- The paper demonstrates simulation-based evidence that blob sharing cuts data availability costs by up to 99% for small rollups.
- The study employs a simulation model using metrics like average blob size and DA costs to quantify performance improvements.
- Findings suggest that smoother blob base fees and reduced transaction loads can improve overall network scalability and validator efficiency.
Blob Sharing in Ethereum Rollups: A Detailed Analysis
Introduction
The paper "180 Days After EIP-4844: Will Blob Sharing Solve Dilemma for Small Rollups?" explores the implications of blob sharing in Ethereum's rollup structures post-EIP-4844. Rollups, a Layer 2 solution, enhance Ethereum's scalability by addressing data availability challenges. However, with the implementation of EIP-4844, smaller rollups face inefficiencies due to fixed blob sizes. The paper examines the effectiveness of blob sharing in addressing these inefficiencies and reducing data availability costs.
Blob Sharing Model
Collected Data and Metrics
The research utilized data from Ethereum blocks spanning approximately six months post-EIP-4844 implementation. It tracked rollup performance in blob usage, focusing on average blob size, DA service quality, and total DA cost in USD. Key indicators were average blob size, DA service quality log functions, and DA costs.
Simulation Model
A simulation was conducted to reconstruct costs and evaluate blob usage efficiency. Key assumptions included constant rollup data rates and uniform gas consumption. The simulation aimed to encapsulate rollup data into blobs, adhering to a structured format that supports efficient sharing. Factors such as blob size, data rate, and transaction fees were meticulously analyzed to ensure comprehensive insights.
Results and Discussion
Main Results
The simulation revealed substantial cost reductions in DA for small rollups, far exceeding initial expectations. Blob sharing led to USD cost reductions of up to 99%, demonstrating significant improvements in efficiency. The smoothening of blob base fees played a pivotal role in achieving these results, as shown by the decrease in the number of blocks with excess blobs.
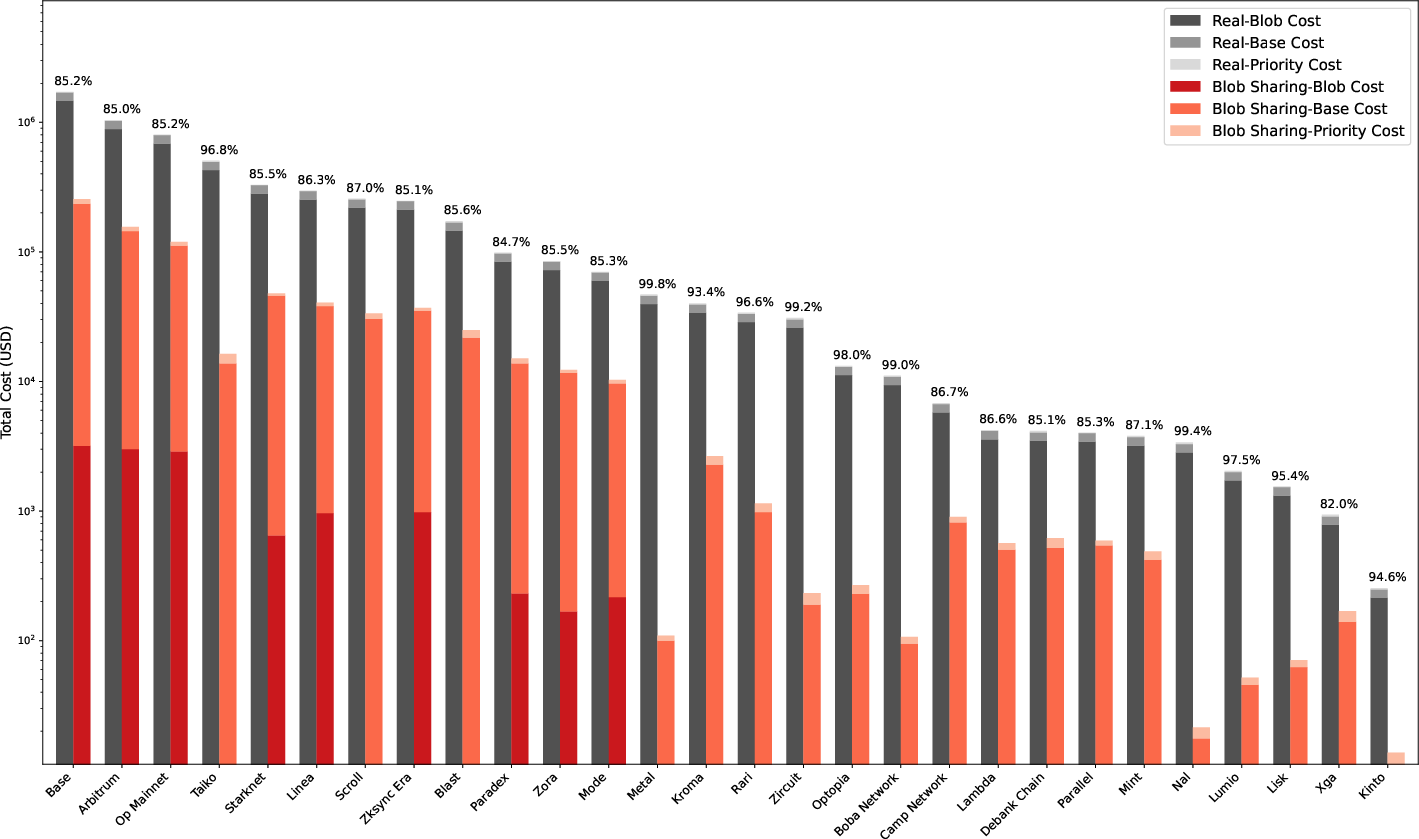
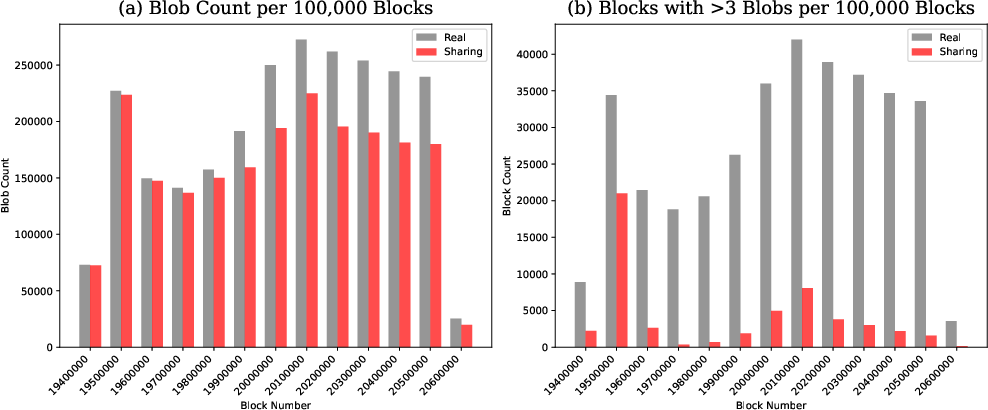
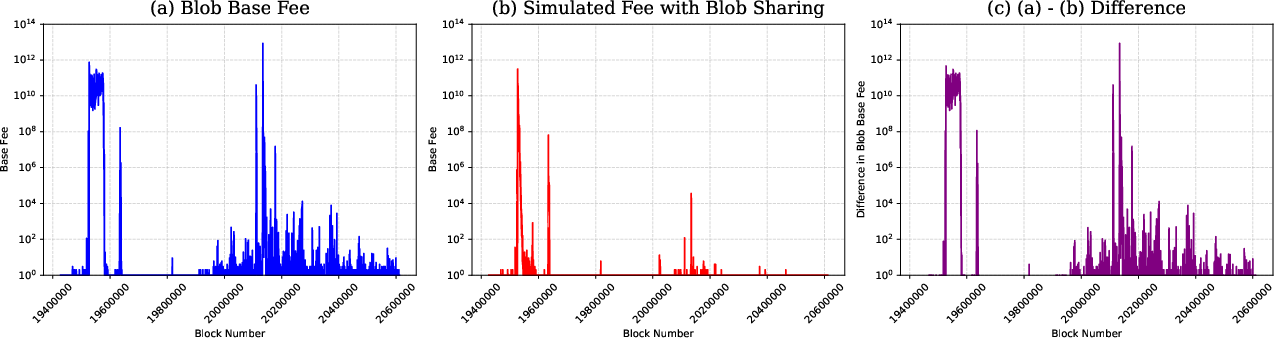
Figure 1: USD Cost Difference between Real and Simulated Blob Sharing.
Fee Differences
Examining the fee structure highlighted how blob sharing effectively reduced exponential increases in blob base fees. The calculations showed that the simulation drastically decreased the number of blobs, highlighting the benefits of sharing in reducing network congestion and associated fees. Bidirectional changes between base fee structures validated the hypothesis, underscoring the systemic benefits of reduced transaction loads.
Concluding Remarks and Future Works
The findings of this research provide compelling evidence that blob sharing not only reduces costs for participating rollups but also bolsters the overall Ethereum ecosystem efficiency. By alleviating transaction burdens, blob sharing offers advantages beyond direct participants, positively impacting validators and network scalability.
Further explorations could include practical implementations of blob sharing protocols and in-depth incentive analyses. Understanding the motivational structures necessary to foster adoption across different rollups will be critical.
In summary, blob sharing presents a viable path forward for Ethereum to enhance its rollup scalability, promising improved data availability costs and service quality.


