- The paper presents FlexMDM, a diffusion model that supports variable-length sequences and any-order token insertion using a dual loss training strategy.
- It leverages continuous-time Markov chains and a stochastic interpolant framework to predict token unmasking and insertion during inference efficiently.
- Experimental results demonstrate nearly 60% improved success in maze planning and enhanced performance on text generation and code infilling tasks.
Any-Order Flexible Length Masked Diffusion
Introduction
The paper introduces Flexible Masked Diffusion Models (FlexMDM), enhancing the capabilities of Masked Diffusion Models (MDM) by allowing for variable-length sequences and token insertion, while maintaining any-order generation. This development addresses limitations in current MDM implementations, where sequences are fixed-length and token insertion isn't supported.
In FlexMDM, sequences are generated by initially inserting mask tokens and subsequently unmasking them through predictions of the expected number of mask tokens to insert and the posterior over clean tokens.

Figure 1: Flexible Masked Diffusion Model (FlexMDM) addresses MDMs' inability to handle variable-length sequences and token insertion while preserving any-order generation power.
Preliminaries: Continuous-Time Markov Chains and Masked Diffusions
FlexMDM is grounded in the stochastic interpolant framework expanded to accommodate variable-length sequences via continuous-time Markov chains (CTMCs). It relates CTMCs to discrete diffusion and utilizes them for sequence generation by inserting and unmasking tokens. The FlexMDM approach uses both insertion and unmasking schedules to define the stochastic interpolant which determines the distribution path between the base and target distributions.

Figure 2: MDM interpolant process diagram.
FlexMDM Training Methodology
Training FlexMDM involves learning two key components: the unmasking posterior similar to MDM, and the number of tokens expected to be inserted. The loss function combines these components to facilitate learning of the correct rate matrix for sequence generation:
- Unmasking Posterior: Models the distribution of a clean token at masked positions.
- Insertion Expectation: Predicts the expected number of tokens to insert between tokens in the sequence.
This duality allows FlexMDM to handle variable-length sequences efficiently at scale.
Inference with FlexMDM
FlexMDM supports adaptive inference where tokens can be unmasked in an arbitrary order, maintaining the theoretical any-order guarantees of MDMs. Its approach leverages tau-leaping for accurate and efficient unmasking and insertion during inference.

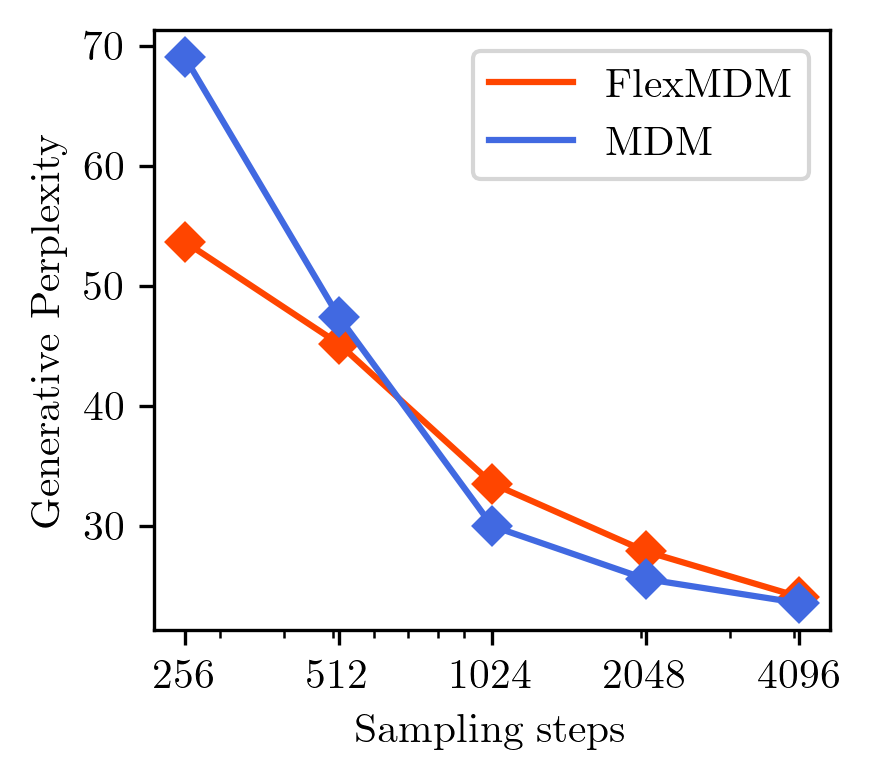
Figure 3: Maze task illustration. The model is given subgoals and is required to connect them.
FlexMDM's inference adaptability is crucial for tasks like maze planning where preassigning token positions is challenging without accurate a priori information.
Experimental Validation
FlexMDM demonstrates strong performance across varying tasks, outperforming baseline MDMs by nearly 60% success rate on synthetic maze planning tasks, proving its efficacy in subgoal-style planning scenarios. Additionally, it shows greater fidelity in modeling length distributions during text generation without compromising sequence perplexity.
For scalability, FlexMDM can retrofit pretrained MDM weights, allowing for rapid task transfer and enhancement in performance metrics on datasets like GSM8K and code infilling benchmarks.
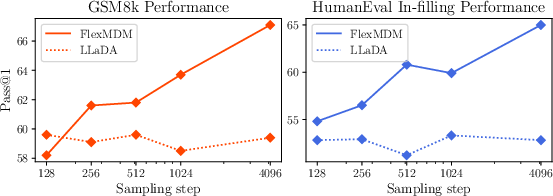
Figure 4: FlexMDM performance exhibits superior scaling when more sampling steps are allocated.
Conclusion
FlexMDM introduces a robust framework for discrete diffusion in variable-length sequences, significantly advancing the capabilities over traditional MDM approaches. It maintains any-order generation flexibly while enabling efficient training and inference even at large scales.
By enabling token insertions in generative models, FlexMDM aligns the state-of-the-art methodology with natural sequence compositions in human language and nature, heralding advances in generative modeling with practical applications across diverse domains.






