- The paper demonstrates that lightweight encoder-decoder models, including T5 and BERT2BERT with sub-300M parameters, effectively standardize radiology reports.
- It uses MIMIC-CXR and CheXpert Plus datasets along with GPT-4 for weak annotation, employing methods like prefix prompting, in-context learning, and LoRA finetuning.
- Results reveal that BERT2BERT initialized from RoBERTa-PM-M3 outperforms T5 and tuned LLMs in both performance and cost-efficiency.
Structuring Radiology Reports: Challenging LLMs with Lightweight Models
Introduction
The paper "Structuring Radiology Reports: Challenging LLMs with Lightweight Models" (2506.00200) addresses the critical task of transforming unstructured radiology reports into standardized formats to improve both interpretability and applicability in ML applications. The unstructured nature of radiology reports commonly used in medical practices often results in inconsistencies that pose challenges in clinical interpretation and ML integration. LLMs have shown potential in automating this transformation but their deployment is limited by computational demands and concerns over data privacy. The paper explores the use of lightweight encoder-decoder models, specifically T5 and BERT2BERT with sub-300M parameters, as alternatives to LLMs for this task.
Methodology
The paper leverages datasets from MIMIC-CXR and CheXpert Plus, using GPT-4 as a weak annotator to create structured labels from free-text reports. Lightweight models, T5 and BERT2BERT, are trained and benchmarked against larger LLMs across various adaptation methods, including prefix prompting, in-context learning (ICL), and LoRA finetuning.
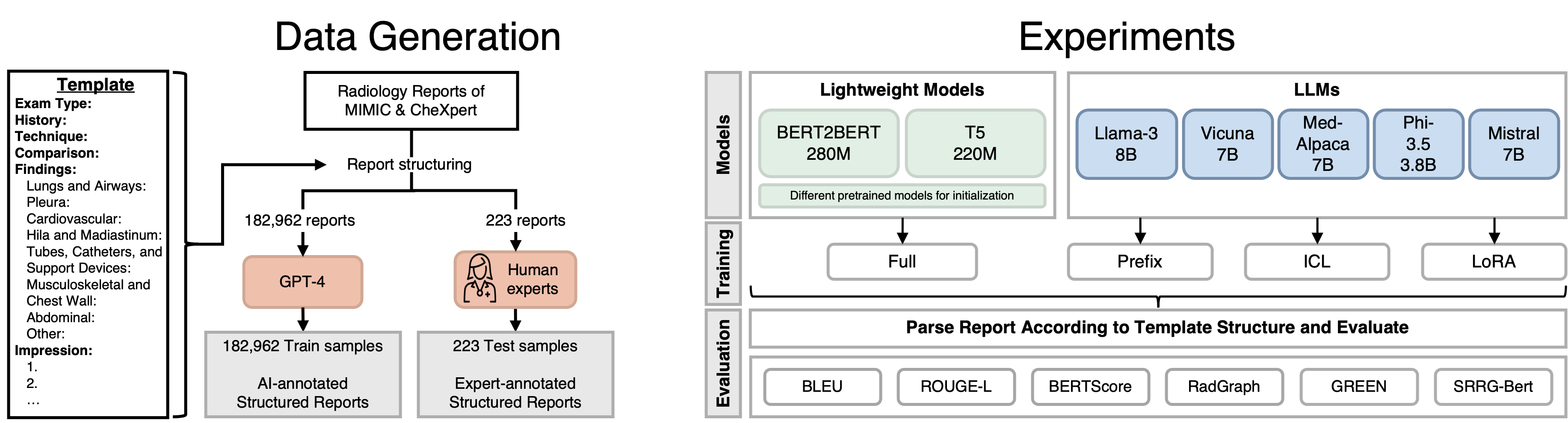
Figure 1: Dataset generation and experimental overview with LLMs and lightweight models.
Benchmarking and Results
The lightweight models were evaluated using several radiology-specific performance metrics such as GREEN and F1-SRR-BERT. The findings indicate that the BERT2BERT model, when initialized from RoBERTa-PM-M3 weights, consistently outperformed its T5 counterpart and even surpassed adaptively tuned LLMs in structuring task performance under most conditions.
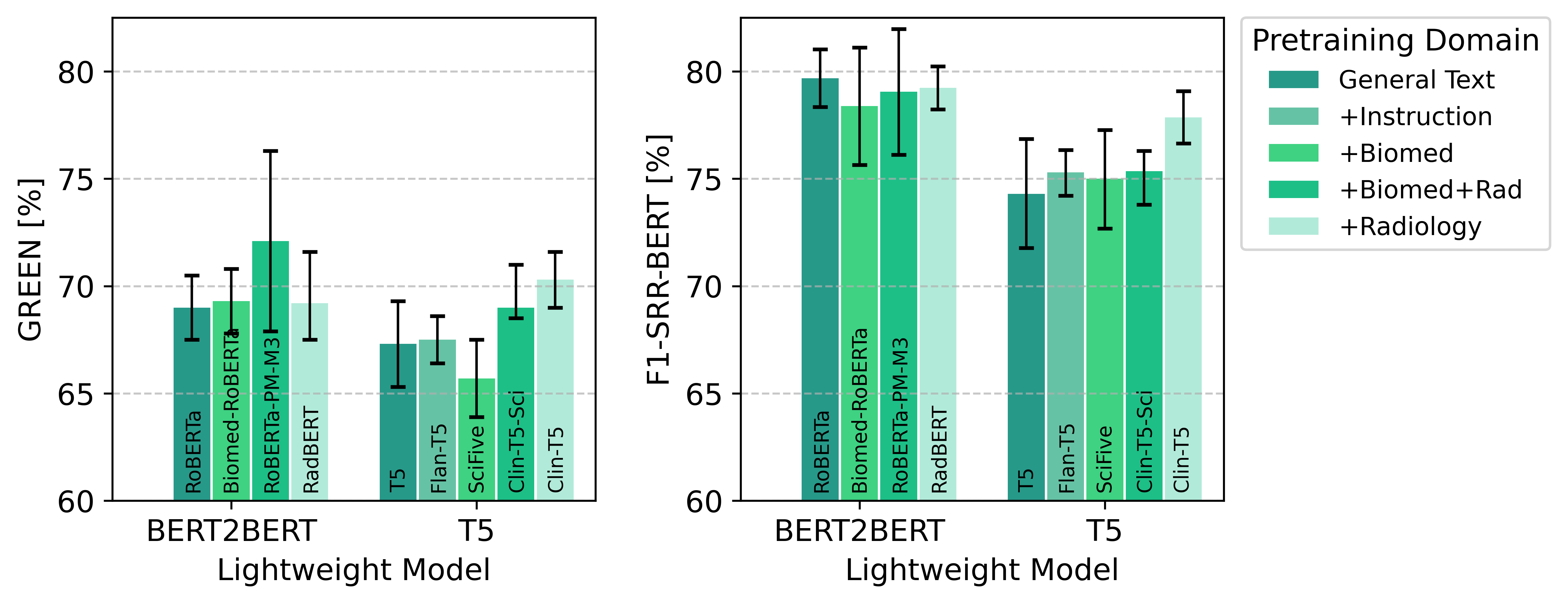
Figure 2: Performance comparison of lightweight models initialized from varying domain-relevant pretrained models.
LoRA finetuning emerged as the most effective adaptation method for the LLMs, significantly enhancing their performance, especially in the Findings section, compared to prefix prompting and ICL.
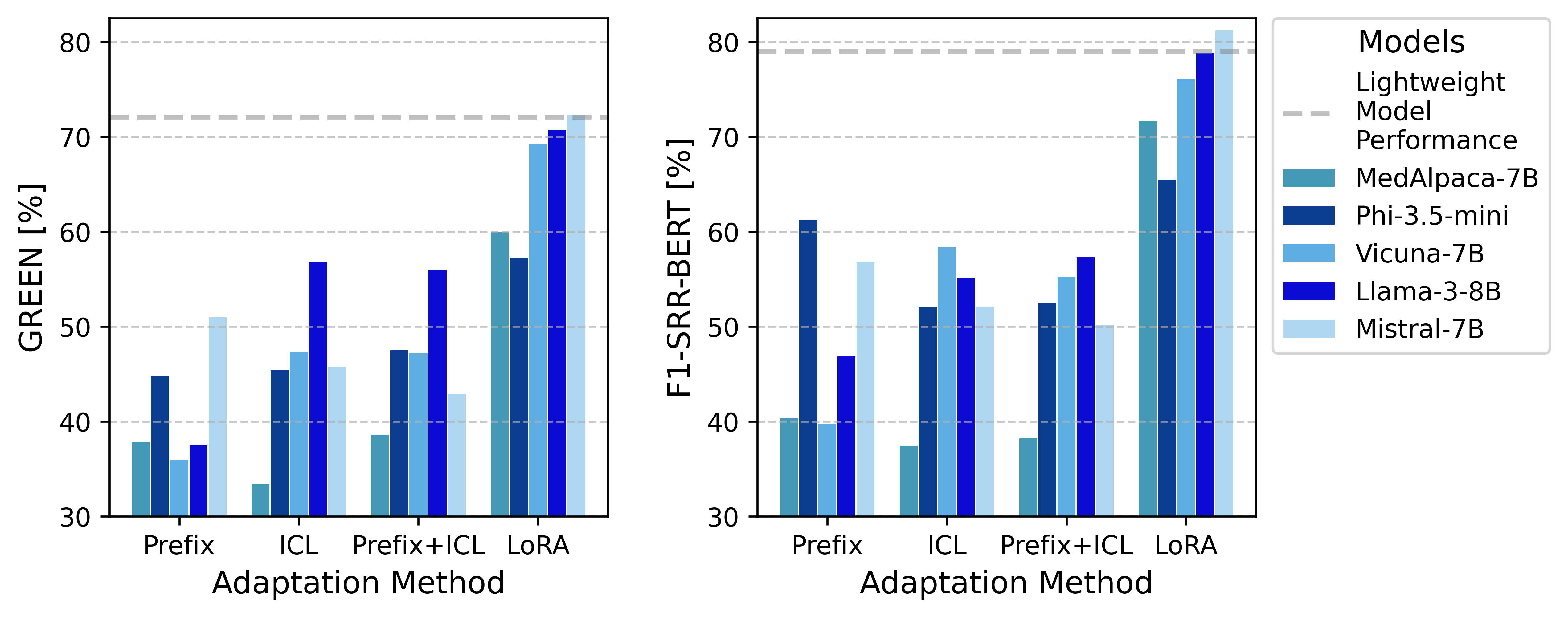
Figure 3: LLM adaptation comparison showing the performance impacts of different tuning methods.
Cost and Efficiency Analysis
The paper highlights the cost-efficiency and sustainability of lightweight models, showing that these models operated with substantially less computational overhead than the LLMs, delivering results faster and with lower environmental impact.
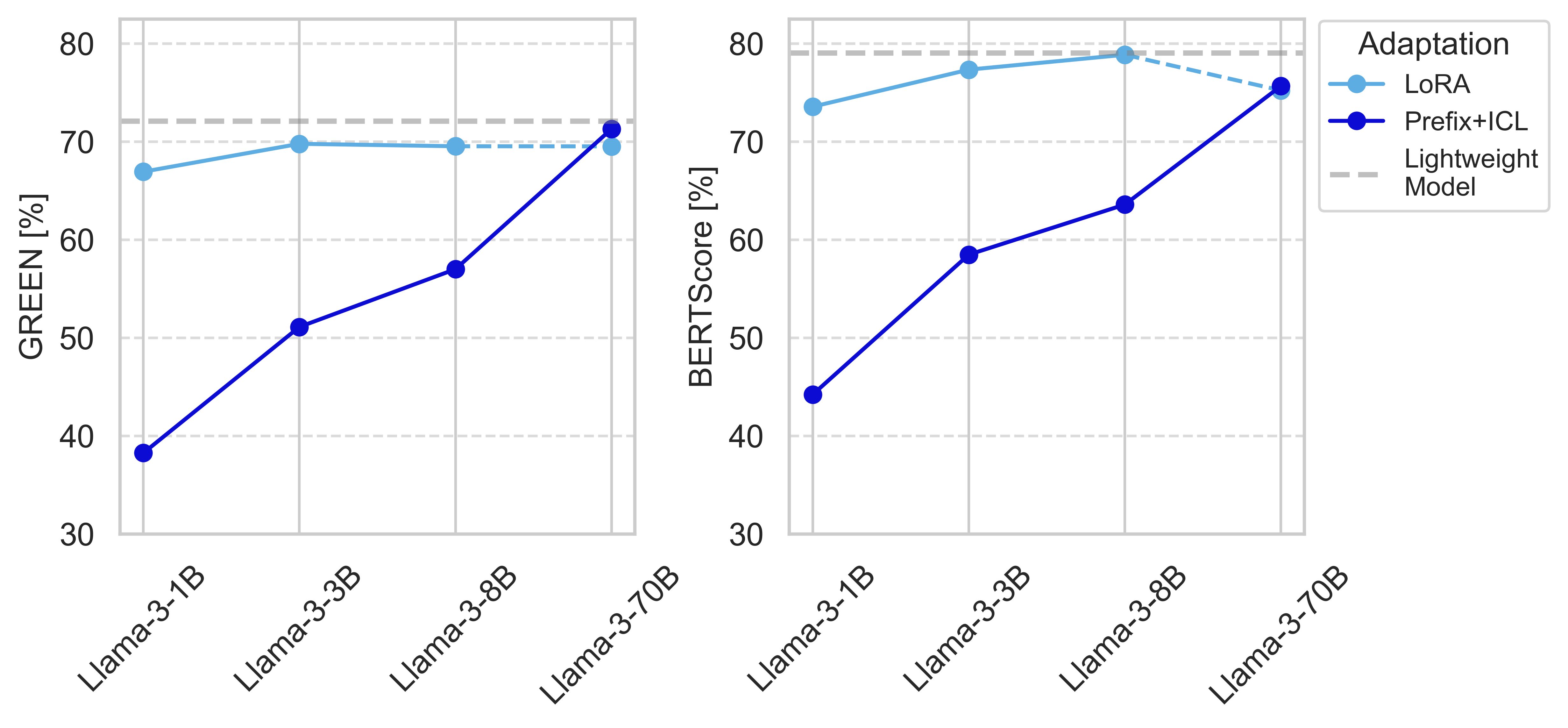
Figure 4: Performance and efficiency trade-offs of LLaMA-3 models across different scales.
Discussion
This paper affirms the practicality of lightweight, task-specific models in healthcare settings where infrastructure limitations prevail. The smaller models' capacity to efficiently process radiology reports makes them a viable solution for standardizing report formats, thereby facilitating enhanced clinical workflows and supporting ML integrations without the complications associated with LLMs.
Implications and Future Work
The paper's findings suggest that well-optimized lightweight models can effectively replace LLMs for specific tasks, mitigating the computational and privacy concerns that accompany LLM deployment. Future research could explore extending the application of lightweight models to other types of clinical reports or exploring hybrid models that balance the strengths of domain-specific knowledge with scalable performance benefits.
Conclusion
This paper presents compelling evidence that lightweight, task-specific models can serve as effective and efficient alternatives to their larger counterparts for the task of structuring radiology reports. The capability to perform effectively within cost and environmental constraints reinforces the importance of lightweight models in clinical practice, potentially guiding future AI developments in healthcare.





