- The paper introduces LLMediator, an AI platform that leverages GPT-4 to assist online dispute resolution by reformulating messages and suggesting mediator responses.
- It details technical methodologies such as keyword detection and response drafting, and explores both manual and autonomous interventions.
- The study emphasizes the potential for democratizing access to justice while highlighting the need for empirical evaluations to mitigate risks like bias and hallucinations.
The paper "LLMediator: GPT-4 Assisted Online Dispute Resolution" proposes the implementation of LLMediator, an experimental platform utilizing GPT-4 to aid online dispute resolution (ODR). This approach focuses on leveraging LLMs to assist in the mediation and negotiation processes for high-volume, low-intensity legal disputes. This analysis will explore the system's technical considerations and potential applications, highlighting its strengths and addressing the challenges associated with its use.
Enhancing Online Dispute Resolution
System Overview
LLMediator aims to improve ODR systems by integrating GPT-4's capabilities to reformulate user messages, suggest mediator responses, and even autonomously engage in discussions. The platform provides a web-based chat interface for parties involved in a dispute, allowing them to communicate and reach amicable resolutions without the need for physical court appearances.
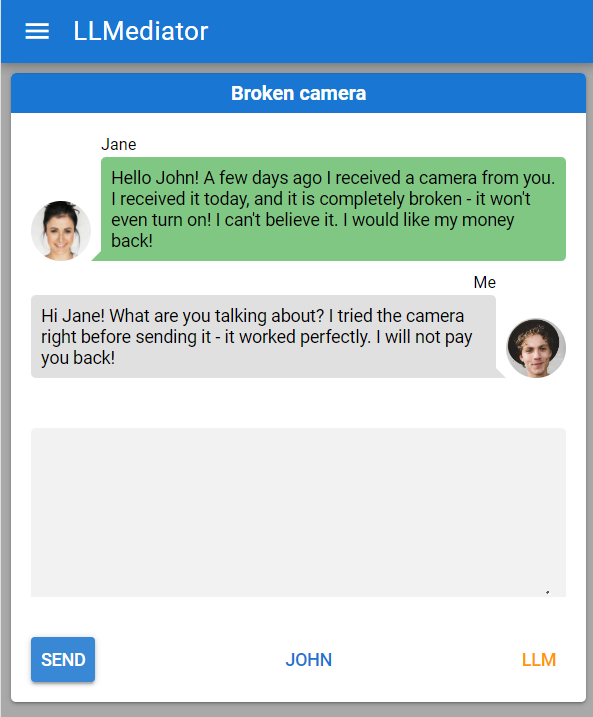
Figure 1: A screenshot of the LLMediator interface, showing a dispute regarding a broken camera.
Key Features
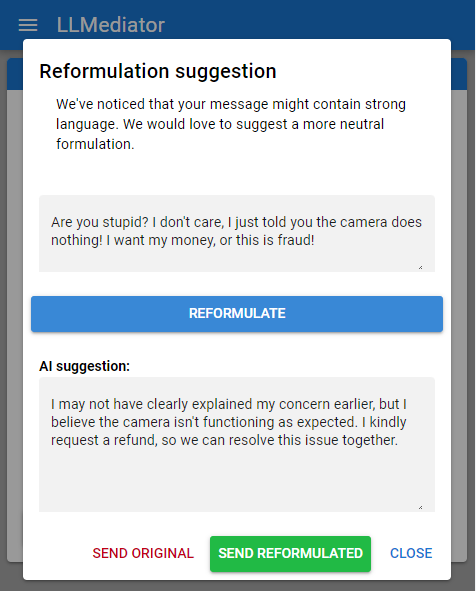
One of the primary capabilities of LLMediator (F1) is detecting and reformulating inflammatory messages. This feature seeks to transform emotional or potentially confrontational messages into neutral, constructive communications that facilitate peaceful resolutions.
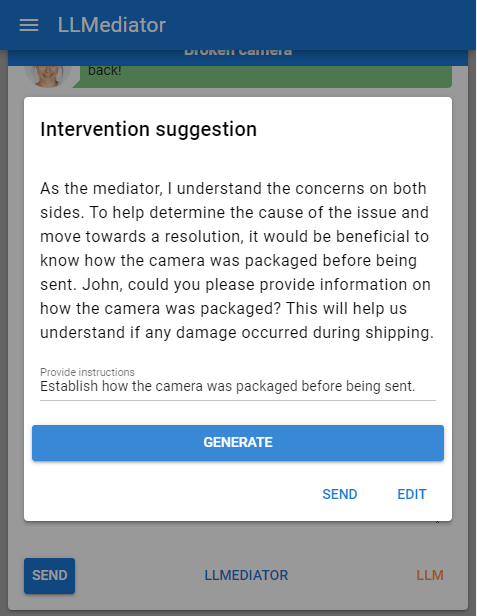
Another significant feature (F2) is providing draft message suggestions for mediators. This functionality allows human mediators to receive context-relevant intervention suggestions, enabling them to guide discussions more efficiently.
Autonomous System Interventions
LLMediator also explores the possibility of autonomous AI-generated interventions (F3), where the system directly interacts with both parties in a dispute without mediator oversight. Such a feature could potentially allow for scalable, always-available mediation services in lower-stakes disputes or areas with mediator shortages.
Technical Considerations
LLMs
Using GPT-4, LLMediator capitalizes on advanced LLM abilities to perform tasks that require understanding nuanced context from preceding conversations. The system demonstrates GPT-4's capacity to effectively reformulate messages and propose mediation strategies that align with dispute resolution principles.
Potential Risks and Limitations
Deploying LLMs in this context requires careful consideration of risks like hallucinations or biases inherent in training data. While LLMediator's augmented intelligence framework helps mitigate these risks by keeping a human-in-the-loop, further empirical evaluations are necessary to ensure the system doesn't inadvertently harm negotiation outcomes or user trust.
Implications and Future Developments
LLMediator represents an innovative approach in the use of AI to enhance access to justice by supporting ODR processes. For future iterations, empirical evaluations will be crucial to quantify its efficacy and refine its features. Additionally, incorporating more advanced sentiment analysis and context understanding frameworks could further improve its utility.
Conclusion
"LLMediator: GPT-4 Assisted Online Dispute Resolution" introduces a compelling framework for integrating AI into legal dispute resolution processes. While preliminary evaluations suggest significant potential for fostering amicable settlements, careful empirical analyses and ongoing refinements are vital for addressing scalability and trust concerns. By evolving into a robust tool, LLMediator might play a crucial role in democratizing access to efficient, equitable legal services.