- The paper presents a novel decision tree framework for evaluating Human-AI Collaboration across different modes.
- It integrates quantitative and qualitative metrics to assess goals, interaction, and task allocation, tailored for sectors like healthcare, manufacturing, and finance.
- The framework offers actionable insights to improve communication clarity, task distribution, and overall collaborative efficiency in human-AI systems.
Evaluating Human-AI Collaboration: A Review and Methodological Framework
The paper "Evaluating Human-AI Collaboration: A Review and Methodological Framework" (arXiv ID: (2407.19098)) presents a comprehensive review of existing methods for evaluating Human-AI Collaboration (HAIC) and introduces a novel framework to address the challenges in measuring the effectiveness of these interactions. This essay explores the core aspects of the framework, discusses its implications, and suggests how it can be practically applied across various domains.
Introduction to Human-AI Collaboration
Human-AI Collaboration (HAIC) encompasses the integration of AI within human-centric environments, aiming to enhance decision-making, efficiency, and innovation across diverse fields. Despite its potential, assessing HAIC's effectiveness is complex due to the multifaceted nature of interactions between human and AI components. The paper proposes a structured framework to improve the evaluation of these systems by considering both quantitative and qualitative metrics, tailored to distinct HAIC modes: AI-Centric, Human-Centric, and Symbiotic.
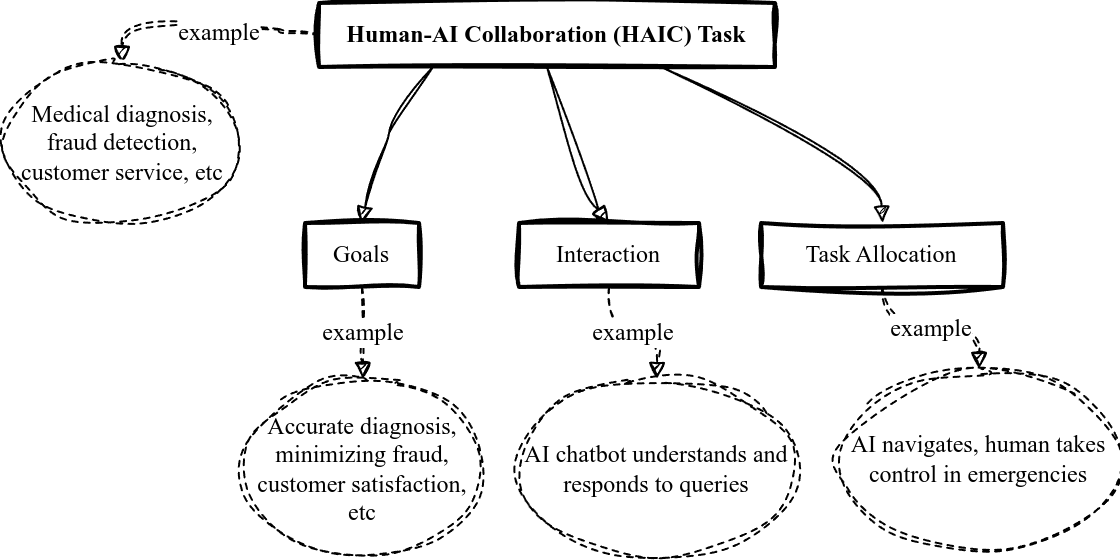
Figure 1: Core elements of Human-AI Collaboration (HAIC) and examples of their application.
Framework Structure
The methodological framework outlined uses a decision tree approach that guides users through selecting appropriate metrics based on HAIC modes. This decision tree aids in identifying relevant factors aligned with goals, interaction methods, and task allocation strategies.
Factors and Metrics
- Goals: Individual and collective goals are assessed through metrics like learning curve and prediction accuracy.
- Interaction: Evaluated via communication clarity, feedback mechanisms, and adaptability to human inputs.
- Task Allocation: Analyzes complementarity, flexibility, efficiency, and responsiveness in task distribution.
The decision tree framework facilitates the application of these metrics, ensuring a structured and adaptable evaluation process.
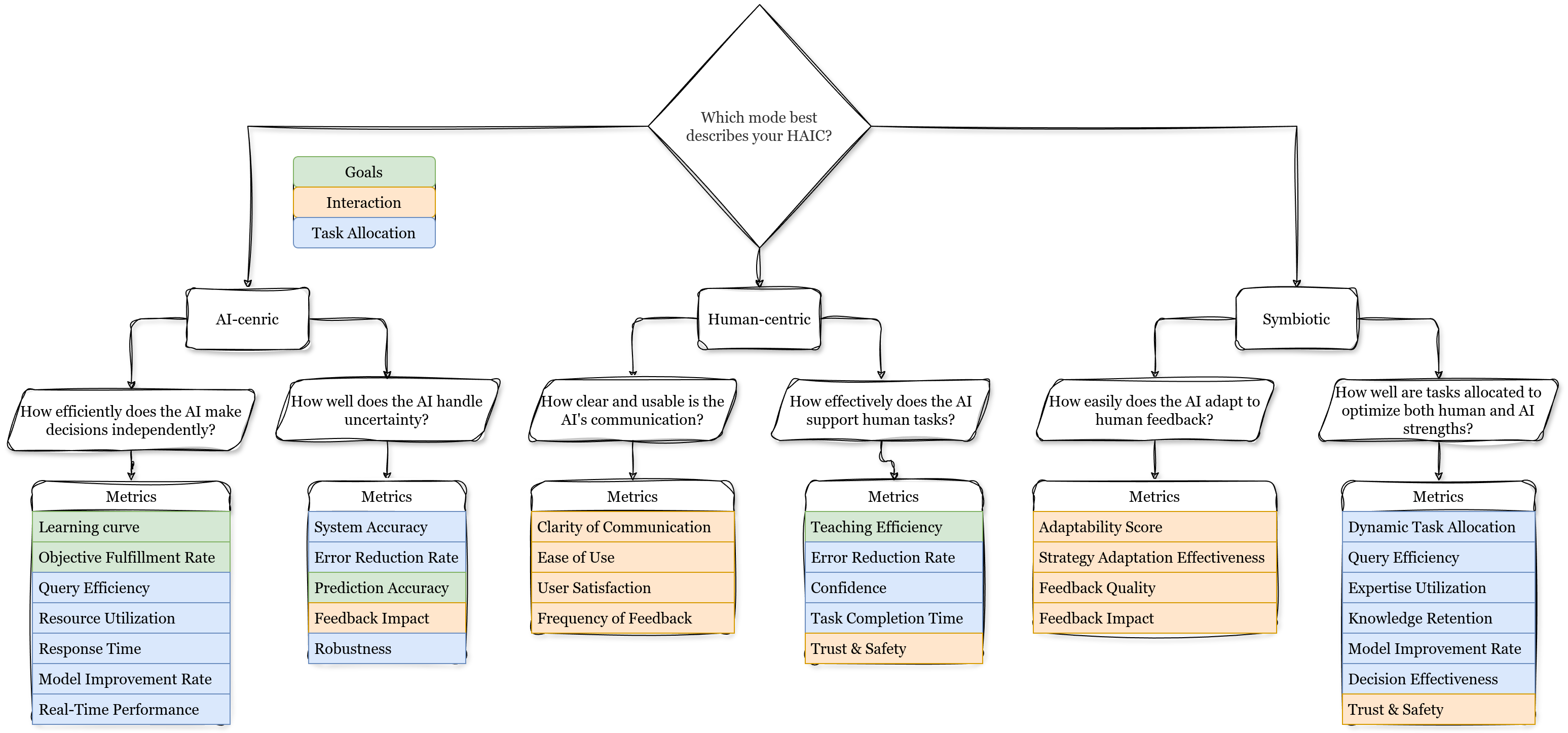
Figure 2: Decision Tree Framework for Evaluating Human-AI Collaboration.
Implications Across Domains
The HAIC evaluation framework is applicable to various sectors such as manufacturing, healthcare, finance, and education, allowing for domain-specific customization to address unique challenges.
Manufacturing
In manufacturing, the symbiotic relationship between human expertise and AI capabilities emphasizes adaptability and safety. Metrics like the adaptability score and confidence ensure that AI systems efficiently complement human operators to optimize production processes.
Healthcare
The healthcare sector benefits from AI's accuracy and efficiency in diagnostics, particularly within medical imaging. The framework suggests assessing prediction accuracy and interaction clarity to improve patient outcomes and streamline diagnostic workflows.
Finance
In finance, HAIC leverages AI's analytical prowess alongside human insight to improve decision-making and reduce fraud. Key metrics include error reduction rate and system accuracy, focusing on enhancing trust and efficiency.
Education
HAIC's role in education involves supplemental AI systems that support personalized learning and teaching strategies. Metrics such as task completion time and learning curves are critical for evaluating how AI tools impact student engagement and educational outcomes.
Challenges in Creative and Linguistic AI
Evaluating HAIC for LLMs and Generative AI poses unique challenges due to their impact on artistic creativity and linguistic interactions. These domains require advanced interpretative metrics to assess the nuances of AI-human collaboration.
Conclusion
The proposed framework offers a robust methodological approach for evaluating Human-AI Collaboration across sectors. By accommodating both quantitative and qualitative metrics tailored to collaboration modes, it provides a comprehensive tool for assessing HAIC effectiveness. Future research should focus on empirical validation of this framework, ensuring its adaptability and relevance in the evolving landscape of AI integration. The framework stands to significantly enhance our understanding of HAIC, fostering improved collaborative systems that leverage the strengths of both humans and AI.



