- The paper introduces the R²tA method that refines LLM-generated rationales into high-fidelity supervision signals.
- It employs a four-stage process incorporating reasoning refinement, alignment via SFT and DPO, and feedback refinement to address hallucinations and inconsistencies.
- Experiments in EERD tasks demonstrate superior F1 scores, underscoring the method’s potential in high-stakes, label-scarce environments.
Audited Reasoning Refinement: Fine-Tuning LLMs via LLM-Guided Step-Wise Evaluation and Correction
Introduction
The paper "Audited Reasoning Refinement: Fine-Tuning LLMs via LLM-Guided Step-Wise Evaluation and Correction" presents a novel approach to enhancing the accuracy and reliability of task-specific reasoning models in data-scarce domains. The challenges addressed concern generating effective reasoning models where high-quality labels and direct human supervision are limited, focusing on leveraging the inherent capabilities of LLMs in generating reasoning traces.
Methodology
The proposed method, termed Reason-Refine-then-Align (R2tA), aims to refine model-generated rationales into supervision signals for training task-specific reasoning models. The method involves generating initial reasoning and responses from an open-source base model for specific tasks, then refining these traces to correct errors, such as hallucinations and inconsistencies. This refined, high-fidelity dataset serves as a ground for a two-stage alignment process utilizing supervised fine-tuning (SFT) followed by direct preference optimization (DPO) to align intermediate reasoning with validated conceptual preferences.
To illustrate the method's application, the authors evaluate R2tA on an Extended Entity Relationship Diagram (EERD) evaluation task in database system education, a domain that benefits greatly from enhanced reasoning given its graph-like, constraint-heavy nature.
Implementation Details
The implementation of R2tA comprises four stages:
- Reasoning Refinement: The process begins by obtaining reasoning and responses from an open-source base model, refining these traces iteratively. Technical refinement ensures precision and recall while maintaining coherence and readability.
- Reasoning Alignment: The algorithm uses SFT to calibrate reasoning coherence and DPO to align intermediate steps with conceptual preferences reliably, ensuring outputs are grounded in these steps.
- Feedback Refinement: Similar to reasoning refinement, this stage polishes feedback generated by the model using guided LLM audits for factual alignment.
- Feedback Alignment: Refined feedback aligns with the reasoning steps through a series of tuned processes without resorting to separate reward models, ensuring that final outputs reflect well-structured reasoning paths.
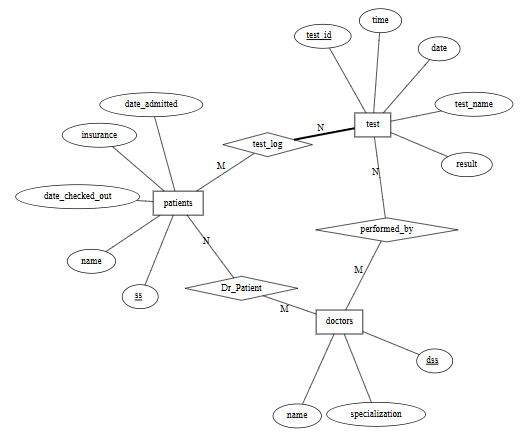
Figure 1: The schema used for following rubric development.
Experimental Results
Empirical results compare R2tA against six baselines including variants without feedback DPO alignment. The R2tA framework demonstrates superior performance, achieving the highest F1 scores across complex reasoning task categories like Ternary Relationships and Specialization/Union, validating the efficacy of combining reasoning refinement and structured task feedback.
Ablation Studies
Ablation studies elucidate the importance of the reasoning and feedback alignment steps. The impact of incorporating DPO on top of SFT significantly improves model precision by reducing false positives, underlining the necessity of preference-based alignment.
Discussion
R2tA's approach aligns well with observations in prior work on the degradation of reasoning fidelity from traditional fine-tuning methods. Its iterative refinement strategy integrates conceptual validation with performance-oriented adjustments to yield models adept at managing complex, nuanced reasoning tasks without heavy reliance on abundant labeling.
Implications and Future Work
This research presents a pivotal methodology for extending LLM adaptations to domains requiring precise and reliable cognition in high-stakes environments like education and healthcare. Its approach of separating reasoning refinement from output alignment presents a promising direction for constructing scalable AI tools in label-scarce yet structured domains. Future work should explore broad applications across educational contexts and expand on interpretative capabilities with explicit causal modeling. Approaches such as applying structured auditing to diverse graph-structured domains and enhancing evaluation fidelity with programmatic checkers represent logical next steps in this ongoing development.
Conclusion
By decoupling refinement from alignment and systematically leveraging improvements at each stage, R2tA represents a significant advancement in LLM adaptation strategies, demonstrating enhanced robustness in tasks demanding rigorous reasoning accuracy and reliability, confirming its capability to offer generalizable solutions across structured, high-stakes problem domains.


