- The paper demonstrates that ASR models achieve improved zero-shot audio classification using template-based prompting and unsupervised reweighting, with Whisper yielding a 9% accuracy gain.
- The study employs a methodology that converts log-likelihoods into class probabilities without additional training, leveraging prior matching and null-input calibration to address biases.
- Experiments across eight datasets reveal that larger ASR models enhance task generalization and outperform traditional baselines in diverse audio classification tasks.
Investigating the Emergent Audio Classification Ability of ASR Foundation Models
This paper examines the zero-shot audio classification capabilities of Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) foundation models such as Whisper and MMS. The research employs no additional training or new parameters, utilizing template-based text prompts and evaluates on eight different datasets. It presents performance improvements through unsupervised reweighting and highlights trends related to model size and task generalization.
Zero-Shot Prompting of ASR Models
The authors employ a template-based method to convert log-likelihoods from audio samples into class probabilities. The whisper model displays promising performance improvements over existing zero-shot baselines, achieving an average accuracy boost of 9% without any model fine-tuning.

Figure 1: This paper looks at zero-shot prompting of ASR foundation models for audio classification, without any further training or introducing any new parameters. We use task-specific prompts and evaluate on various downstream tasks and datasets.
The probability of each class is calculated using generated likelihoods from ASR decoding:
Pe(y=wk∣s)=∑jP(e(t(wj)∣s))P(e(t(wk)∣s))
The highest class probability yields the predicted class:
y^=argmaxwPe(w∣s)
Task Calibration Methodologies
Significant emphasis is placed on mitigating zero-shot biases present in ASR models. The authors explore prior-matching and null-input-based calibration:
- Prior Matching: Reweights output probabilities using unsupervised data to ensure output priors match the expected true priors.
- Null-Input Calibration: Utilizes null-input estimates to approximate biases across class distributions, achieving notable gains without additional data requirements.
These calibration methods are evidenced by improved class distribution and balance:

Figure 2: Predicted class distribution for Whisper large-v2 on RAVDESS. Bar width is proportional to the fraction of decisions per class.
Experimental Results and Analysis
The evaluations are focused on eight datasets, demonstrating Whisper's stronger performance against random and other baselines. With prior matching, Whisper displays average accuracies reaching 48.2% across tasks. Compared to large-scale models like CLAP, Whisper shows consistent performance improvements.







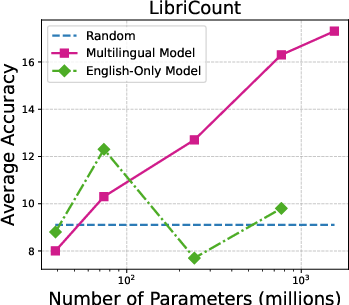
Figure 3: Accuracy on individual audio classification tasks across different sizes of Whisper models.
Robustness to Prompts: The results reveal sensitivity to various prompt formulations. An ensemble of prompts generally results in better performance indicating the versatility and adaptability of zero-shot classification.








Figure 4: Percentage of model predictions for each class with different calibration methods. On ESC-50, we only plot the top 15 classes predicted by the uncalibrated results for illustration.
Scaling and Model Variants
The performance scales with model size, with larger Whisper models demonstrating proficiency in task generalization. Additionally, multilingual versions outperform English-only models in many configurations. The paper underlines that ASR models like MMS show limited zero-shot classification abilities, primarily due to token alignment whereby Whisper’s attention mechanism inherently offers better coverage.

Figure 5: Parameter size vs average accuracy (with prior-matching) for different versions of Whisper models.
Audio Question Answering
Preliminary experiments expand zero-shot capabilities to audio question answering, using datasets like Clotho-AQA. Whisper demonstrates an ability to derive meaningful predictions over random baselines, further cemented by effective decision thresholds illustrated through precision-recall curves.
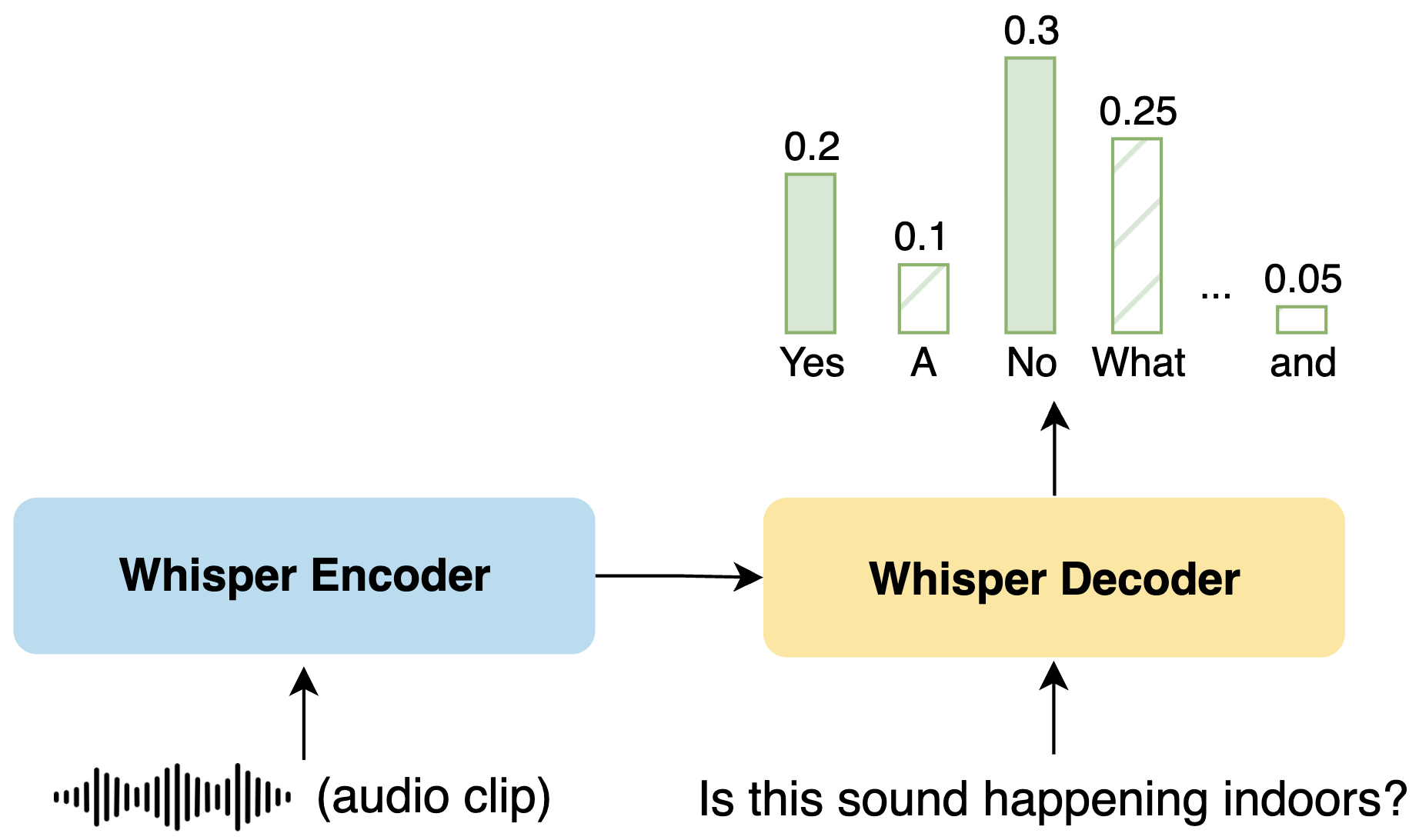
Figure 6: Zero-shot audio question answering method.
Conclusion
This study provides insightful evidence for the emergent capabilities of ASR foundation models in zero-shot audio classification. It opens avenues for leveraging such models with minimal data or parameter changes, optimizing performance using calibration techniques. The research concludes that with scaling, ASR models harness cross-domain capabilities paralleling advances seen in their NLP counterparts.
Overall, this research significantly enhances understanding of ASR models' generalizability, advocating for future exploration of zero-shot methods across ASR-induced tasks like question answering, scene recognition, and more.



















