- The paper demonstrates that combining RL with distribution matching distillation enables student models to exceed the teacher’s performance in few-step synthesis.
- The methodology leverages dynamic strategies like DynaDG and DynaRS to optimize initial training and enhance global structure learning.
- Experimental results show significant improvements in image quality and prompt coherence on benchmarks compared to traditional multi-step models.
Distribution Matching Distillation with Reinforcement Learning
Introduction
The paper "Distribution Matching Distillation Meets Reinforcement Learning" (2511.13649) presents an innovative framework, DMDR, that combines distribution matching distillation (DMD) with reinforcement learning (RL) to enhance diffusion models' efficiency without compromising performance. Diffusion models are renowned for generating high-quality visual content but require computationally expensive iterative denoising steps. Previous approaches distilled these models to fewer steps but were often constrained by the teacher model's performance. DMDR strategically integrates RL into the distillation process, enabling the student model to surpass the teacher model, thus achieving state-of-the-art results in few-step generative models.
Methodology
Distribution Matching Distillation (DMD)
In DMD, a diffusion model trained with multi-step processes functions as a teacher to a few-step student model, aiming to match the teacher's distribution through an optimized trajectory. The primary goal is to align the distribution of the student and teacher by minimizing the Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence, ensuring high fidelity in fewer steps. However, the student's capability is inherently capped by the teacher's distribution.
Reinforcement Learning Integration
DMDR introduces RL into DMD, unlocking the student model's potential to exceed the teacher's capacity without additional external image data. This concurrent training facilitates mode reshaping and coverage, addressing zero forcing issues endemic to traditional DMD, where certain modes might be neglected. RL modifies the distributional objectives, steering the model towards regions of higher reward while utilizing DMD as an effective regularization strategy, mitigating risks like reward hacking. The combined loss function incorporates both distillation and RL terms, creating a balanced optimization process.
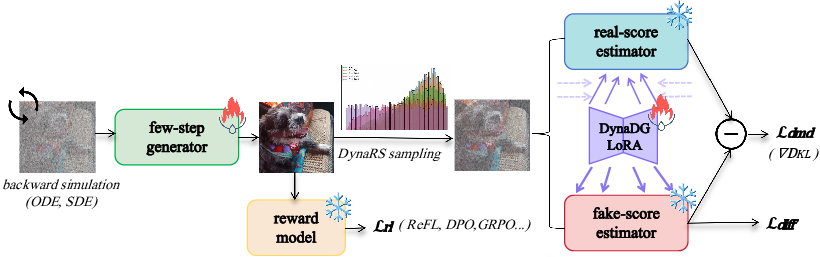
Figure 1: Overview of DMDR, which contains three key elements: (1) A DMD framework to optimize the generator by utilizing the gradient derived from an implicit distribution matching objective; (2) A RL branch to concurrently incorporate reward feedback from the reward model; (3) Two dynamic training strategies to facilitate more efficient and effective distillation during the initial phase.
Dynamic Training Strategies
To address the initial phase where reward models require basic generation capability, DMDR employs dynamic distribution guidance (DynaDG) and dynamic renoise sampling (DynaRS). DynaDG injects a specialized LoRA set in the fake and real score estimators to dynamically adjust the distribution, ensuring more reliable scoring. DynaRS biases renoise sampling towards higher noise levels initially, facilitating the learning of global structures before refining details as training progresses. These strategies accelerate the distillation process and improve initial training phases.
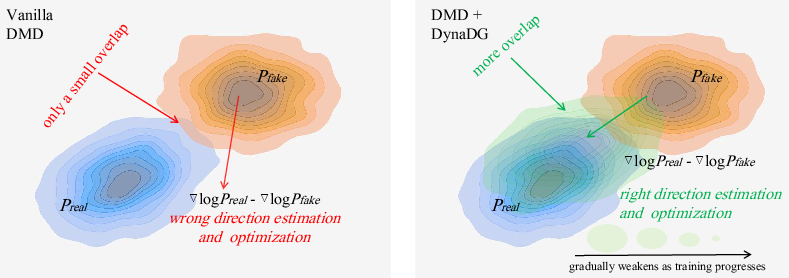
Figure 2: Illustration for our Dynamic Distribution Guidance.
Experimental Results
The DMDR framework demonstrates significant improvements in generating high-quality images with superior prompt coherence in fewer steps compared to existing methods. Validation across various model architectures and RL algorithms confirms the framework's broad applicability. Empirical results show consistent outperformance of the few-step models against their multi-step teachers on benchmarks such as DPG_Bench and GenEval.
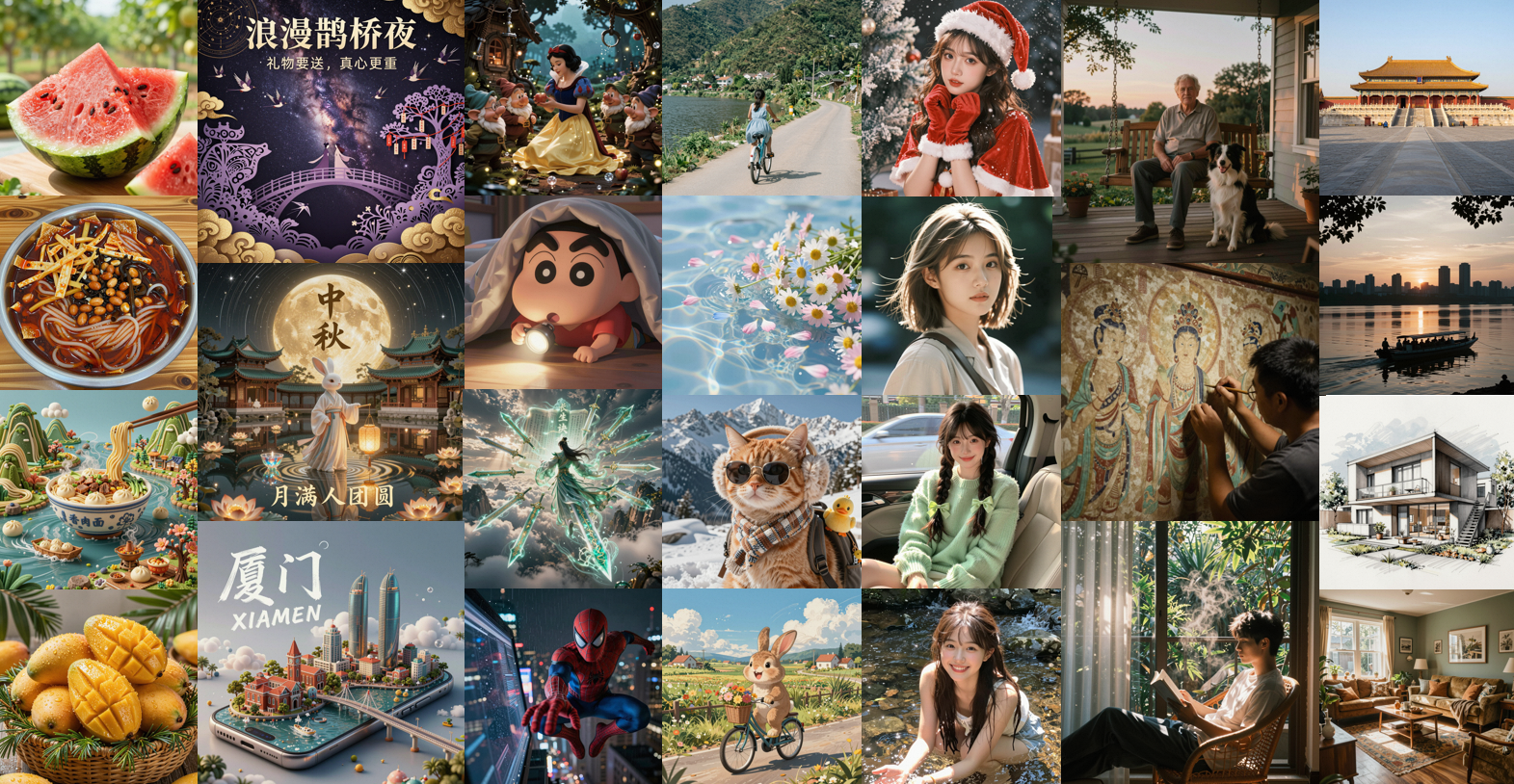

Figure 3: Images generated by Z-Image-Turbo distilled through our DMDR. Demonstrating excellent generation quality, ultra-realistic, outstanding concept understanding, and remarkable text rendering.
Discussion
Implications and Future Work
The integration of RL into the distillation process presents a promising direction for enhancing generative models' efficiency and performance. However, the paper acknowledges certain trade-offs, such as reduced image diversity, and potential biases in reward models affecting some metrics. Future work could explore optimizing balance between quality and diversity and further scaling reward models to overcome existing limitations. Additionally, leveraging advanced RL techniques may refine these results further.
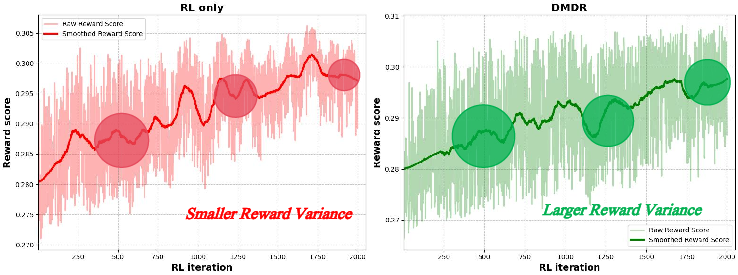
Figure 4: Reward curves comparison during the RL stage. Better to zoom in to check the difference.
Conclusion
DMDR is a novel framework that successfully combines distribution matching distillation with reinforcement learning, resulting in few-step generative models that consistently outperform their multi-step teachers. Leveraging intricate dynamic strategies and comprehensive training regimens, DMDR sets a new benchmark for efficient high-quality image synthesis, paving the way for future explorations in diffusion models and reinforcement learning integration.





