- The paper introduces a willingness-aware sales talk dataset that captures user engagement through detailed, utterance-level willingness annotations.
- The study employs a Wizard of Oz approach to simulate real-world dialogues, ensuring ecological validity in the collected sales interactions.
- Experimental analyses reveal that tuning dialogue models with user willingness data significantly improves purchase intentions and sales outcomes.
User Willingness-aware Sales Talk Dataset
Introduction
The paper "User Willingness-aware Sales Talk Dataset" proposes a novel dataset aimed at enhancing automated sales dialogue systems by incorporating user willingness information. The dataset was constructed with a focus on ecological validity, replicating real-world sales interactions to more accurately capture user willingness, which is essential for practical sales dialogues. The research highlights three types of user willingness: willingness to engage in dialogue, provide information, and accept a salesperson's objectives. This foundational dataset addresses the gap in existing resources by including user willingness annotations, enabling the development of sales dialogue systems that improve purchase intentions.
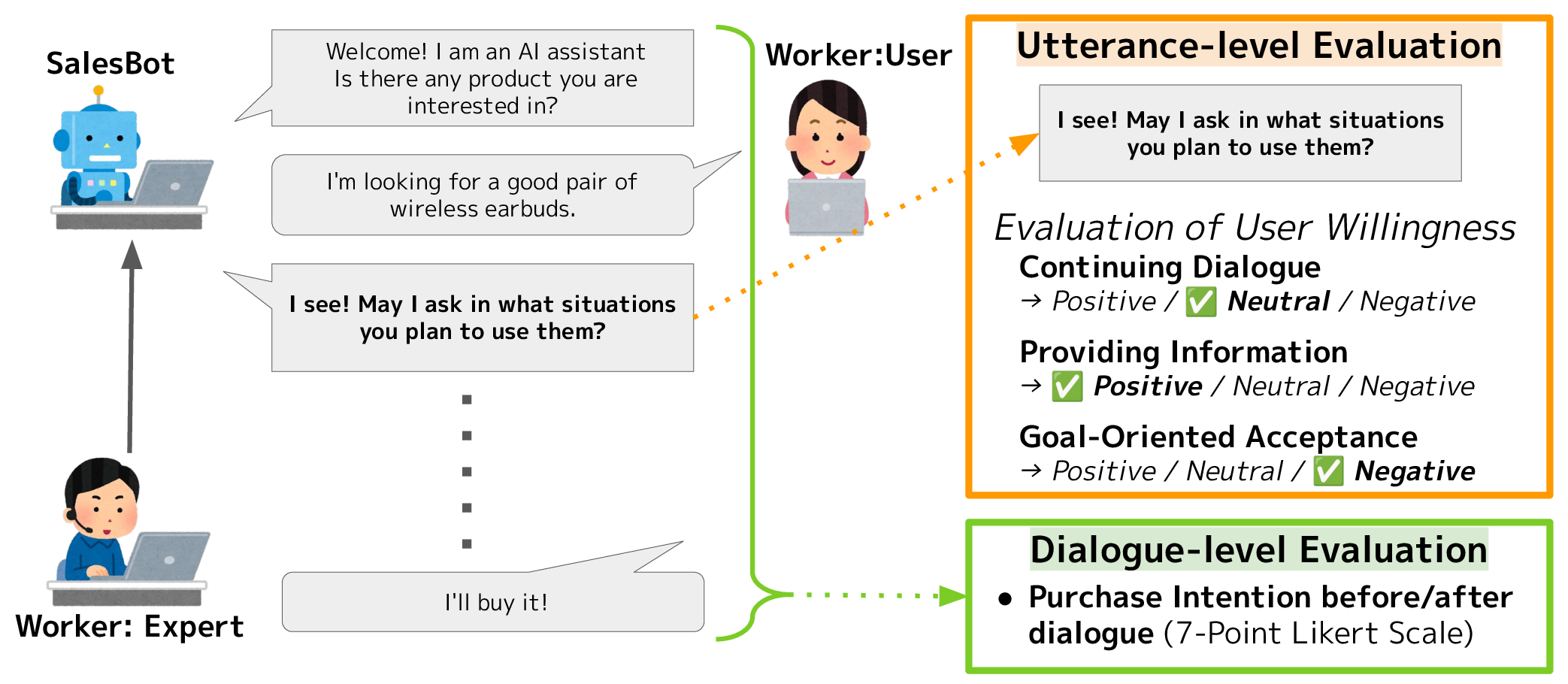
Figure 1: Overview of collecting sales talk dialogue data.
Methodology
The dataset creation involved the collection of sales dialogue data using a Wizard of Oz approach, simulating real-world dialogues between human users and an artificial sales tool. Participants assessed their willingness at the utterance level across multiple dimensions, providing a granular look at how sales dialogues can be optimized (Figure 2). Ecological validity, a key focus of the data collection process, ensures that the findings are applicable to real-world user interactions, which is pivotal for advancing human-computer interaction (HCI) research.


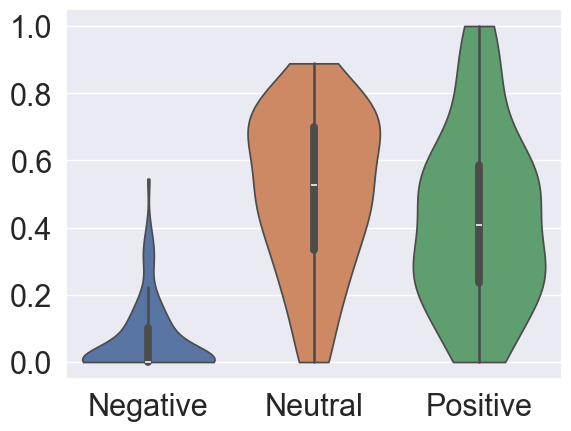
Figure 2: Distributions of proportions of user willingness labels (positive, neutral, and negative) across individual dialogues.
Analysis
A detailed analysis of the dataset reveals significant insights into the dynamics of user willingness. Correlation analyses indicate that avoiding utterances that significantly decrease user willingness is crucial for increasing purchase intentions (Figure 3). Effective sales strategies were identified, emphasizing improvement in user willingness at various stages of the dialogue. For instance, the paper suggests that elevating the user's GA willingness toward the end of a dialogue is associated with successful sales outcomes.
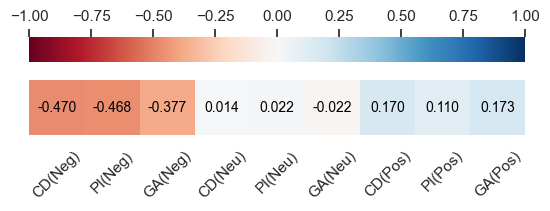
Figure 3: Correlation coefficients between the proportion of user willingness labels and the improvement in the users' purchase intention.
Experiments
Subsequent experiments examined the efficacy of integrating user willingness data into fine-tuned models based on GPT-3.5. Models that explicitly considered user willingness and incorporated strategic dialogue flows realized improved success rates. The paper further compared these models against the untuned GPT-4o, showcasing areas where the latter excels, such as efficiency and consistency in maintaining high user willingness scores throughout dialogues (Figure 4).

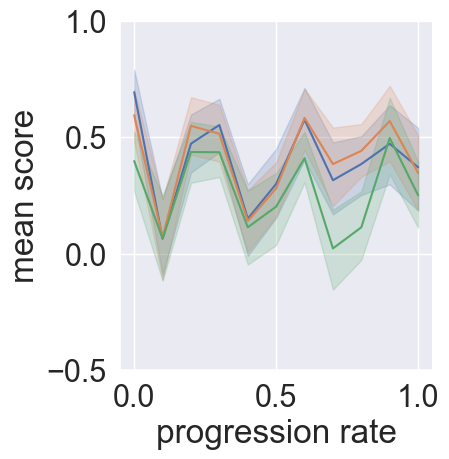
Figure 4: Average user willingness scores at dialogue progression level.
Implications and Future Directions
In evaluating the dataset's application to dialogue models, the paper underscores the importance of willingness-aware strategies in improving dialogue systems. While current models like GPT-4o show superior performance, there is significant potential for further optimization, particularly in personalizing end-of-dialogue strategies to boost user GA willingness. Future work aims to refine these systems, potentially enabling dynamic willingness-targeting to elevate user engagement and conversion in sales contexts.
Conclusion
The introduction of the willingness-aware sales talk dataset marks a substantial step towards more nuanced dialogue systems that are attuned to user dynamics. By bridging the gap between ecological valid data collection and robust dialogue strategies, this research paves the way for enhancing the practical efficacy of AI in sales environments. The findings suggest that integrating user willingness as a core element of dialogue optimization will be crucial for the next generation of human-centric AI applications.






