- The paper demonstrates that strategically modifying FFNs in specific Transformer layers leads to measurable performance improvements.
- It employs systematic experiments across various model sizes and layer configurations to reveal enhanced performance with expanded FFNs in middle layers.
- The study provides empirical evidence that concentrating FFNs in key middle layers optimizes Transformer models for superior NLP task outcomes.
Introduction
The paper "Layerwise Importance Analysis of Feed-Forward Networks in Transformer-based LLMs" (2508.17734) investigates the role of feed-forward networks (FFNs) in Transformer LLMs, specifically focusing on the importance of their positional configurations during pretraining. By manipulating FFNs—expanding their dimensions in certain layers and removing them in others—while maintaining the overall parameter count, the paper elucidates insights on FFNs' layerwise contributions to model performance across various pretraining contexts.
Methodology
Model Modifications
The paper explores an innovative approach by altering FFNs' configurations within Transformer models rather than relying solely on analyses of pretrained models. Figure 1 illustrates the modifications: (a) the baseline model uses standard Transformer layers, (b) certain layers in the experimental model have expanded FFNs, and (c) other layers have deactivated FFNs.
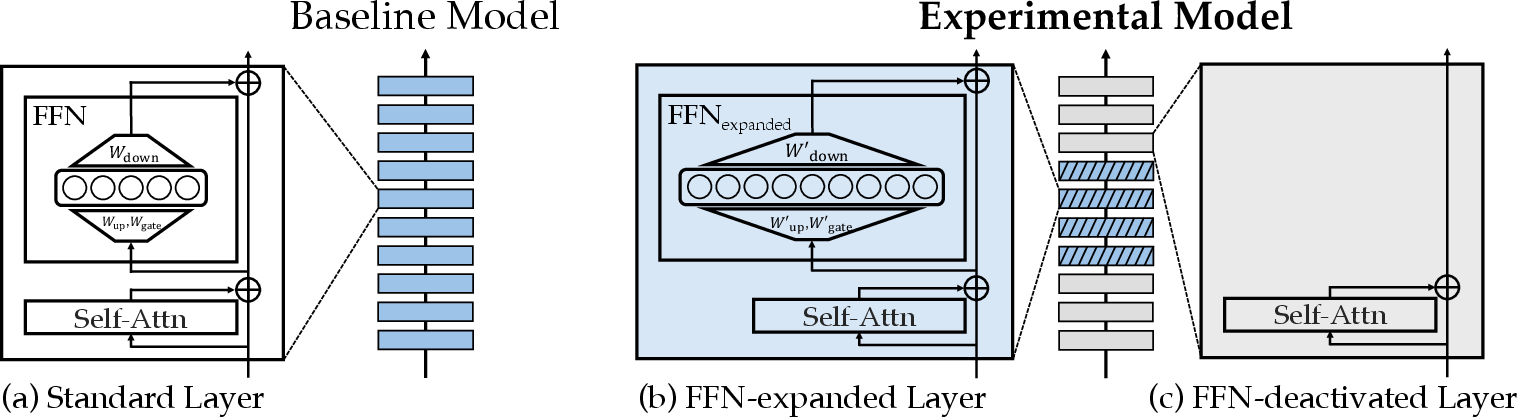
Figure 1: Layer Structure of Baseline and Experimental Models.
Positional Configurations
Experimental models place FFN-expanded layers in three positions: near the input (first), in the middle (middle), and near the output (final), which is significant for assessing FFN layer importance (Figure 2).
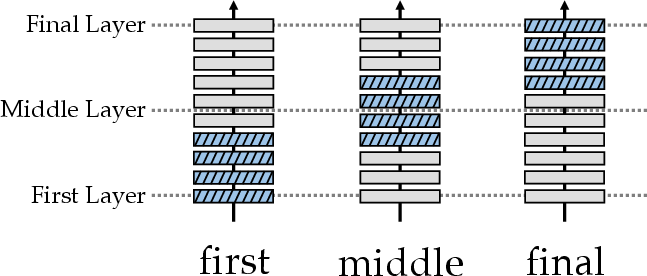
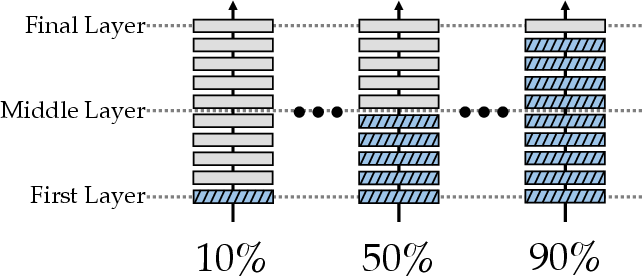
Figure 2: Different Positional Configurations of the FFN-extended Layer.
Experimental Setup
The paper evaluated models of varying sizes (285M, 570M, 1.2B parameters) and layers (12, 24, and 40) to determine how FFN configurations affect relative improvement (RI) across tasks. The RI metric, calculated as a percentage of improvement compared to baseline models, provides insight into FFN importance regarding model scale and layer distribution.
Experimental Results
FFN-expanded Layer Ratio
The experimental results indicate that models with approximately 70%-90% FFN-expanded layers generally outperform standard uniform FFN configurations, particularly in middle to final positioning, where significant task performances are observed.
Figure 3 shows RI by FFN-expanded layer ratio for different placements. Consistently, concentrating FFNs in specific crucial layers enhances overall model performance, while layers positioned in the middle layers tend to yield superior outcomes.
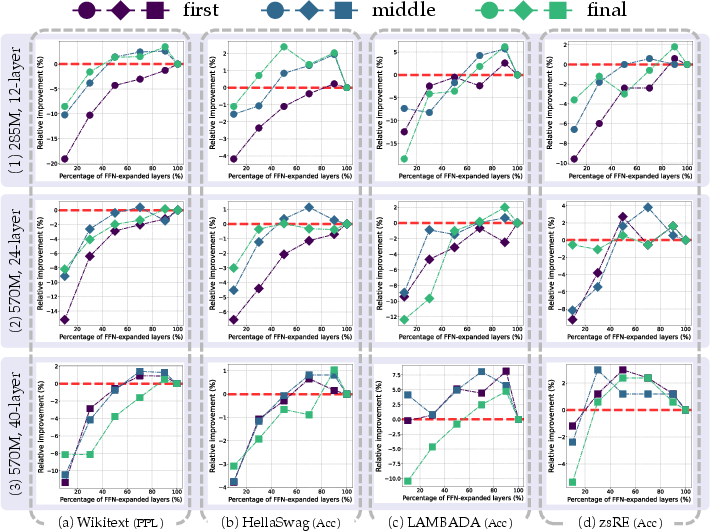
Figure 3: Relative Improvement across Tasks by FFN-expanded Layer Ratio.
Layerwise Importance Analysis
Using a layerwise-importance metric, the paper identifies middle layers as more critical contributors to FFN effectiveness. Figure 4 reflects these standardized layerwise importance scores, emphasizing the importance of FFNs in middle layers across all tested configurations.
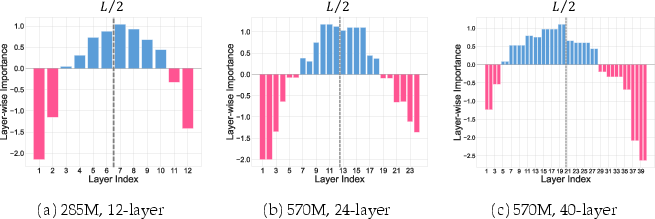
Figure 4: Layerwise Importance Scores.
The paper quantitatively demonstrates that central layers, especially in models with moderate depth, hold key importance for FFN placement, affecting the resulting task performance directly and substantially.
Conclusion
Concentrating FFNs in middle layers provides significant performance improvements for Transformer-based LLMs. The paper establishes that FFNs in middle layers are more impactful than those in initial or final layers, thus optimizing their configurations can effectively enhance model performance. This research provides empirical insights into Transformer architecture design, suggesting that strategic FFN deployment could serve as a valuable method for improving model efficacy in NLP tasks.
By advancing the understanding of FFNs' structural roles and diversifying Transformer model configurations, this paper offers a foundation for future work in optimizing LLMs' architecture, emphasizing strategic FFN deployment for superior model functioning.






