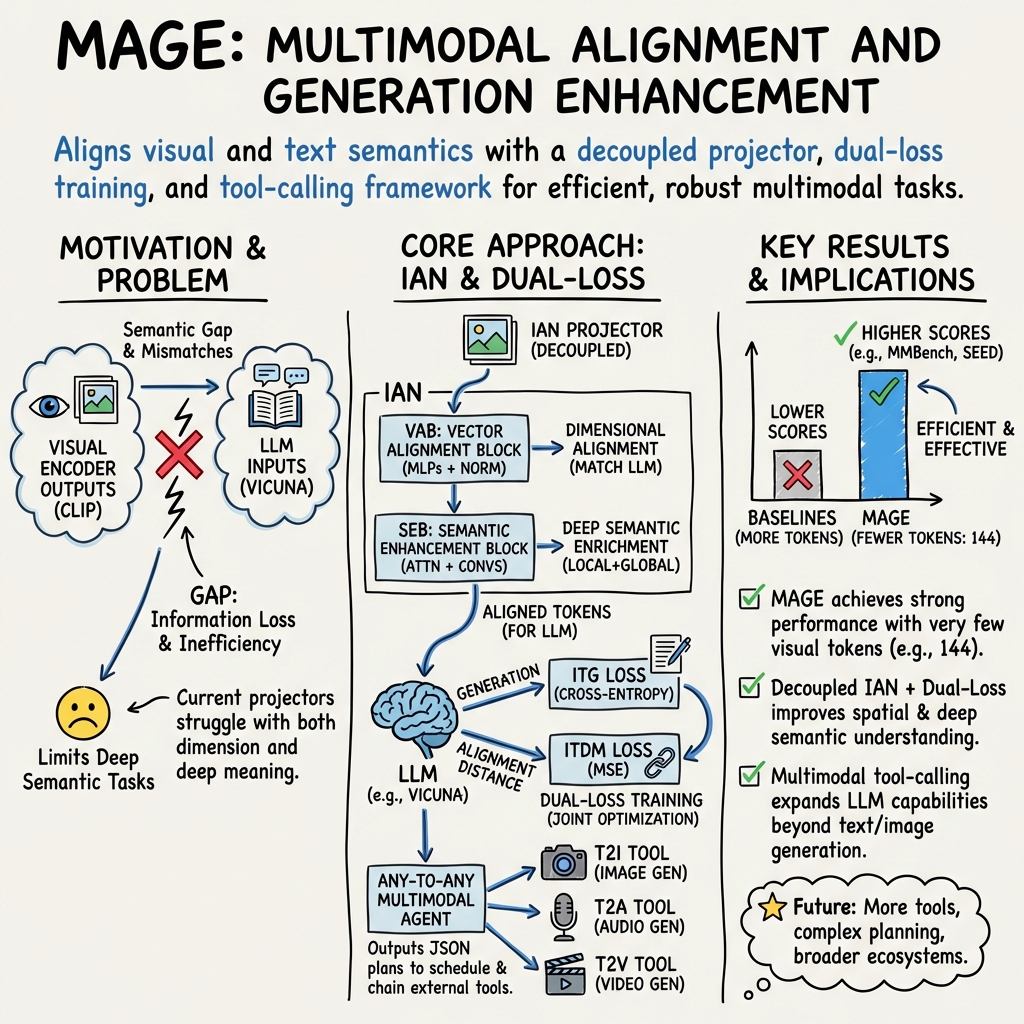
- The paper presents MAGE, a novel framework that integrates visual encoders and language models through an Intelligent Alignment Network for robust multimodal learning.
- It introduces a dual-loss training strategy combining cross-entropy and mean squared error to optimize both vector alignment and semantic enhancement.
- Experimental results on benchmarks like MME, MMBench, and SEED demonstrate improved performance and flexible any-to-any multimodal outputs.
Overview of "MAGE: Multimodal Alignment and Generation Enhancement via Bridging Visual and Semantic Spaces"
Introduction
Multimodal learning, which involves processing and generating information across different types of data such as images and text, poses significant challenges in achieving effective integration of visual encoders and LLMs. The core challenges include semantic gaps and dimensional mismatches between vision and text modalities, resulting in information loss during propagation. Researchers have sought solutions to these issues to enhance the capabilities of multimodal LLMs (MLLMs). The paper "MAGE: Multimodal Alignment and Generation Enhancement via Bridging Visual and Semantic Spaces" proposes a novel framework—MAGE—that aims to bridge semantic spaces of vision and text using an innovative alignment mechanism known as the Intelligent Alignment Network (IAN).

Figure 1: An example of an attention map from the Intelligent Alignment Network (IAN) demonstrating spatial understanding capabilities.
MAGE Framework
Alignment Mechanism
The architecture of MAGE introduces the Intelligent Alignment Network (IAN), which comprises two components: vector alignment and semantic enhancement.
- Vector Alignment Module: This module maps visual feature vectors to a dimensional space consistent with the LLM input, ensuring structural dimensional alignment and eliminating modality gaps.
- Semantic Enhancement Module: After alignment, this module injects high-level semantic information into the visual features, enhancing their expressive power in the semantic space of the LLM.
The paper employs a dual-loss training strategy combining cross-entropy with mean squared error to enhance the alignment effect. This approach simultaneously optimizes both efficiency and semantic alignment, addressing gaps between heterogeneous data.

Figure 2: Detailed architecture of MAGE, illustrating vector alignment and semantic enhancement capabilities of IAN.
Innovative Features
To increase MAGE’s ability for "Any-to-Any" transformation, the framework develops a fine-tuning dataset for multimodal tool-calling instructions, expanding the model’s output capability. This novel architecture supports multimodal outputs which include images, audio, video, and structured task planning.

Figure 3: Hierarchical Workflow demonstrating MAGE's capability in task planning and execution, generating complex outputs.
Experimental Results
The proposed architecture excels across multiple multimodal benchmarks including MME, MMBench, and SEED, demonstrating superior performance in image-text alignment and semantic understanding tasks. Experimental results confirm that MAGE achieves significant performance improvements, outperforming existing methods in resource efficiency and output flexibility.
Implications and Future Directions
Enhancements in Multimodal Applications
The integration of the IAN module elevates MAGE’s proficiency in cross-modal tasks, setting a precedent for further research in bridging the gap between visual and language modalities. The flexible tool invocation framework also highlights potential advancements in developing more adaptive multimodal systems.
Future Research
The study opens new avenues for exploration in enhancing MLLMs to efficiently handle complex tasks across varying modalities. Future work may focus on refining alignment mechanisms and exploring new datasets for training models that accurately capture the deep semantic relationships between visual and textual data.
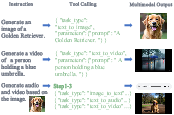
Figure 4: Illustration of MAGE's expanded multimodal applications, emphasizing the integration of tools for complex task generation.
Conclusion
The development of MAGE marks a significant advancement in multimodal learning, offering sophisticated techniques to diminish semantic and dimensional disparities between visual encoders and LLMs. With the Intelligent Alignment Network at its core, MAGE sets a high standard for achieving effective semantic alignment, paving the way for future innovations in multimodal model architectures.