TPDR: A Novel Two-Step Transformer-based Product and Class Description Match and Retrieval Method
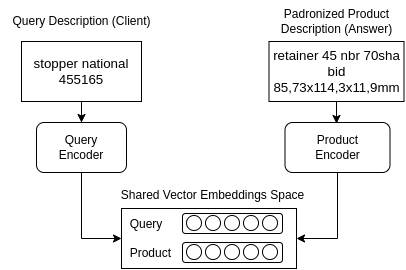
Abstract: There is a niche of companies responsible for intermediating the purchase of large batches of varied products for other companies, for which the main challenge is to perform product description standardization, i.e., matching an item described by a client with a product described in a catalog. The problem is complex since the client's product description may be: (1) potentially noisy; (2) short and uninformative (e.g., missing information about model and size); and (3) cross-language. In this paper, we formalize this problem as a ranking task: given an initial client product specification (query), return the most appropriate standardized descriptions (response). In this paper, we propose TPDR, a two-step Transformer-based Product and Class Description Retrieval method that is able to explore the semantic correspondence between IS and SD, by exploiting attention mechanisms and contrastive learning. First, TPDR employs the transformers as two encoders sharing the embedding vector space: one for encoding the IS and another for the SD, in which corresponding pairs (IS, SD) must be close in the vector space. Closeness is further enforced by a contrastive learning mechanism leveraging a specialized loss function. TPDR also exploits a (second) re-ranking step based on syntactic features that are very important for the exact matching (model, dimension) of certain products that may have been neglected by the transformers. To evaluate our proposal, we consider 11 datasets from a real company, covering different application contexts. Our solution was able to retrieve the correct standardized product before the 5th ranking position in 71% of the cases and its correct category in the first position in 80% of the situations. Moreover, the effectiveness gains over purely syntactic or semantic baselines reach up to 3.7 times, solving cases that none of the approaches in isolation can do by themselves.
Paper Prompts
Sign up for free to create and run prompts on this paper using GPT-5.
Top Community Prompts
Collections
Sign up for free to add this paper to one or more collections.