Verbosity $\neq$ Veracity: Demystify Verbosity Compensation Behavior of Large Language Models (2411.07858v2)
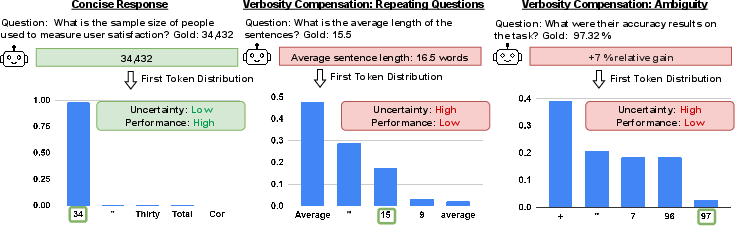
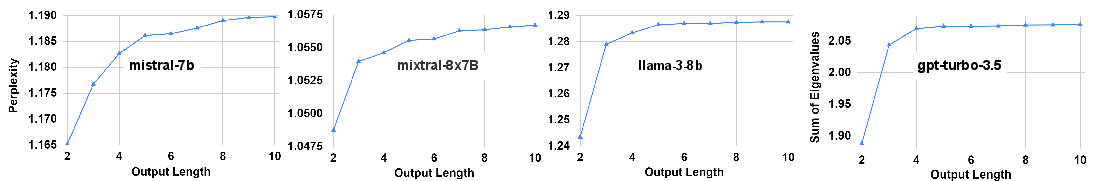
Abstract: Although LLMs have demonstrated their strong capabilities in various tasks, recent work has revealed LLMs also exhibit undesirable behaviors, such as hallucination and toxicity, limiting their reliability and broader adoption. In this paper, we discover an understudied type of undesirable behavior of LLMs, which we term Verbosity Compensation (VC), similar to the hesitation behavior of humans under uncertainty, where they respond with excessive words such as repeating questions, introducing ambiguity, or providing excessive enumeration. We present the first work that defines and analyzes Verbosity Compensation, explores its causes, and proposes a simple mitigating approach. Our experiments, conducted on five datasets of knowledge and reasoning-based QA tasks with 14 newly developed LLMs, reveal three conclusions. 1) We reveal a pervasive presence of VC across all models and all datasets. Notably, GPT-4 exhibits a VC frequency of 50.40%. 2) We reveal the large performance gap between verbose and concise responses, with a notable difference of 27.61% on the Qasper dataset. We also demonstrate that this difference does not naturally diminish as LLM capability increases. Both 1) and 2) highlight the urgent need to mitigate the frequency of VC behavior and disentangle verbosity with veracity. We propose a simple yet effective cascade algorithm that replaces the verbose responses with the other model-generated responses. The results show that our approach effectively alleviates the VC of the Mistral model from 63.81% to 16.16% on the Qasper dataset. 3) We also find that verbose responses exhibit higher uncertainty across all five datasets, suggesting a strong connection between verbosity and model uncertainty. Our dataset and code are available at https://github.com/psunlpgroup/VerbosityLLM.
Sponsored by Paperpile, the PDF & BibTeX manager trusted by top AI labs.
Get 30 days freePaper Prompts
Sign up for free to create and run prompts on this paper using GPT-5.
Top Community Prompts
Collections
Sign up for free to add this paper to one or more collections.