A Survey of LLM-based Automated Program Repair: Taxonomies, Design Paradigms, and Applications
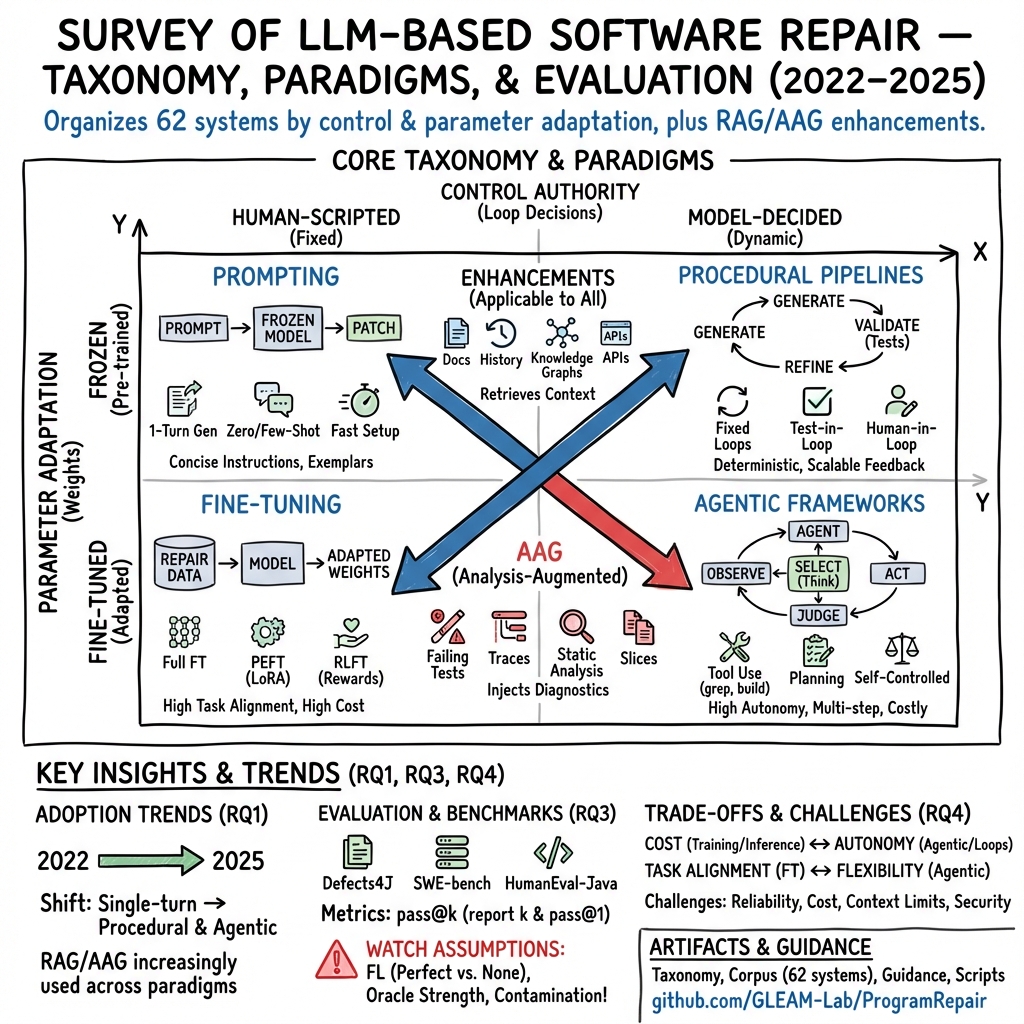
Abstract: LLMs are reshaping automated program repair. We present a unified taxonomy that groups 62 recent LLM-based repair systems into four paradigms defined by parameter adaptation and control authority over the repair loop, and overlays two cross-cutting layers for retrieval and analysis augmentation. Prior surveys have either focused on classical software repair techniques, on LLMs in software engineering more broadly, or on subsets of LLM-based software repair, such as fine-tuning strategies or vulnerability repair. We complement these works by treating fine-tuning, prompting, procedural pipelines, and agentic frameworks as first-class paradigms and systematically mapping representative systems to each of these paradigms. We also consolidate evaluation practice on common benchmarks by recording benchmark scope, pass@k, and fault-localization assumptions to support a more meaningful comparison of reported success rates. We clarify trade-offs among paradigms in task alignment, deployment cost, controllability, and ability to repair multi-hunk or cross-file bugs. We discuss challenges in current LLM-based software repair and outline research directions. Our artifacts, including the representation papers and scripted survey pipeline, are publicly available at https://github.com/GLEAM-Lab/ProgramRepair.
Paper Prompts
Sign up for free to create and run prompts on this paper using GPT-5.
Top Community Prompts
Glossary
- Abstract syntax tree (AST): A tree-structured representation of program syntax used for code analysis and transformation. "abstract-syntax-tree structure"
- Agentic frameworks: Repair workflows in which LLM agents decide actions and control multi-step processes. "agentic frameworks as first-class paradigms"
- Analysis-Augmented Generation (AAG): Augmenting model generation with static or dynamic analysis results to guide or constrain patches. "AAG incorporates static or dynamic program-analysis results"
- Backward citation snowballing: Expanding a literature set by scanning the references of selected papers. "backward citation snowballing"
- Benchmark scope: The coverage and type of defects/tasks included in a benchmark for evaluation. "benchmark scope, pass@k, and fault-localization assumptions"
- BLEU: A sequence-to-sequence evaluation metric based on n-gram overlap with references. "BLEU from 21.3% to 29.3%"
- CodeBLEU: A code-specific metric extending BLEU with syntax and semantic features. "CodeBLEU from 32.5% to 40.9%"
- Cohen's kappa: A statistic measuring inter-rater agreement adjusted for chance. "Cohen's kappa"
- Contamination-resistant benchmark: A dataset designed to limit evaluation leakage from training data. "contamination-resistant benchmark"
- Cross-file bugs: Defects whose fixes span multiple files and require broader context. "cross-file bugs"
- CWE (Common Weakness Enumeration): A standardized catalog of software vulnerability types. "CWE knowledge"
- Data-flow facts: Information describing how data values propagate through program paths and variables. "data-flow facts"
- Defects4J v2: A version of the widely used Java bug benchmark suite for repair evaluation. "Defects4J v2"
- Fault localization: Identifying the location of the bug in the codebase. "fault-localization assumptions"
- Federated learning: Training models across multiple clients without sharing raw data, aggregating updates centrally. "a federated setting"
- Fine-tuning: Updating a pre-trained model’s parameters on task-specific data to improve performance. "Fine-tuning adapts a pre-trained LLM for software repair by updating its weights using bug-fix data."
- Goal Question Metric (GQM): A structured methodology for defining goals, questions, and metrics in empirical studies. "Goal Question Metric (GQM) approach"
- Human-in-the-loop: Workflows that interleave human feedback or decisions within automated processes. "Human-in-the-Loop"
- HumanEval-Java: A benchmark of programming tasks used to evaluate code generation or repair in Java. "HumanEval-Java"
- Knowledge distillation: Training a smaller student model to mimic a larger teacher, preserving performance with lower cost. "Knowledge distillation transfers bug-fixing skill from a large teacher or rule set to a smaller student"
- LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation): A PEFT method injecting low-rank trainable matrices into transformer layers. "LoRA"
- LLM-as-Judge: Using an LLM to critique, score, or accept patches, thereby steering the repair loop. "LLM-as-Judges"
- Multi-hunk bugs: Defects requiring edits across multiple separate code hunks/chunks. "multi-hunk bugs"
- NEFTune: A noise-regularized fine-tuning technique that injects calibrated noise into embeddings. "NEFTune"
- Parameter adaptation: Adjusting model parameters (via tuning) to align the model with a specific task. "parameter adaptation"
- Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT): Fine-tuning only small adapter modules while freezing the backbone to reduce compute/memory. "Parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT)"
- Pass@k: A metric where success is counted if any of k generated candidates passes the evaluation tests. "pass@k"
- Prefix-tuning: A PEFT approach that prepends trainable prefix vectors to model inputs. "prefix-tuning"
- Procedural pipelines: Hard-coded multi-step repair scripts where experts define control flow and stopping criteria. "procedural pipelines"
- QLoRA: A PEFT method combining 4-bit quantization with LoRA adapters for efficient training. "QLoRA"
- Reinforcement Learning Fine-Tuning (RLFT): Fine-tuning with reward signals from execution or security outcomes to optimize for correctness. "RLFT"
- Repository-level: Operating at the scope of full repositories rather than single functions or files. "repository-level"
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG): Enriching model inputs with retrieved external code, docs, or historical fixes. "Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)"
- Self-Controlled System: Systems where LLMs plan workflows, spawn subtasks, select actions, and decide termination. "Self-Controlled System"
- Static analysis: Program analysis performed without execution to infer properties or detect issues. "static-analysis results"
- Test-in-the-Loop: Iterative procedures that use test outcomes to drive patch generation and refinement. "Test-in-the-Loop"
- Tool-Augmented Agents: Agent frameworks where an LLM selects and invokes external tools within a fixed skeleton. "Tool-Augmented Agents"
- Transformers: Attention-based neural architectures foundational to modern code and LLMs. "transformers"
- Utilization mode: A way of organizing systems by how an LLM is used (e.g., generation, judging) rather than control structure. "utilization mode"
- Zero-shot prompting: Prompting a model to perform a task without training or in-context examples. "zero-shot prompting"
Collections
Sign up for free to add this paper to one or more collections.