- The paper presents the OLMoASR framework, demonstrating that rigorous data curation from 3M to 1M hours can reduce word error rate by up to 16.5%.
- It details scalable training using a modified Whisper architecture with techniques like FlashAttention and FSDP with bfloat16 to ensure robust model stability.
- Comparisons with other open-source models highlight that high-quality, publicly available datasets are crucial for advancing zero-shot ASR performance.
OLMoASR: Open Models and Data for Training Robust Speech Recognition Models
The paper presents a comprehensive exploration into the development of robust speech recognition models through the introduction of the OLMoASR framework. This involves both the creation of a large-scale dataset, OLMoASR-Pool, and the deployment of a suite of OLMoASR models trained on a curated subset, OLMoASR-Mix. These initiatives aim to advance the state-of-the-art in zero-shot speech recognition capabilities, addressing the gap in publicly available resources akin to the scale of proprietary models like Whisper.
Dataset Construction and Curation
The cornerstone of this research is the assembly of the OLMoASR-Pool, containing 3 million hours of audio, and its subsequent refinement into the 1 million-hour OLMoASR-Mix dataset through a meticulous curation pipeline.
The data curation involves:
- Audio-text Language Alignment: Using VoxLingua107 and \verb+pycld2+, to ensure English language consistency across audio and transcript pairs.
- Text-based Heuristics: Filtering poor-quality transcriptions, such as those with repeated lines or extreme casing, which account for significant performance degradations in speech recognition.
- Manual-Machine Text Comparison: Implementing WER-based comparisons to remove unaligned or unrelated transcripts, establishing a high-quality training base.
This curation is vital, as demonstrated by performance improvements up to 16.5% in word error rate (WER) from these interventions, reflecting a well-curated dataset's impact on model proficiency.
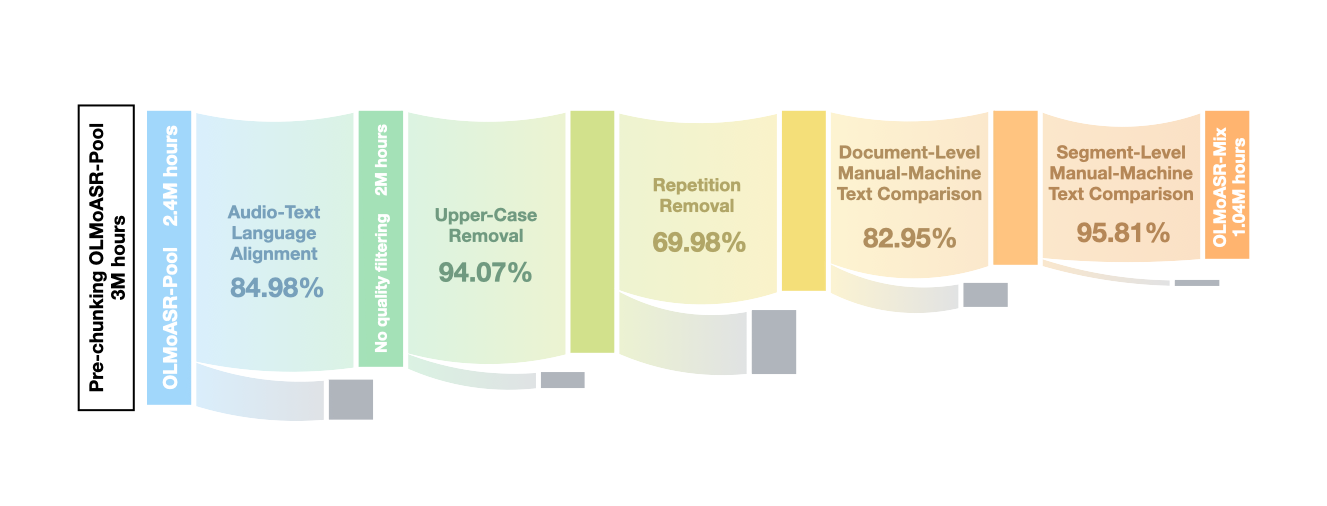
Figure 1: Construction of OLMoASR-Mix from OLMoASR-Pool. Segmentation reduces OLMoASR-Pool from 3M to 2.4M hours.
Model Training and Architecture
The OLMoASR models adhere closely to Whisper's architecture. Key differences include adjustments such as incorporating FlashAttention, optimizing learning rates, and altering batch sizes for more efficient distributed training. Models scale from 39 million to 1.5 billion parameters, underpinning the analysis of performance across varying computational constraints. Crucially, the paper reports that training stability was achieved using FSDP with bfloat16, offering enhanced consistency over FP16.
Experimental Evaluation
Evaluated on a set of 21 diverse datasets, each model in the OLMoASR suite demonstrates competitive or superior zero-shot performance relative to Whisper, particularly at smaller and intermediate scales. The paper highlights that the data curation pipeline profoundly contributes to model robustness, yielding consistent improvements over baselines trained without such filtration.
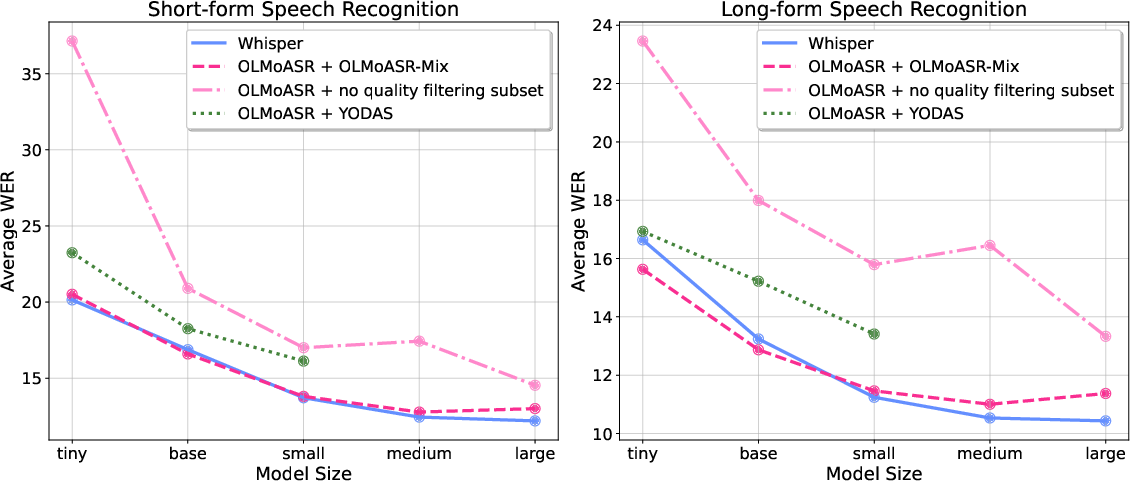
Figure 2: Average performance across 14 short-form speech recognition benchmarks (left) and across 7 long-form speech recognition benchmarks (right) of each baseline for all possible model scales.
Robustness and Scalability
A critical analysis within the paper pertains to the robustness of OLMoASR models. Utilizing effective and relative robustness metrics, the paper illustrates the superiority of OLMoASR models over typical supervised models when subjected to out-of-distribution conditions, thereby validating the robustness imparted by the OLMoASR-Mix dataset.
The scalability experiments revealed non-linear returns; while initial data scale increases led to significant gains, the marginal benefits diminished as more data were added, pointing towards a potential saturation threshold for the given model architecture.
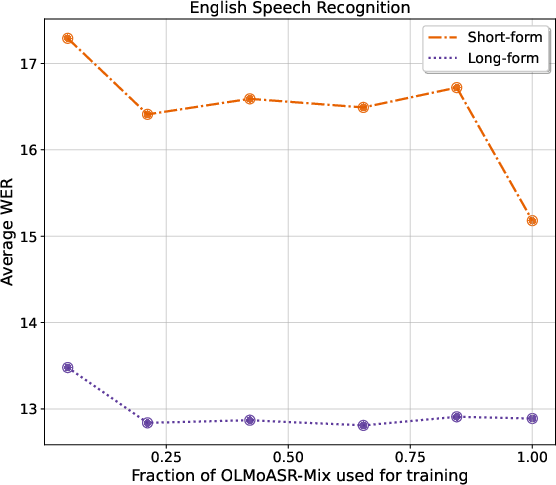
Figure 3: We plot the average performance of OLMoASR-74M on 14 short-form and 7 long-form evaluation sets, while varying the total data trained on.
Comparisons to Existing Models
By comparing OLMoASR models to other open-source speech recognition solutions like OWSM and models trained on varying dataset mixes, the paper reinforces the superiority of the OLMoASR Mix curation strategy. Across the board, OLMoASR models exhibit lower WER, accentuating the advantages of high-quality, curated training data sets even when directly juxtaposed with similarly large sets.
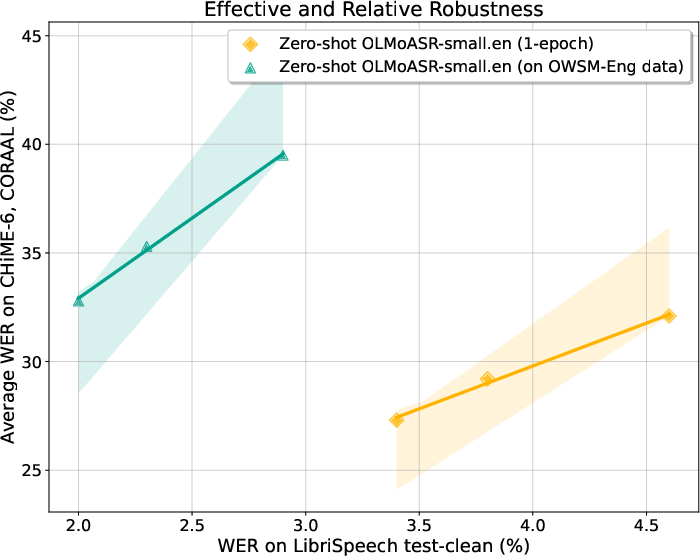
Figure 4: We plot 3 OLMoASR trained on OWSM-Eng data without any robustness interventions and demonstrate their WER on a reference test set and the average WER across 2 out-of-distribution evaluation sets.
Conclusion
In articulating the development of OLMoASR, this paper underscores the indispensable role of data curation in enhancing the robustness and generalization of speech recognition models. It sets a precedent for open, large-scale datasets aimed at democratizing access to high-quality data necessary for model training, facilitating further research in AI transparency, fairness, and bias examination. These contributions could catalyze more open and equitable advancements within the AI community.





