- The paper introduces a novel V2I-based platooning design that addresses communication delays to enhance both plant and string stability.
- It employs massive MIMO antennas and edge computing, using the D-subdivision method to calculate control gains for robust stability under delay conditions.
- Performance simulations validate the design's scalability, rapid error correction, and effective handling of handover constraints in platoon vehicles.
V2I-Based Platooning Design with Delay Awareness
Introduction
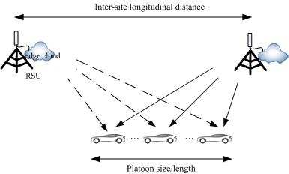
The paper explores a Vehicle-to-Infrastructure (V2I) based platooning system that leverages edge computing to enhance autonomous vehicle control. Traditional Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) systems are prone to string instability, which can lead to traffic disruptions. By utilizing V2I communications, the proposed system addresses communication delays and improves both plant and string stability. This design aims to optimize the platoon's velocity and size while considering radio parameters such as massive MIMO antennas and frequency bands.
System Design and Model
In the V2I-based platooning system, as depicted in the model (Figure 1), vehicles relay their driving state information to a roadside unit (RSU). This RSU, equipped with massive MIMO antennas and edge computing capabilities, processes the information to generate control commands broadcasted back to the vehicles. The control law employed by the RSU ensures homogeneous control inputs, overcoming the limitations associated with vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communication, such as limited range and interference.
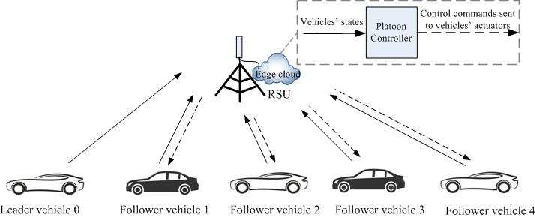
Figure 1: An illustration of V2I-based platooning system with edge computing.
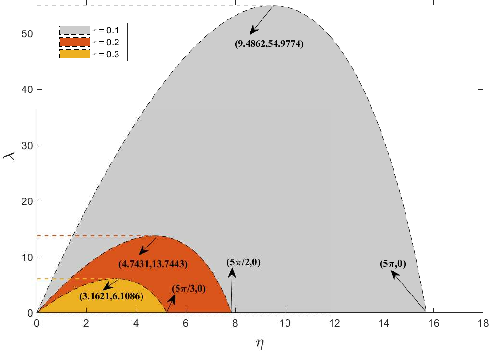
String stability is achieved through the careful selection of control gains, which are determined using the D-subdivision method. This method helps in calculating the feasible regions for control gains to ensure stability under delay conditions.
Stability Analysis
The paper conducts a comprehensive frequency-domain stability analysis, leveraging the Laplace transform to derive the conditions for both plant and string stability.
The performance of the proposed V2I-based platooning system is assessed via simulation, highlighting its advantages in terms of scalability and delay management:
- Efficiency: The V2I framework quickly enables error correction and establishes stability, as demonstrated in various scenarios with differing delay levels and platoon sizes.
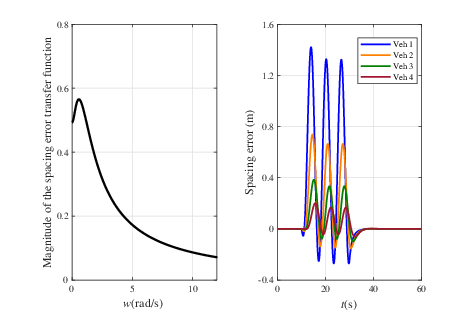
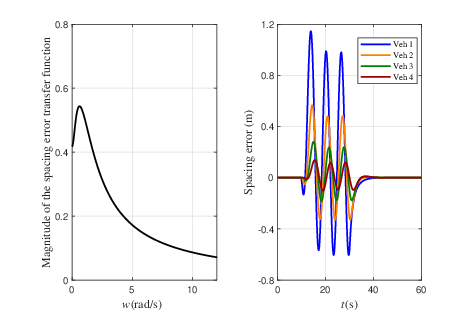
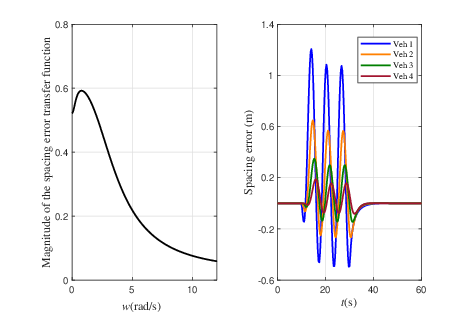
Figure 3: The platooning performance of the proposed design.
- Impact of Control Gains and Delays: Different control gains and delay levels have marked effects on the system, influencing the speed of achieving stability and the magnitude of spacing errors.
- External Factors and Disturbance Robustness: Various scenarios tested show that the platoon is robust to typical disturbances despite variations in size and delays, demonstrating the scalability and applicability of the control design.
Handover and Dual Connectivity
The paper further discusses the implications of choosing the platoon's optimal velocity and its relationship with RSU coverage and handover constraints. Important considerations include:
Conclusion
The research provides a novel framework for V2I-based platooning utilizing edge computing, addressing the challenges of communication delay and stability in autonomous vehicle systems. The design demonstrates significant potential for enhancing traffic flow efficiency and vehicular control in practical scenarios. Future research could explore the integration with more sophisticated vehicular dynamics models and distributed control algorithms to further optimize platooning systems in dense traffic environments.