Unveiling the Role of ChatGPT in Software Development: Insights from Developer-ChatGPT Interactions on GitHub (2505.03901v1)
Abstract: The advent of LLMs has introduced a new paradigm in software engineering, with generative AI tools like ChatGPT gaining widespread adoption among developers. While ChatGPT's potential has been extensively discussed, there is limited empirical evidence exploring its real-world usage by developers. This study bridges this gap by conducting a large-scale empirical analysis of ChatGPT-assisted development activities, leveraging a curated dataset, DevChat, comprising 2,547 unique shared ChatGPT links collected from GitHub between May 2023 and June 2024. Our study examines the characteristics of ChatGPT's usage on GitHub (including the tendency, prompt turns distribution, and link descriptions) and identifies five categories of developers' purposes for sharing developer-ChatGPT conversations during software development. Additionally, we analyzed the development-related activities where developers shared ChatGPT links to facilitate their workflows. We then established a mapping framework among data sources, activities, and SE tasks associated with these shared ChatGPT links. Our study offers a comprehensive view of ChatGPT's application in real-world software development scenarios and provides a foundation for its future integration into software development workflows.
Paper Prompts
Sign up for free to create and run prompts on this paper using GPT-5.
Top Community Prompts
Explain it Like I'm 14
Overview
This paper looks at how real software developers use ChatGPT while working on code. The authors collected and studied thousands of public links to ChatGPT conversations that developers shared on GitHub. Their goal was to understand when, why, and how ChatGPT is used in everyday programming tasks.
Key Objectives
To make things simple, the paper asked four main questions:
- How are developers using ChatGPT during software development?
- Why do developers share their ChatGPT conversations on GitHub?
- In what kinds of development activities do these shared conversations show up?
- What specific software tasks are ChatGPT helping with?
Methods and Approach
Here’s how the researchers did it, explained with everyday ideas:
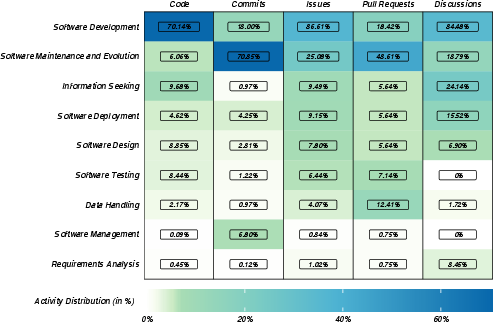
- Finding the conversations: Since May 2023, ChatGPT has let users share a link to their chat. The team searched GitHub (a site where developers store and discuss code) for these shared links in five places:
- Code (files and comments inside repositories)
- Commits (the “save points” of code changes)
- Issues (bug reports or task tickets)
- Pull Requests (code change reviews before merging)
- Discussions (forum-like posts)
- Getting past limits: GitHub searches can only show so many results at once. To work around this, the team split searches by programming language and time (month-by-month) and used both the official GitHub API and a web crawler when needed.
- Cleaning the data: They removed broken links, non-English content, and duplicates. After this careful filtering, they ended up with a clean dataset called DevChat containing 2,547 unique shared ChatGPT links.
- Understanding the chats: They looked at things like:
- “Prompt turns” (how many back-and-forth messages between developer and ChatGPT—like a text conversation thread)
- Whether people included a description explaining the shared link
- What the conversation was used for (purpose), what activity it related to, and what specific software task it helped with
- Sorting and grouping (the “Constant Comparison” method): Think of this like sorting lots of sticky notes into labeled piles. The authors read many conversations, created simple labels (like “generate code” or “fix a bug”), grouped similar ones together, and then connected how these groups relate. They also checked each other’s labeling to keep it reliable.
Main Findings and Why They Matter
Where developers share ChatGPT links most
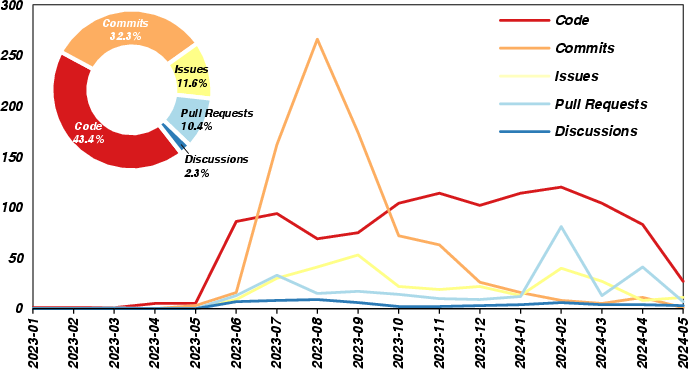
- Most links came from Code (43.4%) and Commits (32.3%). That means people mainly used and shared ChatGPT while writing or changing code.
- The number of shared links peaked around August 2023 and kept growing over time—showing strong interest and adoption.
Why it matters: This suggests ChatGPT is becoming a regular tool in coding and version control, not just something used in discussions or planning.
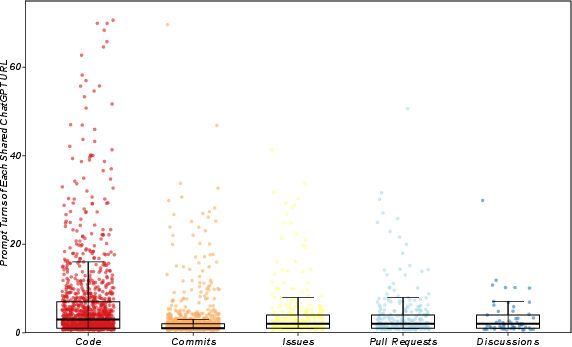
How they talk to ChatGPT
- Many conversations were short and focused: most common were two or three messages back-and-forth.
- Longer chats happened more in Code, which makes sense for tricky tasks like debugging or step-by-step code generation.
Why it matters: ChatGPT is often used like a quick helper for specific tasks, and sometimes as a deeper partner for complex coding.
Do people explain the shared links?
- Most shared links had a description or context (about 83%), especially in Commits (almost all had descriptions), Pull Requests, and Discussions.
- In Code, descriptions were more mixed—some had helpful context, some didn’t.
Why it matters: Good descriptions help teammates understand why the chat is useful, especially in collaborative workflows.
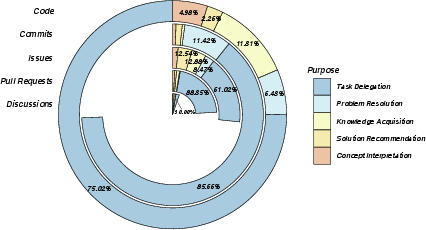
Why developers share these chats (five main purposes)
- Task Delegation: The most common purpose. Developers ask ChatGPT to do repetitive tasks like generating boilerplate code or writing a README.
- Problem Resolution: Using ChatGPT to debug or fix errors—more common in Issues and Commits.
- Knowledge Acquisition: Learning or clarifying concepts—more common in Discussions and Issues.
- Solution Recommendation: Getting suggestions, best practices, or approaches—also more common in Discussions and Issues.
- Concept Interpretation: Asking ChatGPT to explain ideas or structures—used less overall, but helpful for quick understanding.
Why it matters: ChatGPT isn’t just a code generator—it also teaches, recommends, and troubleshoots. But most shared uses focus on “getting tasks done.”
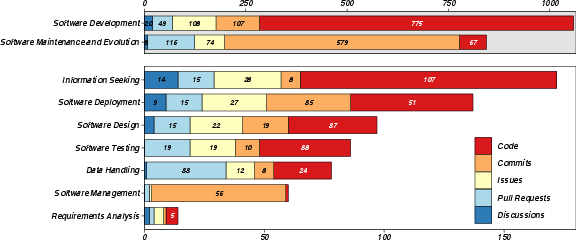
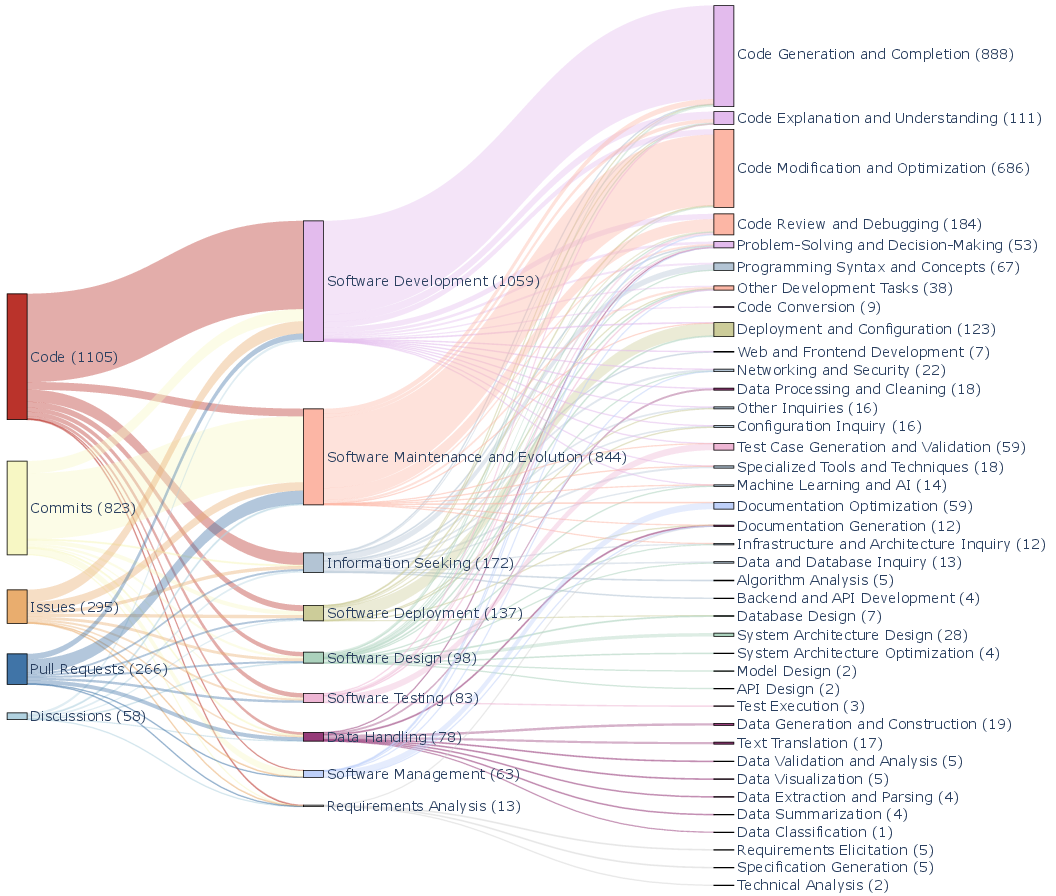
What development activities and tasks are involved
- Activities covered both standard software stages (like requirements, design, development, testing, deployment, maintenance) and supporting activities (like handling data and searching for info).
- The most common activities were Software Development and Software Maintenance & Evolution.
- They mapped 39 specific software engineering tasks. The top ones were:
- Code Generation and Completion (making and finishing code)
- Code Modification and Optimization (improving or changing existing code)
Why it matters: This gives a clear picture of where ChatGPT fits best today—hands-on programming and improving existing code.
Implications and Potential Impact
- Better tools and workflows: Knowing how developers use ChatGPT can help teams design smarter tools and processes (for example, easier ways to attach chat links to commits with clear descriptions).
- Productivity boost: Since many uses are short, specific tasks, integrating ChatGPT into editors and code review tools can save time without much overhead.
- Human review still needed: Because ChatGPT can be wrong or miss context, developers should keep checking results—especially for tricky bugs or important changes.
- Training and onboarding: ChatGPT’s role in knowledge and solution recommendations suggests it can help new team members learn faster.
- Future research: The DevChat dataset offers a foundation for deeper studies, like how prompts affect code quality, or which activities benefit most from AI assistance.
In short, ChatGPT is becoming a practical, everyday assistant in software development, especially for writing, editing, and fixing code. With good practices and human oversight, it can make teams faster and more effective.
Collections
Sign up for free to add this paper to one or more collections.