- The paper introduces ECMNet, a hybrid CNN-Mamba architecture that enhances semantic segmentation with a U-shaped encoder-decoder and a novel Feature Fusion Module (FFM).
- It achieves 70.6% mIoU on Cityscapes and 73.6% on CamVid with only 0.87M parameters and 8.27G FLOPs, successfully balancing accuracy and computational efficiency.
- The design incorporates modules like EDAB and MSAU to capture multi-scale features and global context, enabling efficient segmentation in resource-constrained settings.
Lightweight Semantic Segmentation via CNN-Mamba Hybrid Network
This paper introduces ECMNet, a novel and efficient CNN-Mamba hybrid network designed for lightweight semantic segmentation. The architecture leverages a U-shaped encoder-decoder structure enhanced with a Feature Fusion Module (FFM) to capture global context information. By integrating CNNs with Mamba, ECMNet aims to address the limitations of each individual architecture, achieving an improved balance between accuracy and computational efficiency. The authors showcase strong numerical results, achieving 70.6\% mIoU on Cityscapes and 73.6\% mIoU on CamVid datasets with only 0.87M parameters and 8.27G FLOPs.
Core Network Components
The ECMNet architecture comprises four primary components: a CNN encoder, a CNN decoder, a Mamba-based FFM, and long skip connections enhanced with Multi-Scale Attention Units (MSAUs). The CNN encoder-decoder extracts localized features for detailed spatial representation. The Mamba-based FFM captures complex spatial information and long-range feature dependencies using a state space model (SSM), optimizing global feature representations and computational complexity. The long skip connections facilitate the integration of low-level spatial information and high-level semantic information, enhancing segmentation quality.
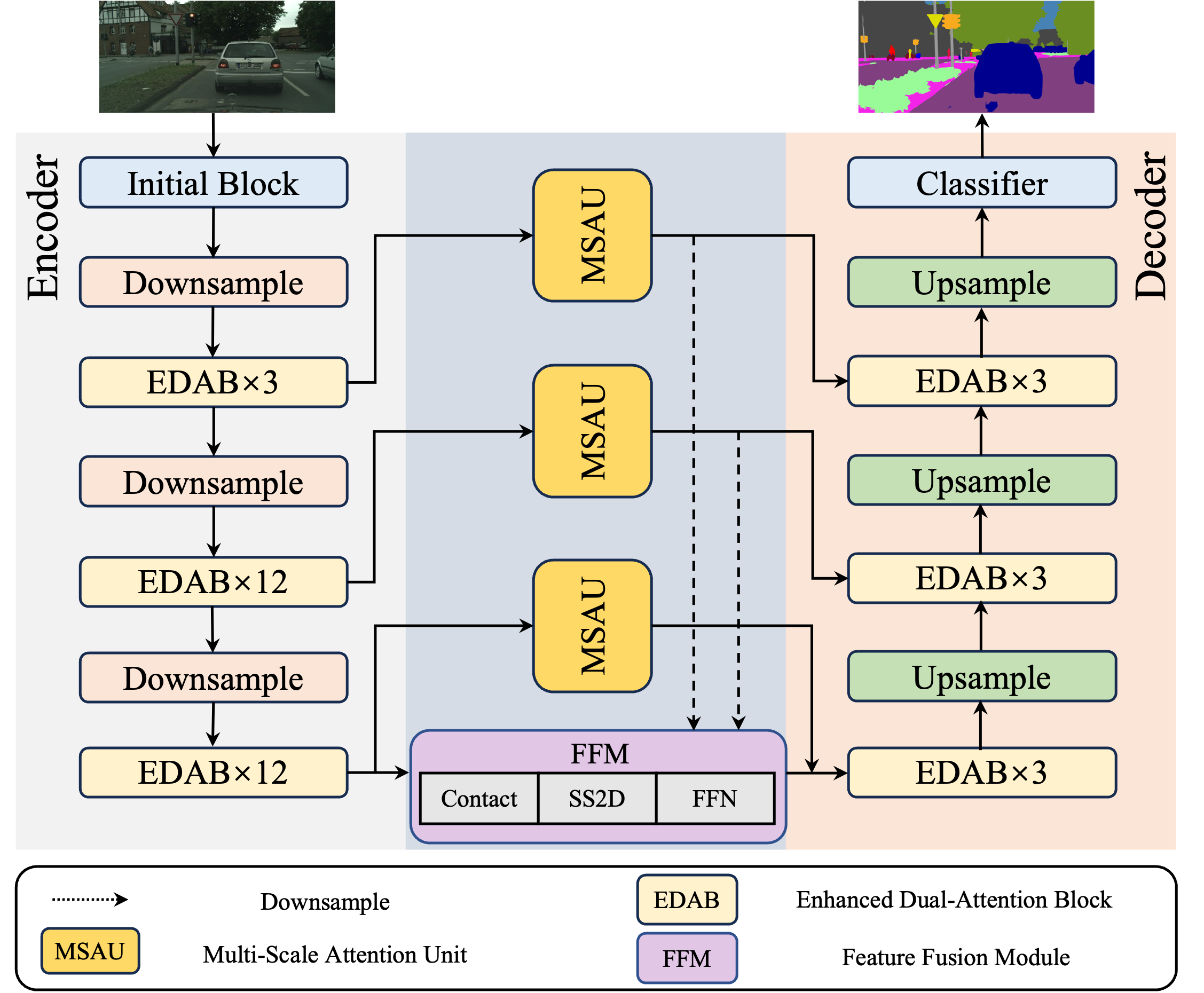
Figure 1: The overall network architecture of Efficient CNN-Mamba Network (EMCNet).
Enhanced Dual-Attention Block (EDAB)
The EDAB module focuses on extracting multi-dimensional semantic information while minimizing network parameters. It employs a bottleneck structure with a 1×1 convolution to reduce the number of channels, complemented by 3×1 and 1×3 convolutions to compensate for any loss in accuracy. The core of EDAB lies in its two-branch path, capturing local and global feature information. One branch processes local and short-distance features, while the parallel branch uses atrous convolution for global feature integration. Channel Attention (CA) and Dual-Direction Attention (DDA) are utilized in the two branches to build different attention matrices, learning multi-dimensional feature information and improving feature expression. The output is then processed by a 1×1 point-wise convolution, and a channel shuffle strategy is applied to establish inter-channel correlations. The detailed operation is as follows:
Fup_branch=Conv1×3(Conv3×1(Conv1×1(x))), Fmid_branch_1=ConvCA(Conv1×3,D(Conv3×1,D(Fup_branch))), Fmid_branch_2=ConvDDA(Conv1×3,D,R(Conv3×1,D,R(Fup_branch))), Y1=ConvCS(f1×1(Fup_branch+Fmid_branch_1+Fmid_branch_2)+x),
where x denotes the input of the EDAB, Y1 denotes the output feature map of the EDAB, and Convk×k(⋅) are normal convolution operation.
Multi-Scale Attention Unit (MSAU)
The MSAU module is designed to enhance feature representation by combining low-level spatial details with high-level semantic information. Inspired by U-Net, the MSAU uses same-resolution connections to integrate feature maps. The MSAU operates through two branches: Multi-Scale Spatial Aggregation and Channel Aggregation. In the Multi-Scale Spatial Aggregation branch, the input feature map undergoes a 1×1 convolution to reduce the number of channels, followed by depth-separable convolutions of different sizes (3×3, 5×5, and 7×7). The outputs are then fused, and a spatial attention map is generated. The Channel Aggregation branch uses average pooling and max pooling to capture channel statistics, and the results are multiplied with the spatial aggregation results. The detail operation can be defined as:
X1=Conv(3×3)(Conv(1×1)(x))+Conv(5×5)(Conv(1×1)(x))+Conv(7×7)(Conv(1×1)(x)), X2=Conv(1×1)(X1⊗Sigmoid(Conv(7×7)(Pool(x)))), X3=Conv(1×1)(ReLU(Conv(1×1)(AvgPool(Conv(3×3)(x))))), X4=Conv(1×1)(ReLU(Conv(1×1)(MaxPool(Conv(3×3)(x))))), Y2=x+(X2⊗(X3+X4))
where x denotes the input of the MSAU and Y2 represents the output feature map of the MSAU.
Feature Fusion Module (FFM)
The FFM leverages the effectiveness of Mamba in linear-complexity sequence modeling by introducing a 2D-Selective-Scan (SS2D) block. The FFM integrates different scale feature information from the MSAU and the encoder through concatenation. The SS2D block extracts and fuses features through a series of linear transformations and 2D convolution operations, enhancing feature representation. A Feed-Forward Network (FFN) then performs a nonlinear transformation to adjust the weight distribution of features. The complete operation is shown as follows:
XFFN=FFN(SS2D(Concat(xencoder,xMSAU1,xMSAU2))), Y3=XFFN+xencoder
where xencoder,xMSAU1,xMSAU2 denotes the out of the Encoder and MSAU respectively, and Y3 denotes the output feature map of the FFM.
Experimental Results
The paper presents extensive ablation studies and comparisons with state-of-the-art methods on the Cityscapes and CamVid datasets. The ablation studies validate the effectiveness of each module in ECMNet. The results demonstrate that ECMNet achieves a better balance between performance and parameters compared to other lightweight semantic segmentation models. Specifically, ECMNet achieves 70.6\% mIoU on the Cityscapes dataset and 73.6\% mIoU on the CamVid dataset with only 0.87M parameters.
Figure 2: The simple structure of the baseline model.
Conclusion
ECMNet presents a compelling approach to lightweight semantic segmentation by integrating CNNs and Mamba. The proposed architecture, featuring the FFM, EDAB, and MSAU modules, achieves a superior balance between model size and performance. The experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness and generalization ability of ECMNet on standard benchmark datasets. This research paves the way for efficient and accurate semantic segmentation in resource-constrained environments.



