- The paper introduces GraphFC, which represents claims as graphs using <subject, relation, object> triplets for precise and structured verification.
- It employs a three-phase process—graph construction, guided planning, and guided checking—to break down complex claims and mitigate ambiguity.
- Experiments on HOVER, FEVEROUS, and SciFact show significant improvements in verification accuracy, especially in complex multi-hop reasoning tasks.
A Graph-based Verification Framework for Fact-Checking
Introduction
The presented paper introduces a novel framework titled GraphFC, a graph-based approach to fact-checking, aimed at overcoming inherent limitations in existing methodologies that leverage LLMs. Traditional methods frequently encounter challenges related to insufficient decomposition of claims and ambiguity in mention resolution. The paper proposes representing claims as graphs comprising triplets—<subject, relation, object>—to address these issues. This representation enables a more granular decomposition, thereby reducing complexity and verifying claims by providing explicit relational constraints.
Methodology
GraphFC comprises three main components: graph construction, graph-guided planning, and graph-guided checking.
- Graph Construction: This involves transforming natural language claims and evidence into graph structures. The claim is parsed into triplets. Known entities in the claim are mapped within this structure, while unknown entities are placeholders requiring contextual inference.
- Graph-Guided Planning: This component organizes and prioritizes the order of triplet verification. Triplets without unknown entities are prioritized to allow early grounding of references, preventing ambiguity.
- Graph-Guided Checking: This involves two subtasks—graph matching and graph completion. Known triplets are directly matched with the evidence graph, and incomplete triplets undergo graph completion tasks to infer unknown entities' identities, proving the higher robustness of GraphFC against the former text-based approaches.
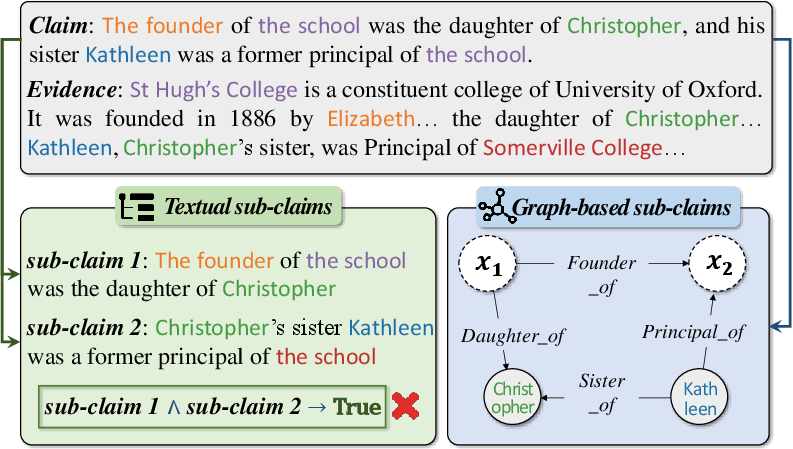
Figure 1: An illustration demonstrating the differences between existing textual sub-claims and our graph-based sub-claims. The example is from the HOVER dataset.
Experimental Setup and Results
Extensive experiments were conducted on multiple datasets, including HOVER, FEVEROUS, and SciFact, comparing GraphFC to established baseline methods. The results consistently demonstrated that GraphFC achieved superior accuracy, particularly as the complexity of claims increased from 2 to 4-hop reasoning tasks.
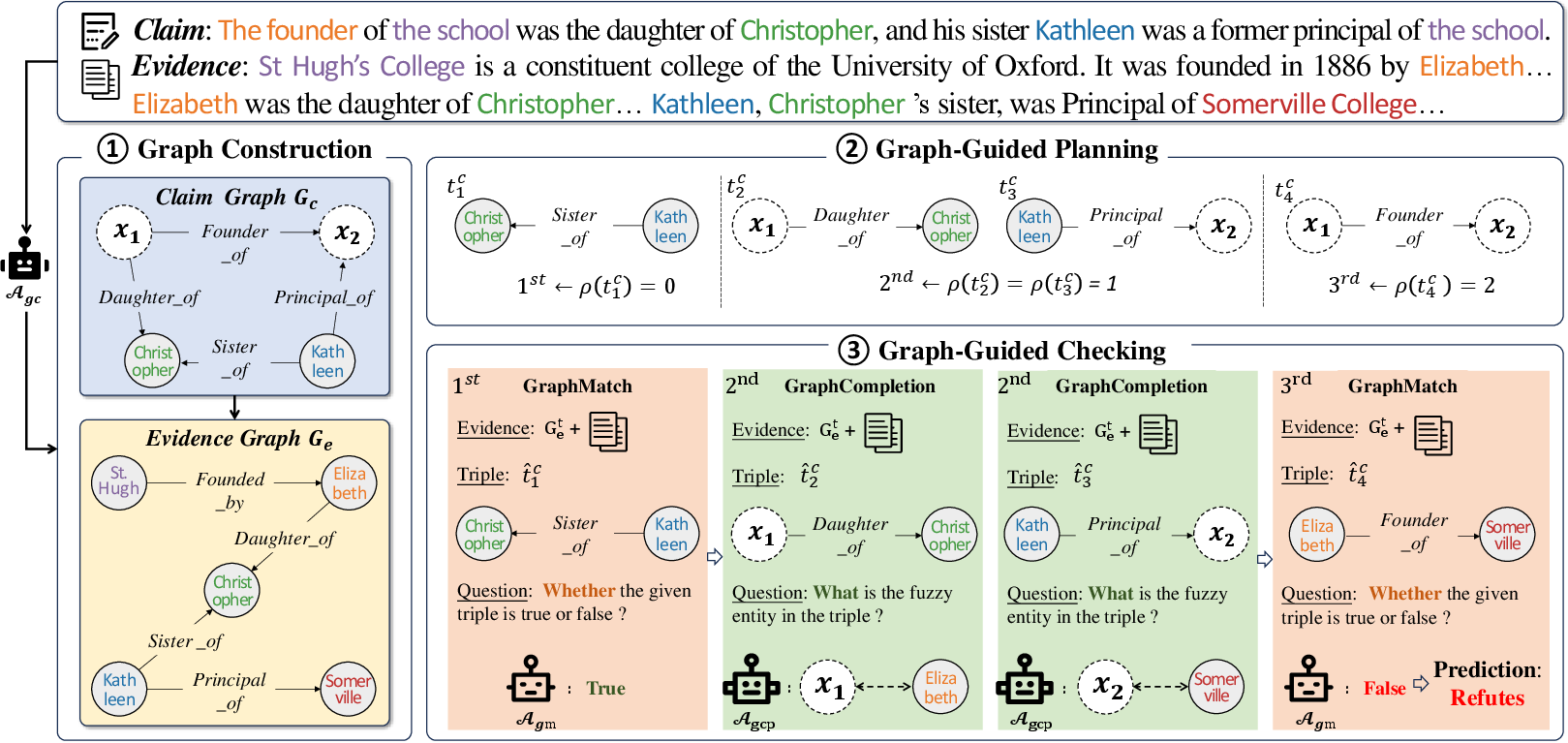
Figure 2: Overeview of {GraphFC}.
This improvement is attributable to the framework's ability to effectively break down complex claims into manageable units for verification, without the loss of contextual information, evident from the significant performance gains over traditional decomposition methods.
Ablation Studies
Ablation studies further validate the effectiveness of the proposed components. Removing the evidence graph construction or graph-guided planning notably reduced performance, underscoring their importance in maintaining claim structure and verification sequence integrity.

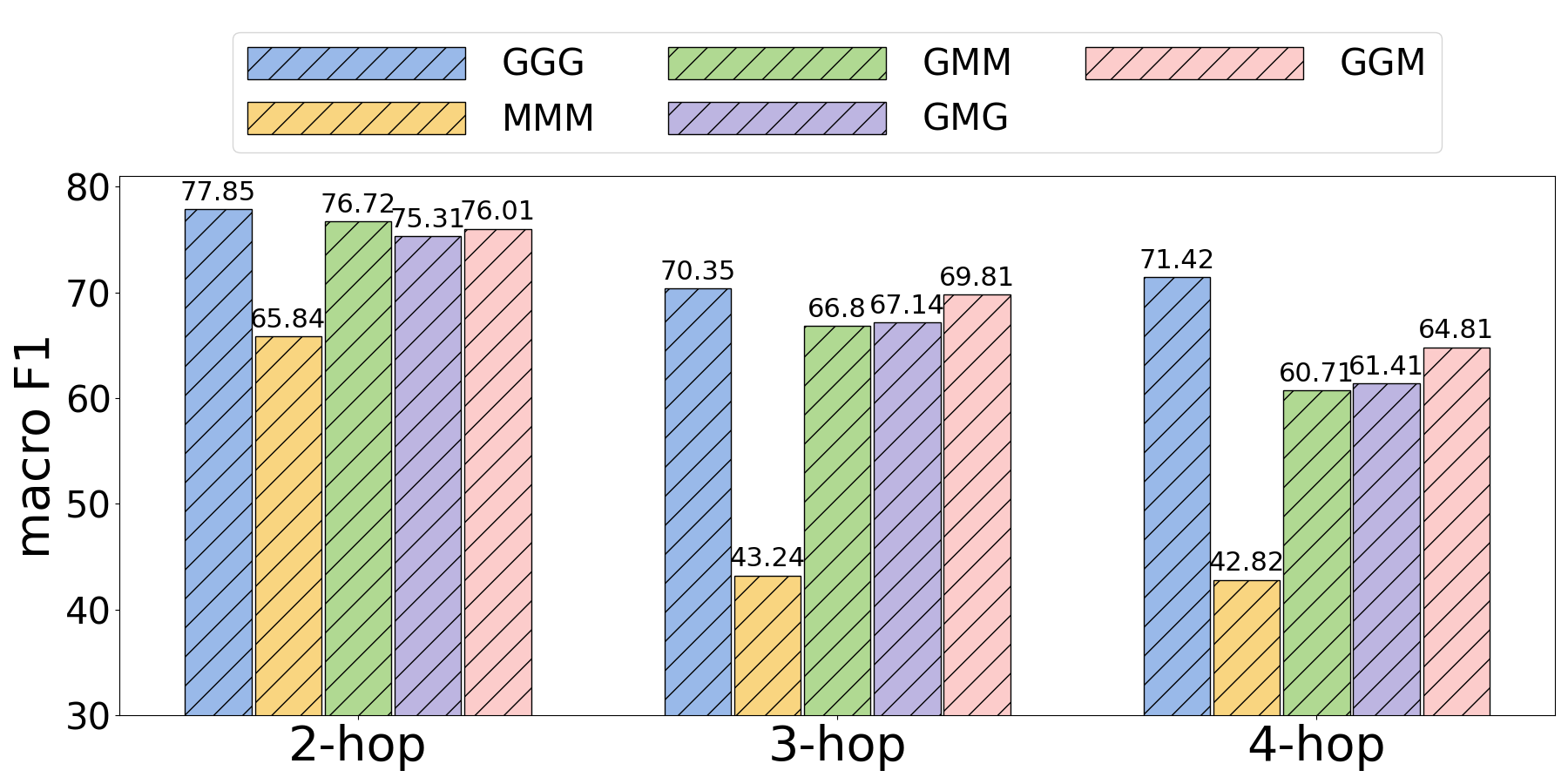
Figure 3: Ablation studies of {GraphFC}.
Implications and Future Work
The implementation of GraphFC provides a formidable tool in the field of fact-checking, particularly in domains requiring rigorous verification like scientific research or journalism, where context preservation and accurate claim verification are vital. By structuring claims as graph entities, future developments could explore automated graph formation for even more complex claim structures or integrate domain-specific knowledge graphs to enhance context accuracy.
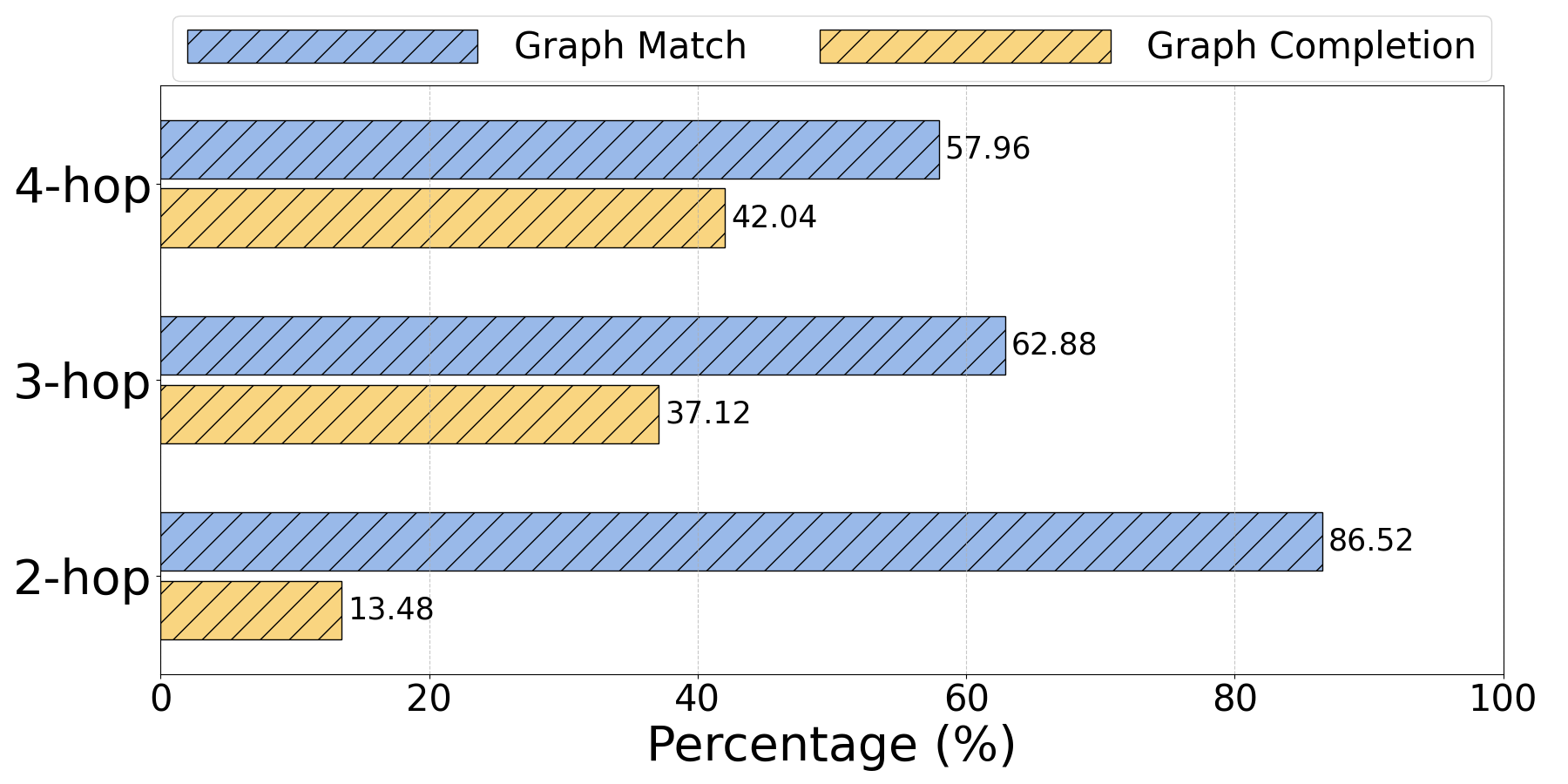
Figure 4: Distribution of task proportions for graph match and graph completion on HOVER.
Conclusion
GraphFC marks a significant step towards refining fact-checking technologies, offering an approach that mitigates decomposition and mention ambiguity challenges. As AI continues to evolve, integrating more sophisticated reasoning and contextual understanding capabilities into frameworks like GraphFC will be critical in advancing automated verification tools' efficacy and reliability. Moving forward, extending GraphFC's applicability across diverse datasets and fine-tuning graph construction algorithms for speed and efficiency could further solidify its standing in real-world applications.






