- The paper demonstrates that domain-specific pretraining using ModernBERT and a custom BPE tokenizer yields superior masked token accuracy and lower training loss on patent texts.
- It incorporates advanced techniques such as FlashAttention, rotary positional embeddings, and GLU feed-forward layers to enhance both accuracy and computational efficiency.
- The model outperforms previous baselines including PatentBERT in multiple patent classification tasks, indicating its practical value for legal tech applications.
Patent LLM Pretraining with ModernBERT
Introduction and Research Context
The development of specialized BERT-based models for domain-specific applications has emerged as a promising strategy in NLP, particularly in areas like legal and biomedical text analysis where standard BERT models tend to underperform due to the unique linguistic characteristics of these domains. Patent documents epitomize such a challenge, with their unique blend of legal and technical language. This paper addresses this gap through the introduction of domain-specific models based on the ModernBERT architecture optimized for patent texts.
Methodological Advancements
Architectural and Training Innovations
The paper leverages recent enhancements in transformer architectures, incorporating techniques like FlashAttention, rotary positional embeddings, and GLU feed-forward layers, to refine the ModernBERT design. These improvements not only enhance model performance but also boost training efficiency, making the models viable for computationally constrained environments. Specifically, the adaptation of these techniques to the patent-pretraining context represents a notable innovation, especially considering the sheer volume of data involved — a curated corpus comprising over 60 million patent records.
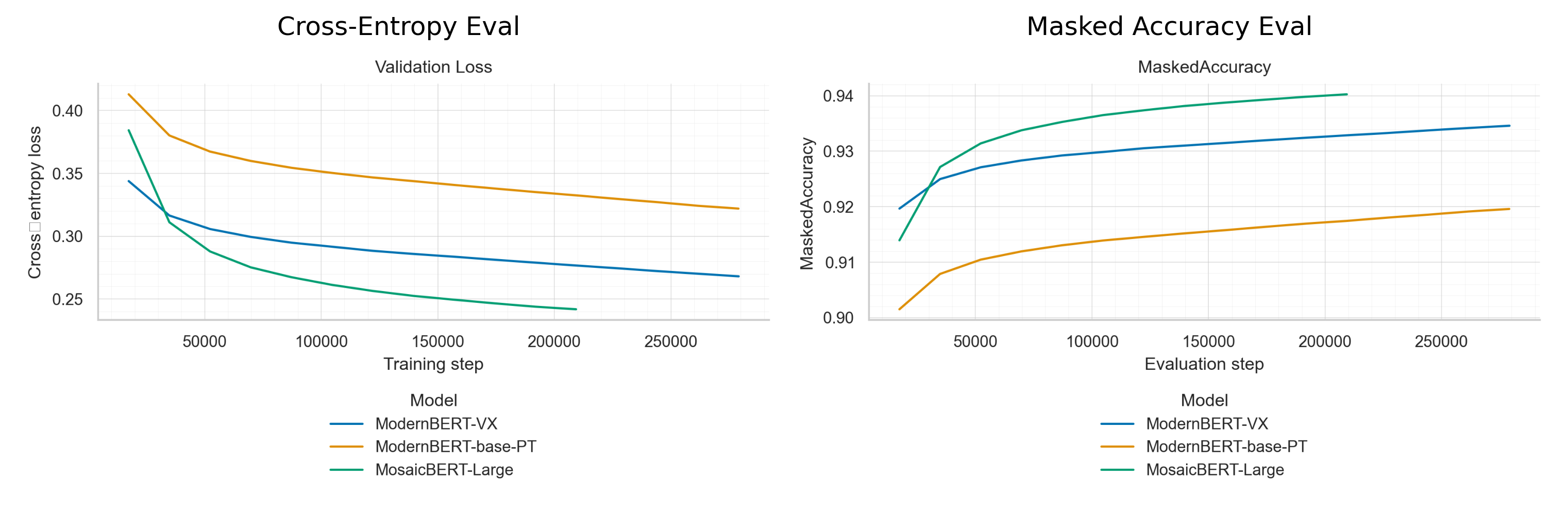
Figure 1: Pretraining loss and MLM accuracy for ModernBERT-base-PT, ModernBERT-base-VX, and Mosaic-BERT-large.
Data Handling and Tokenization
The dataset used for pretraining is meticulously constructed, incorporating both public patent data and proprietary content, providing a robust foundation for pretraining. The tokenization strategy also reflects a customized approach, with a domain-specific BPE tokenizer that enhances the representation of patent text by effectively capturing frequent subword patterns, which are crucial for dealing with domain-specific terminology.
Evaluation and Results
The pretraining phase reveals that the models, particularly when using the custom BPE tokenizer, achieve both lower loss and higher masked token accuracy compared to counterparts utilizing standard WordPiece tokenization methods. This indicates the efficacy of the BPE tokenizer in providing a more compact and efficient text representation.
Downstream Task Evaluation
The real test of the pretraining effectiveness comes from downstream evaluations across several patent classification tasks. Notably, ModernBERT-base-PT consistently outperformed the standard ModernBERT model in accuracy across three of four datasets, and delivered competitive results against PatentBERT, a model pretrained specifically with patent data from USPTO.
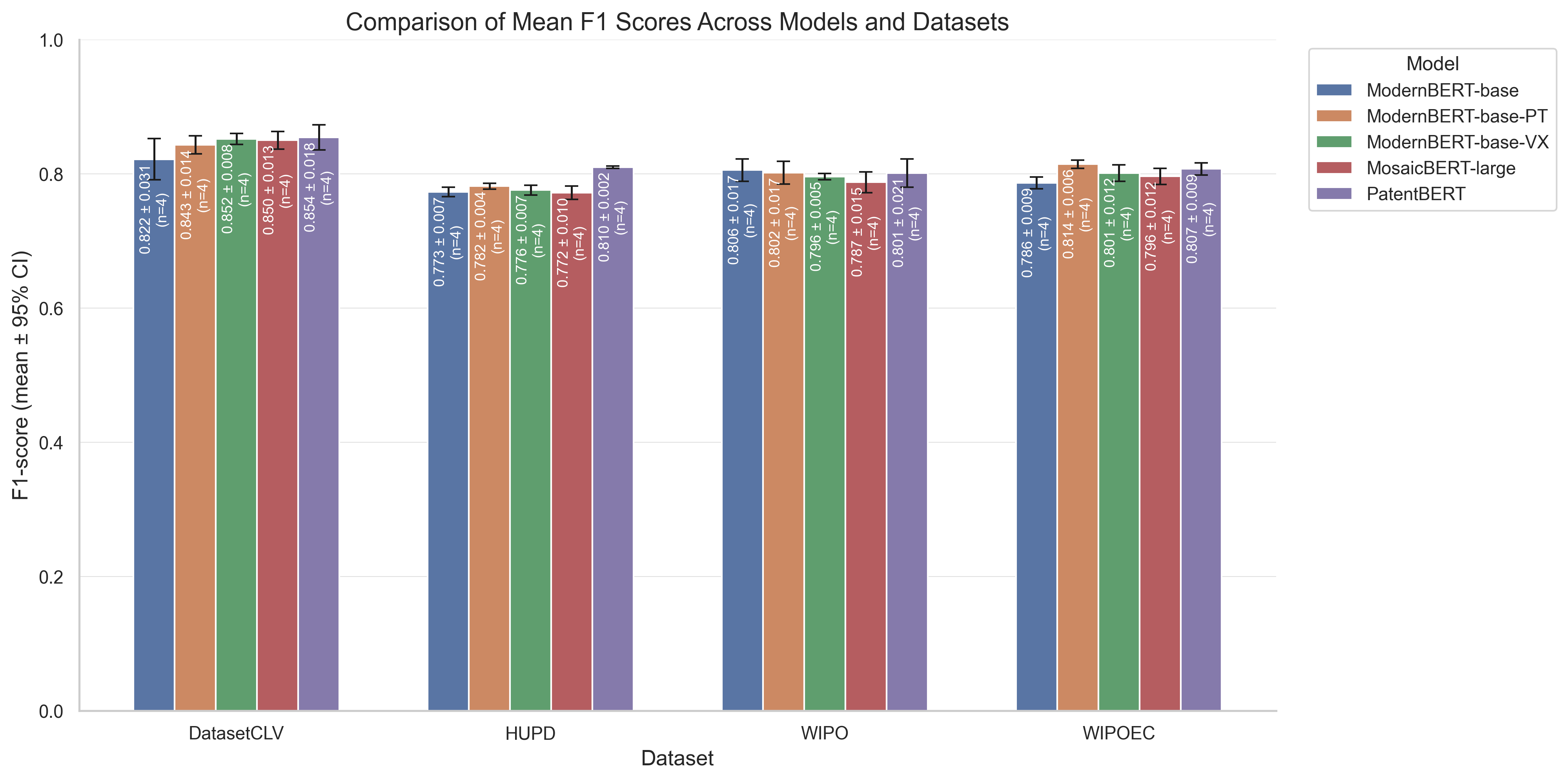
Figure 2: Test micro-F1 scores across models and datasets.
Computational Efficiency
Efficiency gains were substantial, with FlashAttention-based ModernBERT variants achieving significant throughput improvements over PatentBERT and MosaicBERT-large, demonstrating this approach's suitability for time-sensitive applications. These efficiency metrics are crucial for practical deployments, where faster inference times translate into cost savings and reduced latency.
Practical and Theoretical Implications
Impact on Patent NLP Tasks
These results underscore the importance of domain-specific pretraining coupled with architectural innovations to enhance NLP model performance on specialized tasks like patent classification. The improvements in speed and accuracy promise enhanced capabilities in patent analysis applications, potentially facilitating more efficient patent searches and classifications in legal tech.
Future Directions
Future research could involve extending this approach to multilingual patents, expanding beyond English to accommodate the global patent landscape. Additionally, exploring complementary pretraining tasks could further enrich the model's utility, such as incorporating contrastive learning objectives that might better capture inter-document relationships.
Conclusion
This research demonstrates the tangible benefits of domain-specific pretraining combined with state-of-the-art architectural enhancements for advancing NLP in the patent domain. ModernBERT-PT emerges as a potent tool for patent classification, offering both improved accuracy and computational efficiency. The insights gained from scaling models and customizing tokenization provide valuable guidance for further developments in domain-specific NLP applications.
By addressing the nuances of patent-language processing and optimizing transformer architectures accordingly, this research lays the groundwork for future innovations in specialized LLMs. Such advancements will be instrumental in harnessing the full potential of NLP for legally and technically complex documentation, paving the way for more intelligent and efficient text processing solutions in various specialized fields.



