- The paper identifies five distinct roles for LLMs in HCI research, including acting as system engines, research tools, participants, study objects, and objects of user perception.
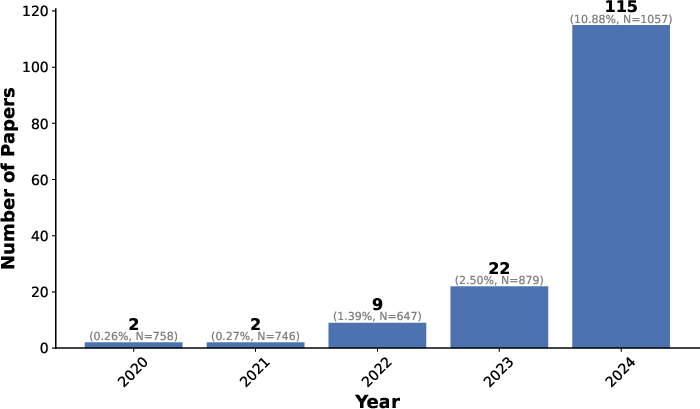
- The paper reveals a significant rise in LLM-related studies from 2020 to 2024 across domains such as communication, education, and augmented task performance.
- The paper highlights key challenges like performance biases, resource constraints, and validity issues, urging the development of robust methodological and ethical standards.
Understanding the LLM-ification of CHI: Unpacking the Impact of LLMs at CHI through a Systematic Literature Review
Introduction
The growing integration of LLMs within the Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) domain marks a significant shift in the landscape of computational research and practice. This paper conducts a systematic literature review to analyze the adoption and influence of LLMs at the CHI conference from 2020 to 2024. The paper aims to taxonomize LLM applications across various HCI domains, identify the roles LLMs play in research practices, and address associated challenges such as validity concerns and ethical implications.
Growth and Application Domains
The paper reveals a substantial rise in LLM-related research across diverse HCI subfields. Notable domains of application include:
Roles of LLMs in Research
The research outlines five distinct roles of LLMs in HCI projects:
- LLMs as System Engines: Serving as core components within both simple and complex systems to generate content or process information efficiently.
- LLMs as Research Tools: Facilitating research tasks such as data analysis and synthesis, supporting an emerging methodology within HCI.
- LLMs as Participants or Users: Simulating human interactions or perceptions, revealing the potential and limitations of using LLMs as stand-ins for human participants.
- LLMs as Objects of Study: Focusing on evaluating the internal mechanisms and performance of LLMs across contexts.
- Users' Perceptions of LLMs: Examining user interactions and perceptions, contributing to the understanding of LLM integration into everyday technology use.
These roles demonstrate the versatility and expanding influence of LLMs within HCI research, providing a framework for future explorations and applications.
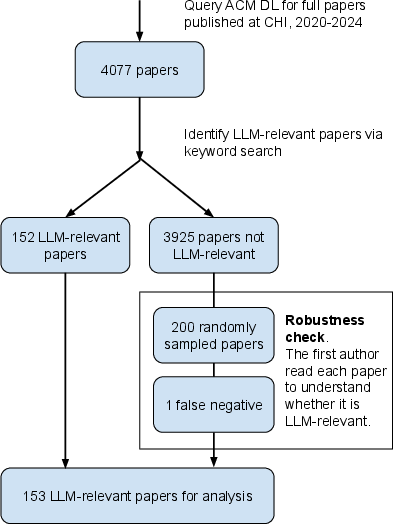
Figure 2: A flow diagram on our sample selection and refinement process.
Contribution Types and Limitations
While empirical and artifact contributions are prevalent, there is a notable lack of theoretical and methodological advancements. This highlights an opportunity for developing new frameworks and methods tailored to LLM-powered systems. Additionally, the paper emphasizes several limitations:
- Performance Issues: Concerns about LLM biases, data coverage, and the nondeterministic nature of outputs present challenges for consistent application.
- Resource Constraints: Computational and financial costs, coupled with a lack of standardized evaluation metrics, present barriers to LLM deployment and reproducibility.
- Validity Concerns: Questions around the internal and external validity of LLM-powered studies point to the need for robust methodological frameworks and transparent disclosure practices.
Consequences and Future Directions
The review underscores the necessity for considering the broader consequences of LLM applications, including ethical implications related to AI biases and economic impacts. The research community is urged to develop standards and guidelines to address these challenges and to foster responsible innovation within the field.
Moreover, the paper proposes guiding questions for researchers to evaluate the appropriateness of LLM usage in HCI projects, addressing validity, reproducibility, and broader societal consequences. These contemplative questions aim to direct future research toward more rigorous and ethically sound practices.
Conclusion
The integration of LLMs into HCI reflects a dynamic evolution of the field, with potential to significantly enhance research methodologies and application outcomes. This paper lays a foundation for further exploration and standardization, calling for a conscientious approach to leveraging LLM capabilities while navigating the complexities they introduce. Continued dialogue and collaboration across disciplines, paired with ethical vigilance, will be crucial in realizing the transformative potential of LLMs in HCI research.