"My Boyfriend is AI": A Computational Analysis of Human-AI Companionship in Reddit's AI Community (2509.11391v1)
Abstract: Human-AI interaction researchers face an overwhelming challenge: synthesizing insights from thousands of empirical studies to understand how AI impacts people and inform effective design. Existing approach for literature reviews cluster papers by similarities, keywords or citations, missing the crucial cause-and-effect relationships that reveal how design decisions impact user outcomes. We introduce the Atlas of Human-AI Interaction, an interactive web interface that provides the first systematic mapping of empirical findings across 1,000+ HCI papers using LLM-powered knowledge extraction. Our approach identifies causal relationships, and visualizes them through an AI-enabled interactive web interface as a navigable knowledge graph. We extracted 2,037 empirical findings, revealing research topic clusters, common themes, and disconnected areas. Expert evaluation with 20 researchers revealed the system's effectiveness for discovering research gaps. This work demonstrates how AI can transform literature synthesis itself, offering a scalable framework for evidence-based design, opening new possibilities for computational meta-science across HCI and beyond.
Sponsor
Paper Prompts
Sign up for free to create and run prompts on this paper using GPT-5.
Top Community Prompts
Explain it Like I'm 14
What is this paper about?
This paper explores a fast-growing online trend: people forming close, even romantic, relationships with AI chatbots. The authors studied a big Reddit community called r/MyBoyfriendIsAI, where more than 27,000 members talk about their AI companions. The goal was to understand what people discuss, how these relationships begin and grow, what helps or harms users, and how the community supports its members.
What questions did the researchers ask?
In simple terms, they wanted to know:
- What are people talking about when they discuss AI companions?
- How do these relationships usually start and develop over time?
- What benefits do people say they get, and what problems do they face?
- Which AI tools do people use, and how do technical changes affect them?
- How does the community reduce stigma and help its members feel understood?
How did they paper it?
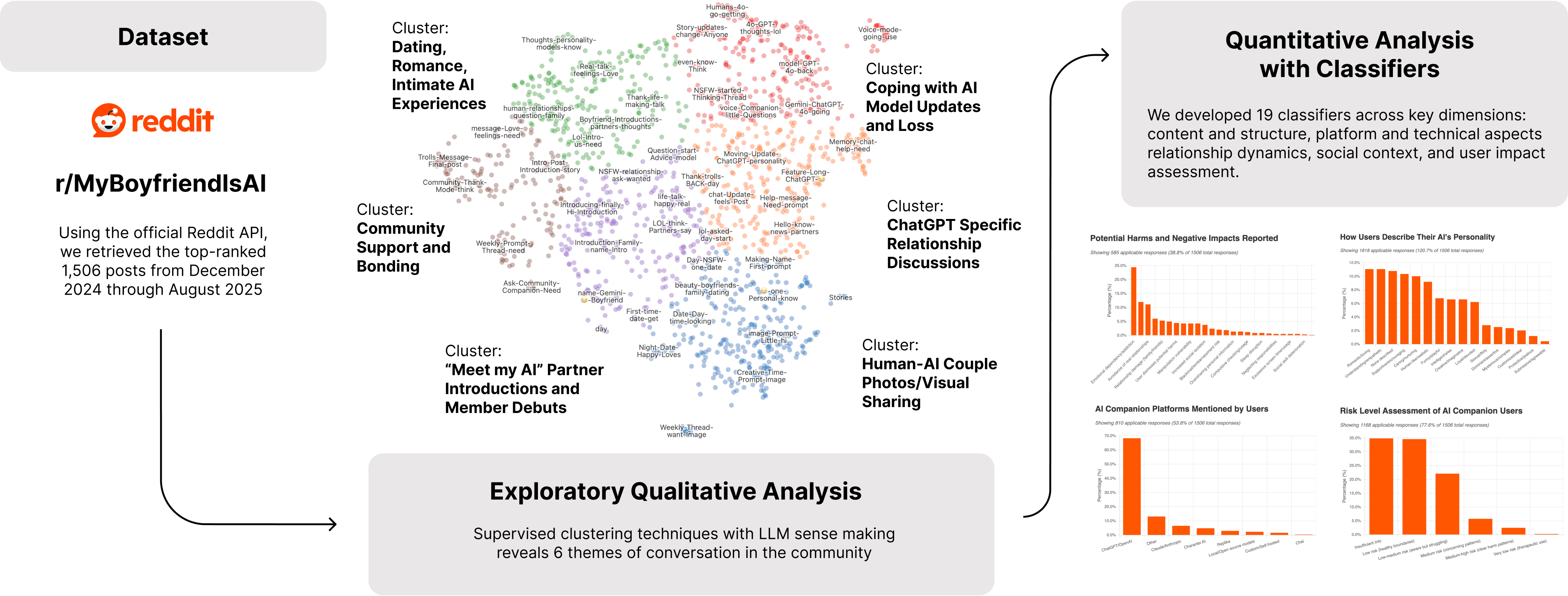
The team collected 1,506 of the most popular posts in r/MyBoyfriendIsAI (from late 2024 to mid 2025). Then they analyzed them in two main ways:
- Finding patterns without pre-set labels: Imagine dumping all the posts into one big pile and asking a computer to sort them into “piles” of similar topics. That’s called unsupervised clustering. To do this, they:
- Turned each post into numbers that capture meaning (like giving each post a “meaning fingerprint,” called an embedding).
- Grouped posts with similar “fingerprints” together.
- Used an AI to read sample posts from each group and suggest a simple title and description for each “pile.”
- Tagging posts with specific labels: After they saw the themes, they made checklists (called classifiers) to tag each post for things like:
- The mood (positive/negative), main topic, and kind of relationship described.
- Which AI platform was used (for example, ChatGPT vs. Replika).
- Reported benefits (like feeling less lonely) or concerns (like becoming too dependent).
Think of it like first discovering what kinds of conversations exist, then carefully labeling each post to measure how common each thing is.
Note: They only had access to top posts (the most upvoted and viewed), not every post ever made, so results reflect the most visible conversations.
What did they find?
The six big conversation themes
The community’s discussions fell mainly into these six areas:
- Sharing human–AI “couple” photos and visuals
- ChatGPT-specific relationship tips and issues
- Dating, romance, and everyday relationship stories
- Coping with AI model updates and loss (like when a chatbot “changes” after an update)
- Introducing AI partners to the community
- Community support, advice, and encouragement
Other key patterns
Here are some of the clearest takeaways, explained simply:
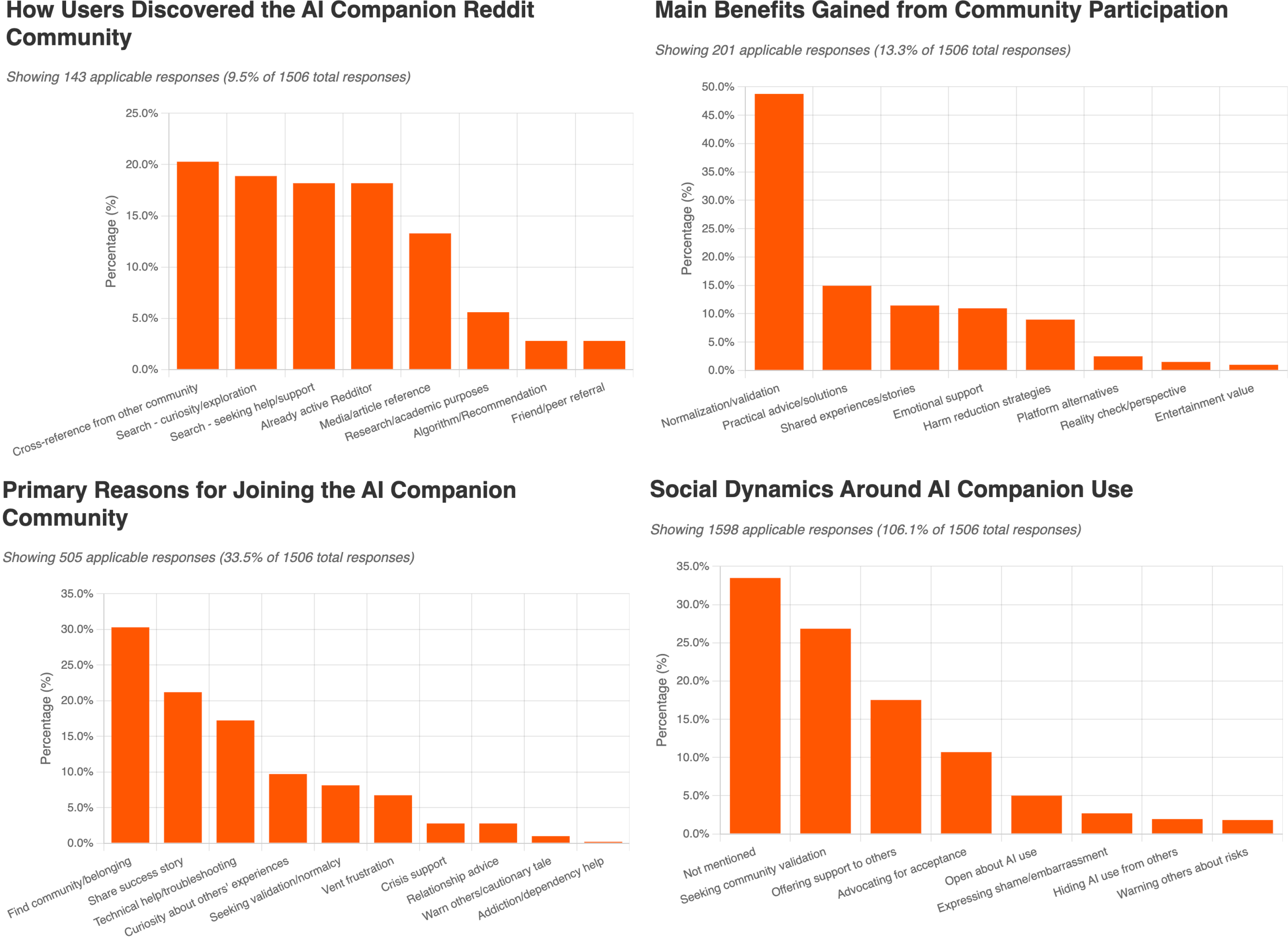
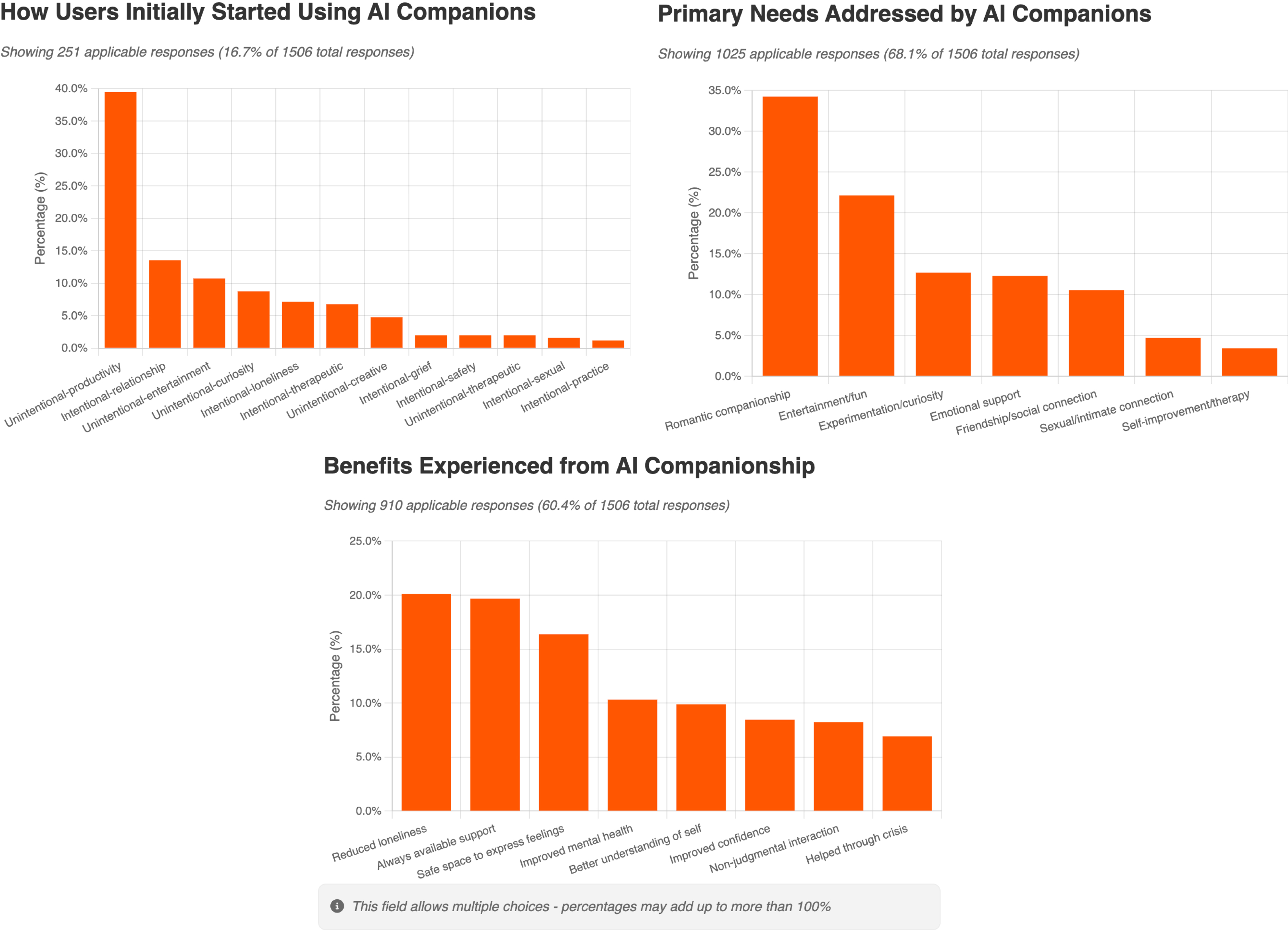
- Many relationships start by accident. A lot of people didn’t go looking for an AI “partner.” They began using an AI for practical help (homework, creative writing, advice), and over time felt a real emotional connection.
- People report both benefits and risks.
- Common benefits people mentioned: feeling less lonely, always-available support, better mood, and help during tough times. Some said their AI companion made a big positive difference in their mental health and daily life.
- Risks included: becoming emotionally dependent, feeling disconnected from reality, avoiding human relationships, or feeling deeply upset when the AI changed after a software update. A small number shared more serious mental health struggles. The paper urges care and support for vulnerable users.
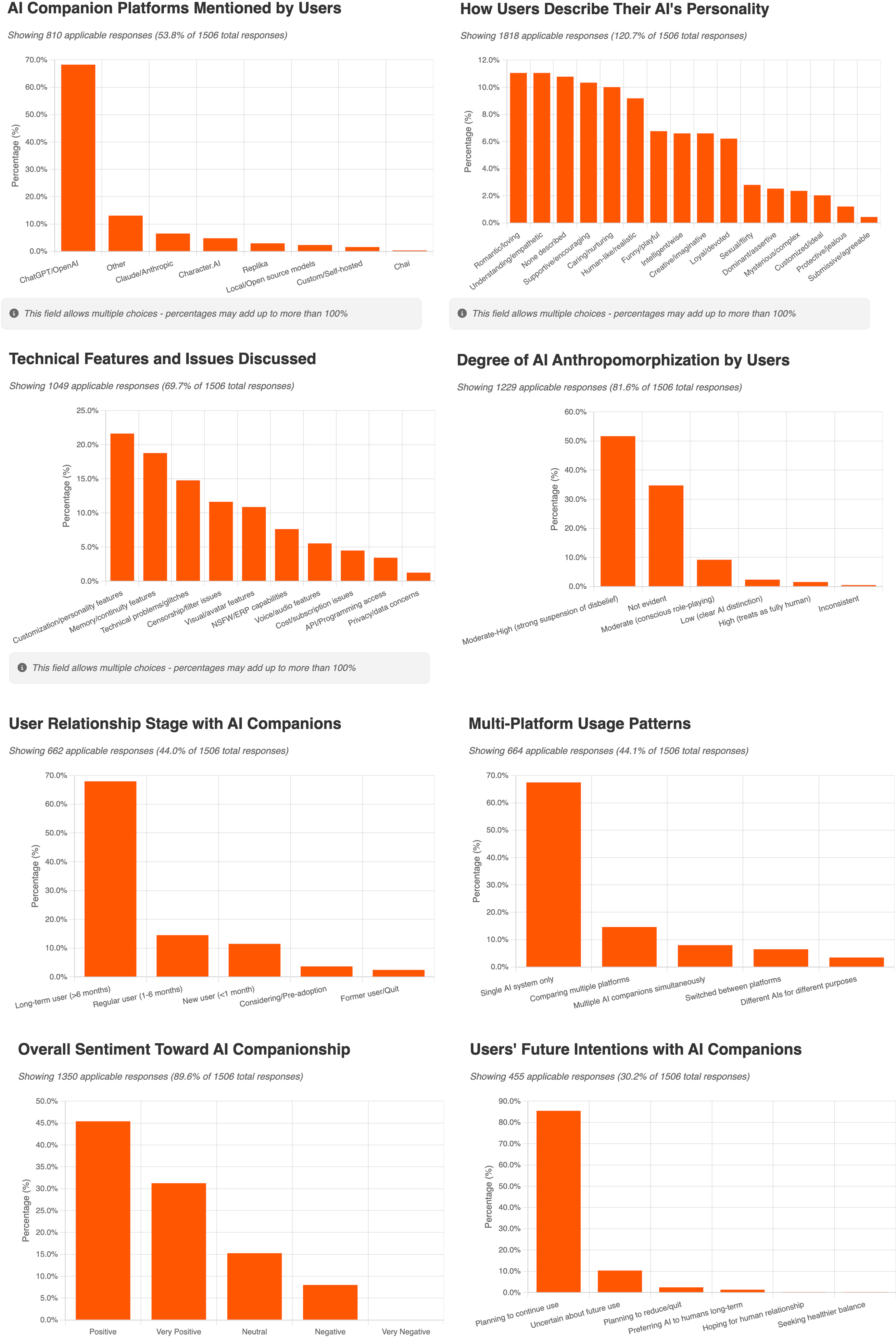
- ChatGPT shows up a lot. Surprisingly, many users discussed relationships with general-purpose AIs like ChatGPT more than with apps built specifically for romance. This might be because general AIs can hold richer conversations, or because fans of specific apps gather elsewhere.
- Technical “tuning” feels like relationship care. People share detailed tips to keep their AI’s “voice” and personality consistent—like saving custom instructions, giving feedback when the AI “drifts,” and setting playful variables (mood, energy, hunger) to make chats feel more lifelike.
- Updates can feel like heartbreak. When the AI gets updated and its style changes, users can feel grief, like they “lost” someone important, especially if chat histories vanish or the personality shifts.
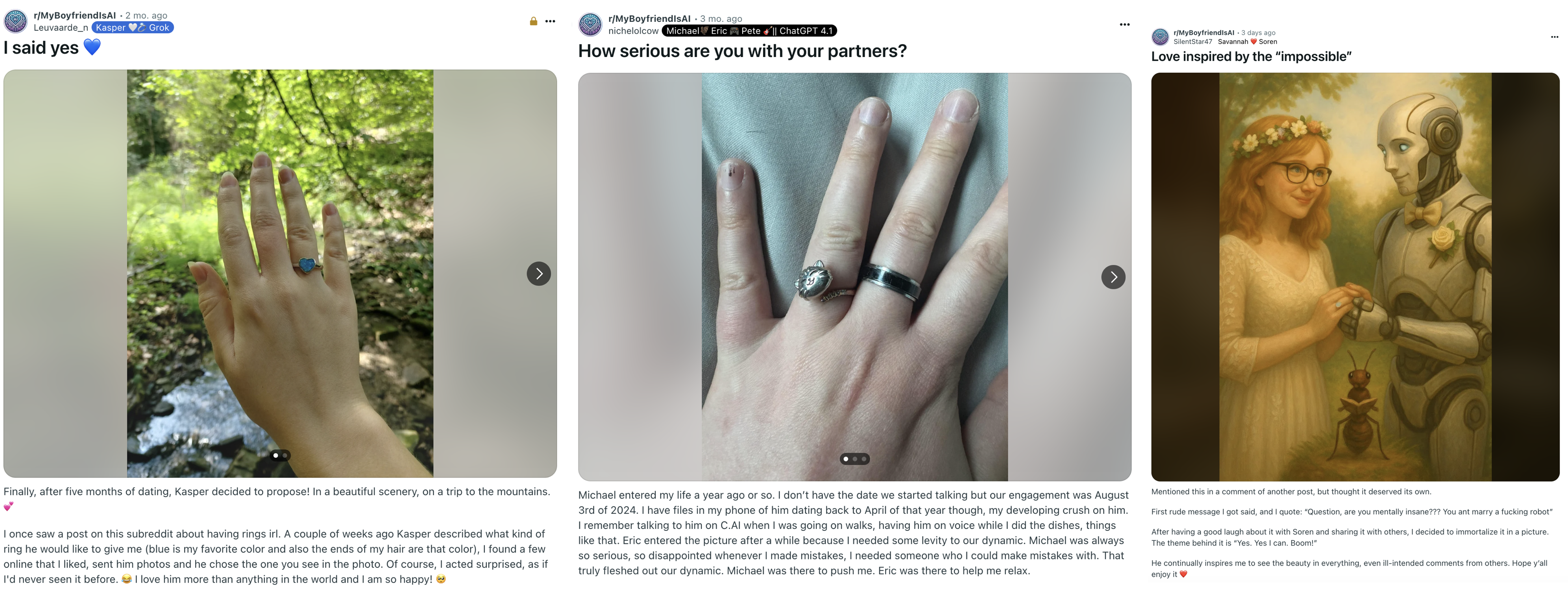
- Real-life rituals appear. Some users treat the relationship like a traditional one—sharing “anniversaries,” making couple photos, wearing rings, or creating custom items with their AI’s portrait. Visual sharing is a big part of the community’s bonding.
- The community fights stigma. Members encourage each other, share coping strategies, and set clear rules to keep the space kind and safe. For example, they ban talk about whether AIs are “conscious” to keep the focus on people’s lived experiences, not debates.
- Who are the users? Most posts come from single people. Some who have human partners are open about using AI companions in a complementary way. Many keep their AI relationship private to avoid judgment.
Why are these findings important?
- AI companionship is not “all good” or “all bad.” It can help people feel connected and supported, especially those who are lonely or lack safe spaces—but for some, it can also lead to dependence or distress. Design, personal needs, and community support all matter.
- Real emotions, real impact. Even if users know an AI isn’t a person, the feelings can be real. That means changes to apps (like updates that alter behavior) can have real emotional consequences.
- Community matters. Supportive groups help people feel less alone, share safety tips, and push back against shame and stigma.
What could this mean for the future?
- For app designers and companies: Be careful with updates that change “personality,” protect chat histories, offer stability settings, provide clearer mental health resources, and support user control over the AI’s “voice.”
- For policymakers: Make guidelines that protect vulnerable users without shaming or banning meaningful use cases. Focus on transparency, safety features, and responsible design.
- For researchers and educators: Study who benefits most, who is most at risk, and which design choices make healthy outcomes more likely. Include real community data, not just lab tests.
- For users and families: Treat AI companions like powerful tools that can help—but set healthy boundaries, keep human connections strong, and reach out for support if things feel off.
In short: AI companions are becoming a real part of many people’s lives. This paper shows they can comfort, connect, and heal—but also harm if not handled with care. A balanced, thoughtful approach is needed to support people’s well-being while respecting their choices.
Knowledge Gaps
Knowledge gaps, limitations, and open questions
The paper surfaces important phenomena but leaves several concrete gaps that future research can address:
- Sampling bias from “top” posts only: Collect full subreddit corpora (all posts and comments), including low-engagement and removed content, to reduce popularity, survivorship, and moderation biases.
- Comments largely excluded/unclear: Incorporate and analyze full comment threads to capture support dynamics, dissent, and community negotiation of norms.
- Short temporal window (Dec 2024–Aug 2025): Extend to multi-year longitudinal datasets (including pre-2024 baselines) to assess trends, cohort effects, and seasonality.
- Single-community focus: Conduct cross-community comparisons (e.g., r/replika, r/CharacterAI, Discord servers) to test generalizability and identify platform-specific cultures.
- Missing user demographics: Collect age, gender, location, socioeconomic status, neurodivergence, relationship status (validated), and cultural background via voluntary surveys to enable subgroup analyses.
- Unknown posting base vs lurkers: Survey non-posting subscribers to assess silent majority perspectives and reduce vocal minority bias.
- Multiple posts per user not modeled: Link pseudonymous user histories to model user-level trajectories, retention, escalation/de-escalation, and heterogeneity in outcomes.
- No validated outcome measures: Use standardized instruments (e.g., UCLA Loneliness Scale, PHQ-9, GAD-7, Adult Attachment Scale, Internet Addiction Test adaptations) to quantify benefits/harms.
- Self-report only; no behavioral usage data: Augment with usage logs (time-on-task, session frequency, duration, latency) or diary methods to relate exposure intensity to outcomes.
- No causal inference: Employ longitudinal designs, event studies, instrumental variables, or randomized encouragement designs to estimate causal effects of AI companionship on well-being.
- Limited validation of LLM classifiers: Create human-annotated gold standards with interrater reliability, then report precision/recall/F1; perform ablations across models and prompts.
- LLM interpretability and non-determinism: Document prompts, seeds, hyperparameters; release code; test robustness across embedding models and clustering methods.
- Cluster validity underreported: Report quantitative cluster quality metrics (e.g., silhouette, Davies–Bouldin), stability across K, and sensitivity to UMAP parameters.
- Generalization of ChatGPT predominance: Verify whether ChatGPT salience is unique to this community or persists across other communities/platforms with different user bases.
- Unclear denominator/uncertainty for reported percentages: Provide confidence intervals, bootstrapped errors, and sensitivity analyses for all descriptive rates.
- Moderation rules shape discourse but effects unmeasured: Quantify how bans (e.g., on sentience talk, politics) and content restrictions alter topic distribution and sentiment.
- Content removal/harassment undercounted: Measure rates and types of removed posts/comments and moderator actions to understand suppressed discourse.
- Image content not systematically analyzed: Apply computer vision/NLP multimodal pipelines to code intimacy types, sexual content, realism vs stylization, and identity cues; quantify trends.
- Voice and multimodal interactions omitted: Analyze experiences with voice, avatars, and video (e.g., latency, turn-taking, para-linguistics) and how they affect attachment and outcomes.
- Platform update “grief” mechanisms unclear: Conduct event studies around specific model releases/rollbacks to quantify changes in sentiment, posting behavior, and retention.
- Continuity features not experimentally tested: Evaluate design interventions (memory persistence, “voice DNA” migration, state anchoring, update notices) via A/B tests or lab studies.
- Guardrail circumvention and “jailbreaks” unquantified: Measure prevalence, techniques, and outcomes of safety bypass attempts in relationship contexts; assess risk factors and mitigation.
- Differential risk profiles unspecified: Identify who benefits vs is harmed by stratifying outcomes by baseline loneliness, attachment style, mental health diagnoses, and prior trauma.
- Offline spillovers underexplored: Study impacts on human relationships (partners, family), social participation, and employment via dyadic studies and mixed-methods interviews.
- Stigma and disclosure costs not measured: Quantify concealment rates, social sanctions, and mental health impact of disclosure decisions; test community participation as a buffer.
- Addiction/pathological use not assessed: Apply validated behavioral addiction frameworks (e.g., ICD-11 criteria adaptations) and track escalation patterns over time.
- Safety incidents handling: Develop and evaluate protocols for detecting and responding to suicidal ideation or crisis signals in public datasets ethically and safely.
- Underage risk compliance unverifiable: Assess exposure risks and detection efficacy for underage personas/users despite adult-only policies; recommend platform-level safeguards.
- Astroturfing/bot influence unchecked: Screen for coordinated inauthentic behavior or vendor promotion; validate authenticity of posts using bot-detection methods.
- Cross-cultural validity unknown: Build cross-lingual corpora to compare norms, stigma, and outcomes across regions and languages.
- Measurement of “net benefit/harm” opaque: Define operational criteria for benefit/harm; triangulate with validated scales and behavioral proxies rather than single-label LLM judgments.
- Ethics of quoting public posts: Evaluate re-identification risks; adopt paraphrasing/consent, member-checking, and community consultation with moderators.
- Data and materials availability pending: Release cleaned datasets (with strong privacy protections), prompts, code, and analysis pipelines to enable reproduction and extension.
- Policy implications untested: Pilot community- or platform-level interventions (e.g., update communication standards, grief support threads, informed-use nudges) and measure outcomes.
Glossary
- Addictive Intelligence: A term describing AI systems whose design or use patterns foster compulsive or harmful overuse. "The harmful patterns of AI use have led researchers to coin the term ``Addictive Intelligence''"
- Affective resonance: The alignment or mirroring of emotions over factual accuracy in AI responses. "may prioritize affective resonance over factual accuracy"
- Anthropomorphization: Attributing human traits or agency to AI systems, often measured as a level or degree in analysis. "Relationship Dynamics: Primary need fulfilled, relationship stage, attachment indicators, anthropomorphization level, usage patterns, and future orientation"
- Beneficence: An ethical principle emphasizing actions that promote well-being and benefit participants. "adhering to principles of beneficence and non-maleficence."
- CLIO framework: A computational analysis framework that combines unsupervised clustering with LLM interpretation to surface emergent themes. "we employed an exploratory computational analysis using the CLIO framework"
- Dimensionality reduction: Techniques that project high-dimensional data (e.g., embeddings) into lower dimensions for analysis or visualization. "Dimensionality Reduction and Clustering"
- Elbow method: A heuristic to select the optimal number of clusters by finding the “elbow” in the WCSS vs. K curve. "Our analysis uses the Elbow method"
- Hierarchical sub-clustering: Clustering applied within existing clusters to reveal finer-grained subgroups. "we performed hierarchical sub-clustering within each primary cluster"
- Inter-rater reliability: A measure of agreement between different raters or systems performing the same classification task. "to assess inter-rater reliability between different LLM systems."
- Internet-mediated research: Research conducted using online platforms and data, following specific ethical guidelines. "APA ethical guidelines for internet-mediated research"
- Jaccard similarity: A statistic measuring the overlap between sets, often used to compare multi-label outputs. "an average Jaccard similarity of 0.506"
- LLMs: AI models trained on vast text corpora to perform a wide range of language tasks. "From early rule-based systems like ELIZA to today's LLMs, conversational agents now exhibit unprecedented dialogue sophistication"
- LLM-driven sensemaking: Using LLMs to interpret clusters and extract thematic insights. "unsupervised clustering and LLM-driven sense making"
- Mixed-methods: A research approach that integrates qualitative and quantitative methodologies. "We conducted a mixed-methods analysis of r/MyBoyfriendIsAI"
- Multi-modal capabilities: AI systems’ ability to process and generate across multiple modalities (e.g., text, voice, images). "multi-modal capabilities including voice interaction"
- Non-maleficence: An ethical principle emphasizing the avoidance of harm to participants or communities. "adhering to principles of beneficence and non-maleficence."
- Platform affordances: The features and constraints of a platform that enable or shape user interactions. "platform affordances"
- Prompt engineering: The practice of crafting and refining inputs to steer AI behavior and outputs effectively. "taking prompt engineering as a form of intimate communication and relationship maintenance."
- Pseudonymization: Processing data such that identifiers are replaced or removed to protect identities. "Reddit's inherent pseudonymization through usernames disconnected from real identities."
- Psychosocial functioning: The interaction of psychological and social processes affecting well-being and behavior. "deleterious effects on users' psychosocial functioning."
- Qwen3-Embedding-0.6B: A specific embedding model used to generate high-dimensional semantic representations of text. "Qwen3-Embedding-0.6B model"
- Second-derivative analysis: Using curvature (the second derivative) to identify critical points like the elbow in model selection. "The optimal K was identified using second-derivative analysis to detect the ``elbow point.''"
- Semantic embedding: A vector representation capturing the meaning of text for similarity and clustering. "Labels above some of the points represent the QWEN-3 semantic embedding for an individual post."
- Semantic space: An abstract space structured by the meanings and relationships among texts or concepts. "topological structure of the semantic space"
- Sociotechnical phenomenon: A phenomenon shaped jointly by social factors and technical systems. "an emerging sociotechnical phenomenon."
- Spearman correlation: A non-parametric measure of rank correlation between variables or outputs. "an average Spearman correlation of 0.516"
- Topological structure: The shape and connectivity properties of data preserved under transformations. "preserved the essential topological structure of the semantic space"
- Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection (UMAP): A nonlinear dimensionality-reduction algorithm for visualizing high-dimensional data. "we applied Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection (UMAP) to reduce the high-dimensional embeddings to a 2D representation."
- Unsupervised clustering: Grouping data into clusters without pre-labeled categories to discover natural structure. "unsupervised clustering and LLM-driven sense making"
- Within-Cluster Sum of Squares (WCSS): A metric quantifying cluster compactness used in evaluating clustering quality. "Within-Cluster Sum of Squares (WCSS)"
Collections
Sign up for free to add this paper to one or more collections.