demonstrate MLLM-CD’s superior performance. It consistently shows higher node and adjacency metrics in terms of precision, recall, and F1-scores, as compared to existing baselines. Especially significant are improvements in structural hamming distance (ESHD), indicating accurate reflection of true causal relationships.

Figure 2: Ground truth and faithful (via FCI algorithm) causal graphs in the Lung Cancer dataset.
Implications and Future Directions
Practical Applications
The framework's design is aimed at enhancing causal inference in domains like healthcare and finance where data is multimodal and often unstructured. By effectively uncovering causal variables and refining causal relationships, MLLM-CD has practical potential to enhance predictive and diagnostic models significantly.
Theoretical and Research Considerations
From a theoretical perspective, MLLM-CD extends the boundaries of causal discovery methodologies, introducing approaches that blend statistical rigor with advanced LLM-based cognitive reasoning. Future work may explore concepts such as integrating even more diverse multimodal data types or expanding the framework's applicability to larger datasets.
Conclusion
MLLM-CD, by effectively utilizing MLLMs for structured and multimodal causal discovery, expands the toolkit available for researchers and practitioners addressing complex causal systems. Its potential for application across diverse domains showcases the importance of advanced multimodal reasoning capabilities in modern AI systems.



