- The paper presents Clinical ModernBERT, a model that integrates innovations like RoPE, Flash Attention, and an 8,192-token context to enhance biomedical text processing.
- The methodology combines large-scale pre-training on 40M PubMed abstracts and MIMIC-IV notes with structured medical ontologies for improved semantic understanding.
- Empirical results demonstrate superior performance in both short-context and long-context tasks while offering efficiency and scalability in clinical settings.
Clinical ModernBERT: An Efficient and Long Context Encoder for Biomedical Text
Introduction to Clinical ModernBERT
The development of LLMs tailored for biomedical text has advanced significantly, aiming to address specific challenges associated with the domain's complexity and varied nature. Clinical ModernBERT is a specialized transformer-based encoder leveraging architectural innovations from ModernBERT to enhance performance in biomedical and clinical settings. This model is built upon large-scale datasets, including biomedical literature, clinical notes, and medical ontologies, effectively integrating domain-specific knowledge into its pre-training.
Architectural Innovations
Clinical ModernBERT adopts several enhancements originally introduced in ModernBERT, such as Rotary Positional Embeddings (RoPE), Flash Attention, and an extended context length of up to 8,192 tokens. These features contribute to a more efficient and scalable performance compared to previous models:
- Rotary Positional Embeddings (RoPE): This approach embeds positional information in a rotation-based format, facilitating improved generalization for longer sequences.
- Flash Attention: Reduces the memory and computational cost of self-attention mechanisms, enabling efficient handling of extended contexts.
- Extended Context Length: Supports sequences up to 8,192 tokens, enabling processing of long-form biomedical documents.
Pre-Training Methodology
The pre-training phase utilizes a diverse corpus, combining structured medical ontologies with unstructured clinical and biomedical texts. This setup ensures that Clinical ModernBERT can effectively handle the specialized vocabulary and syntax typical of biomedical literature.
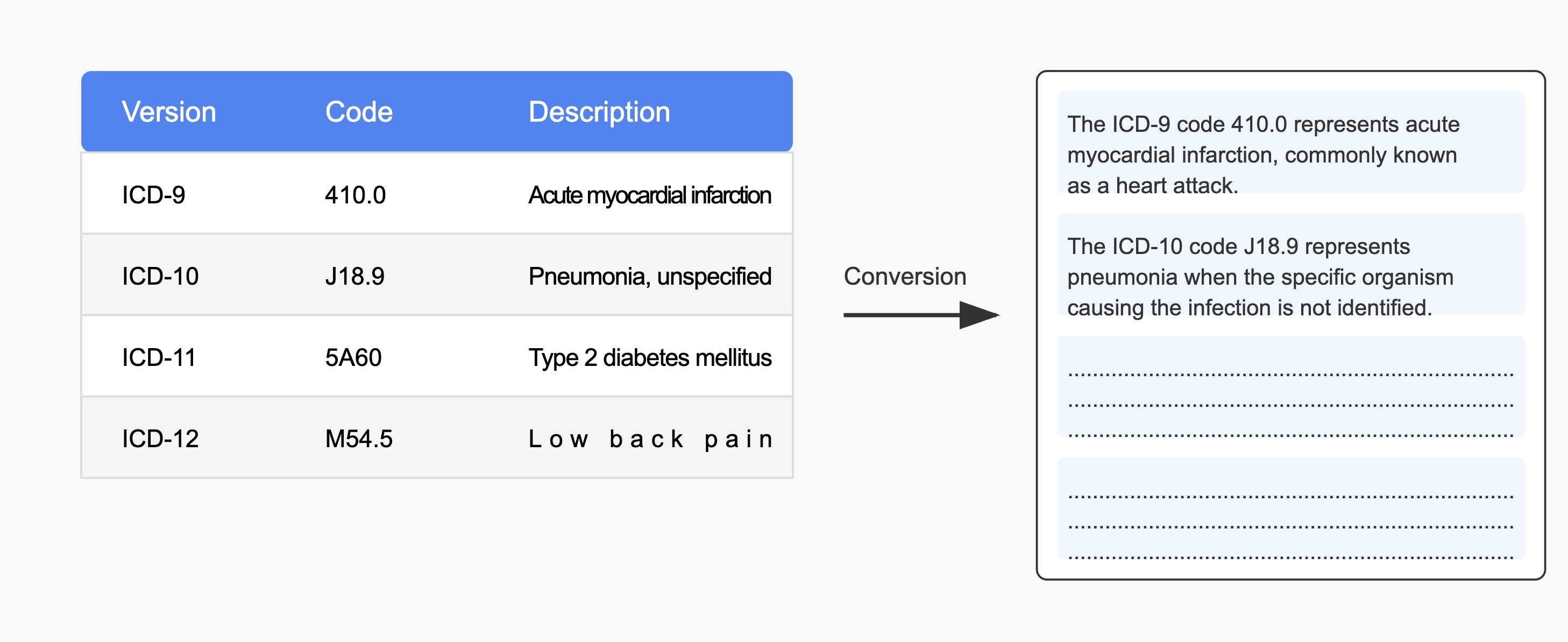
Figure 1: Medical Code Ontologies Construction: An illustration of structured ontology construction across multiple ICD code versions.
Clinical ModernBERT's pre-training includes approximately 40 million PubMed abstracts and clinical notes from the MIMIC-IV dataset. The incorporation of structured medical ontologies provides a robust framework for encoding medical concepts, enhancing semantic learning and facilitating tasks like entity normalization and concept linking.
Empirical Validation
The effectiveness of Clinical ModernBERT is demonstrated through a series of benchmarks and latent space analyses. It consistently outperforms other baseline models, including BioClinicalBERT and Clinical Longformer, across various NLP tasks, reflecting substantial improvements in domain adaptation and representational capacity.
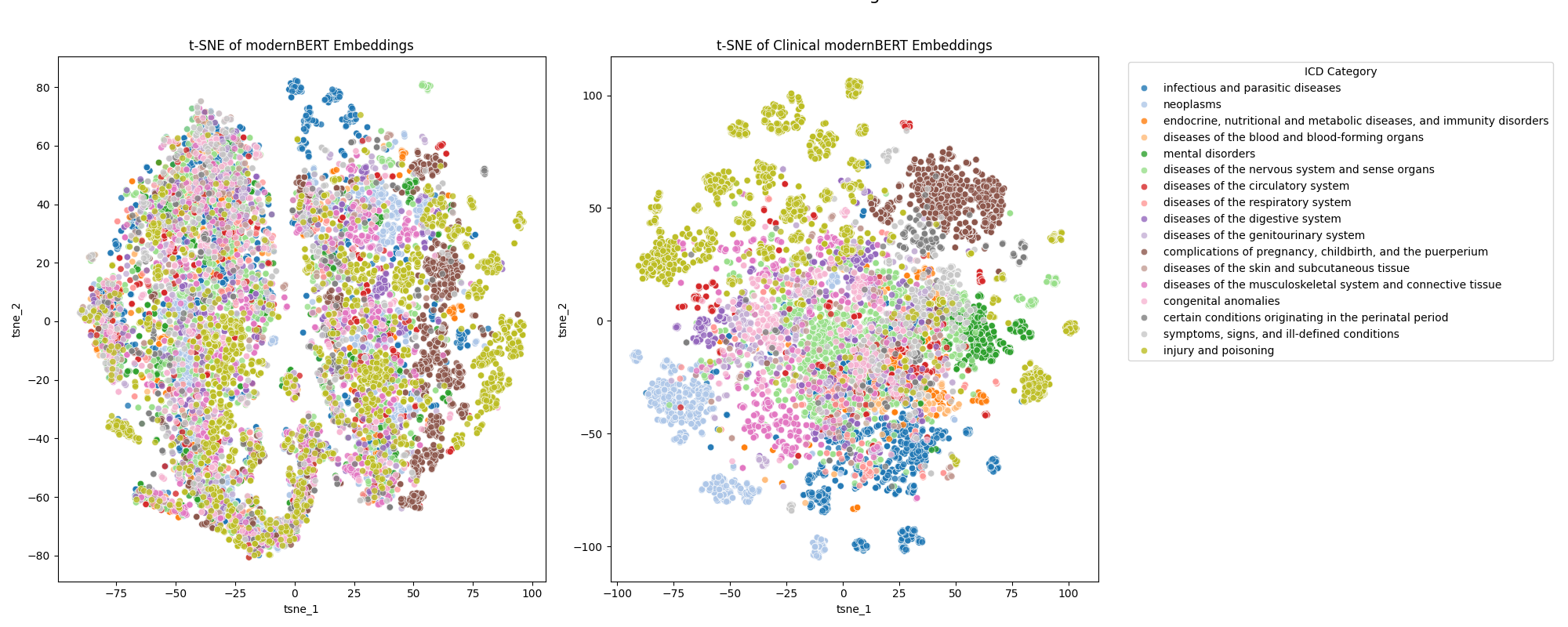
Figure 2: ICD-9 tSNE Latent Space Visualization: A tSNE visualization of the ICD 9 Diagnoses codes using modernBERT versus Clinical ModernBERT.
The model achieves competitive results on both short-context tasks like EHR classification and long-context tasks such as those found in the i2b2 shared task suite. Additionally, the efficiency gains from Flash Attention and optimized encoding strategies allow for practical deployments in resource-constrained clinical settings.
Efficiency and Scalability
Clinical ModernBERT exhibits significant computational benefits over existing models, as shown in comparative performance analyses. Its lower processing times across varying data volumes make it particularly suitable for real-world clinical applications where efficiency and scalability are critical.
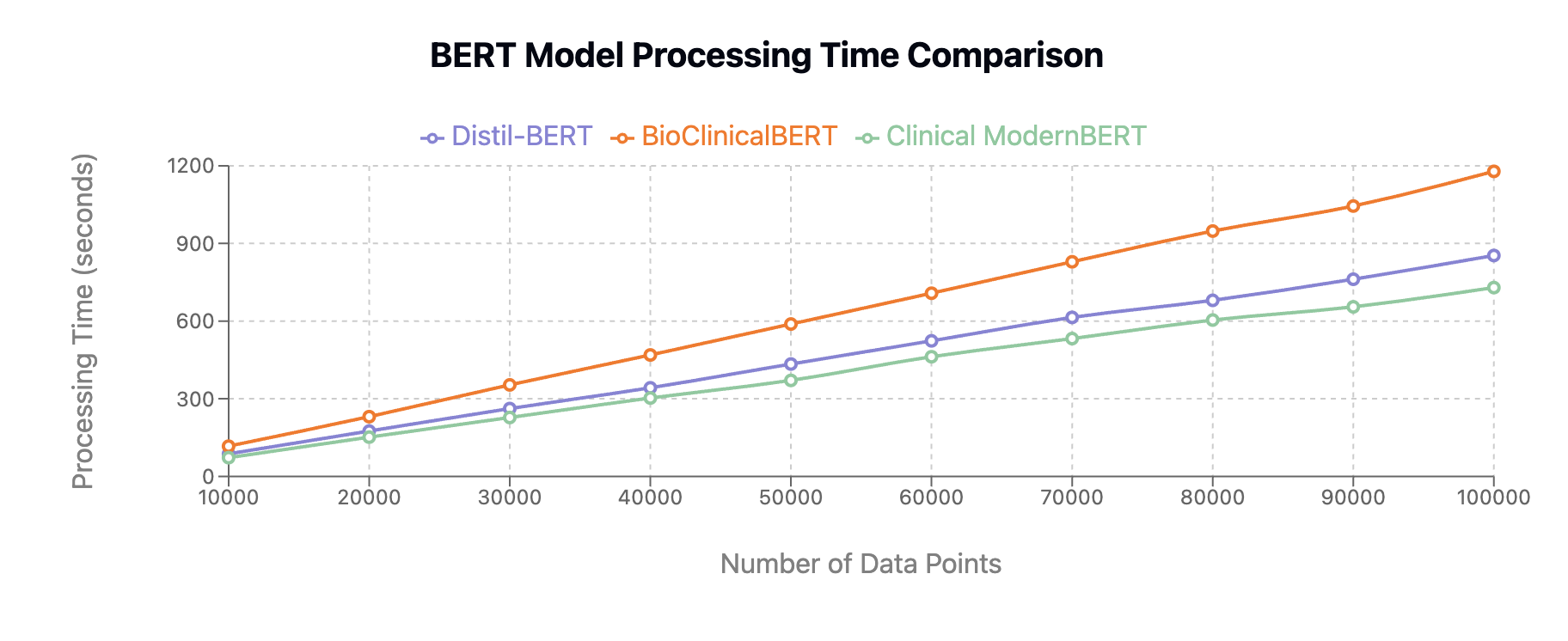
Figure 3: Comparative Performance Analysis of BERT Models: Demonstrating processing time requirements across three BERT variants as data volume increases.
Conclusion
Clinical ModernBERT represents a substantial advancement in biomedical NLP, emphasizing efficient, long-context processing tailored for specialized medical domains. It integrates architectural innovations and domain-specific pre-training, yielding a model that outperforms predecessors in both practical and theoretical dimensions. Future developments may explore the integration of Clinical ModernBERT with multimodal medical data, expanding its applicability and effectiveness in clinical decision support systems. As the model is publicly available, it stands to contribute significantly to ongoing research and development efforts in medical NLP applications.




