- The paper introduces Semantic Anchoring, a hybrid model combining symbolic linguistic cues with dense vector retrieval to enhance long-term conversational memory.
- It leverages syntactic parsing, coreference resolution, and discourse tagging, achieving up to 18% improvement in factual recall and better discourse coherence on benchmark datasets.
- The integration of neural and symbolic processing in the framework offers a robust solution for maintaining dialogue context, paving the way for real-time and multilingual conversational applications.
Semantic Anchoring for Conversational Memory Enhancement
Introduction
The paper "Semantic Anchoring in Agentic Memory: Leveraging Linguistic Structures for Persistent Conversational Context" addresses the challenge of maintaining long-term conversational memory in LLMs. It highlights the limitations of existing conversational memory techniques, such as full-context prompting and vector-based Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), which inadequately capture complex linguistic structures. The authors propose a novel architecture named Semantic Anchoring that integrates linguistic features—syntactic dependencies, discourse relations, and coreference links—into the memory retrieval and indexing process, enhancing both recall efficacy and discourse coherence.
Methodology
The Semantic Anchoring framework augments dense vector storage with symbolic linguistic cues, establishing a hybrid model that supports richer retrieval functionalities. Key elements include:
- Syntactic Parsing: Utilizes biaffine dependency parsers to extract dependency trees from utterances, capturing grammatical relations that aid in resolving elliptical references.
- Coreference Resolution: Links entity mentions across dialogue turns through persistent IDs, which is critical for entity continuity across sessions.
- Discourse Tagging: Assigns labels to inter-utterance relations to preserve conversational flow such as Elaboration or Contrast.
- Hybrid Storage: Combines dense embeddings in FAISS with symbolic indexes based on coreference IDs, dependency features, and discourse tags.
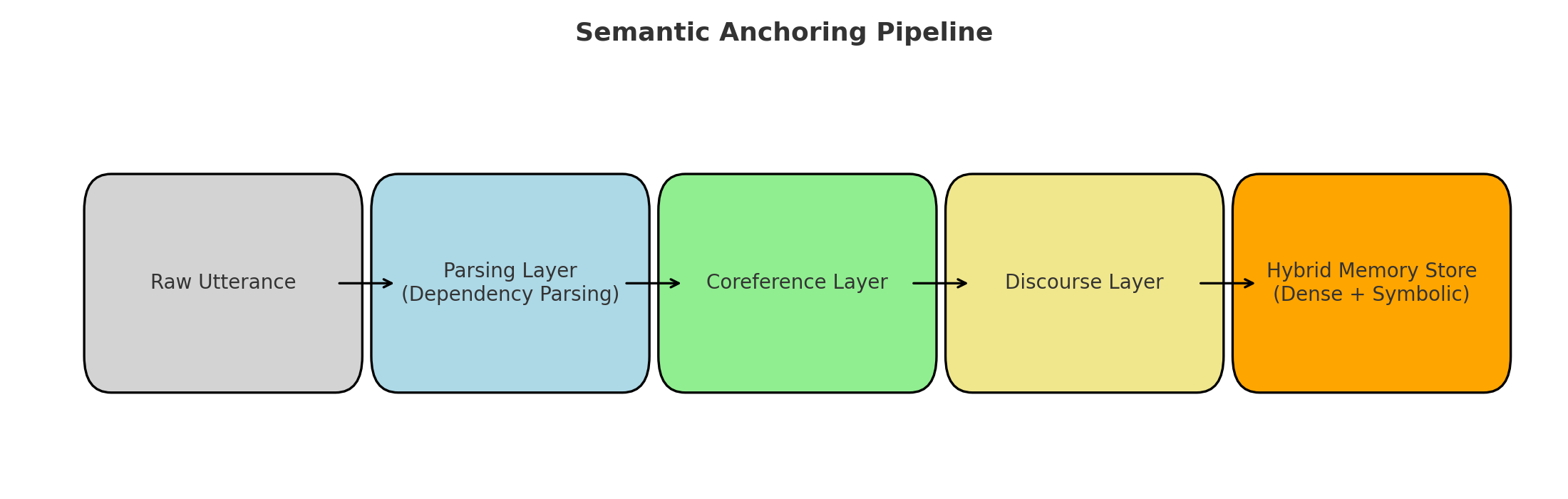
Figure 1: Architecture of Semantic Anchoring. Input utterances are processed through a parsing layer, coreference resolver, and discourse tagger before being combined with dense retrieval in a hybrid index. Retrieved candidates are scored and passed to the LLM context.
The framework computes retrieval scores by combining semantic similarity, entity matches, and discourse alignment, enhancing interpretability and robustness in memory retrieval scenarios.
Experimental Results
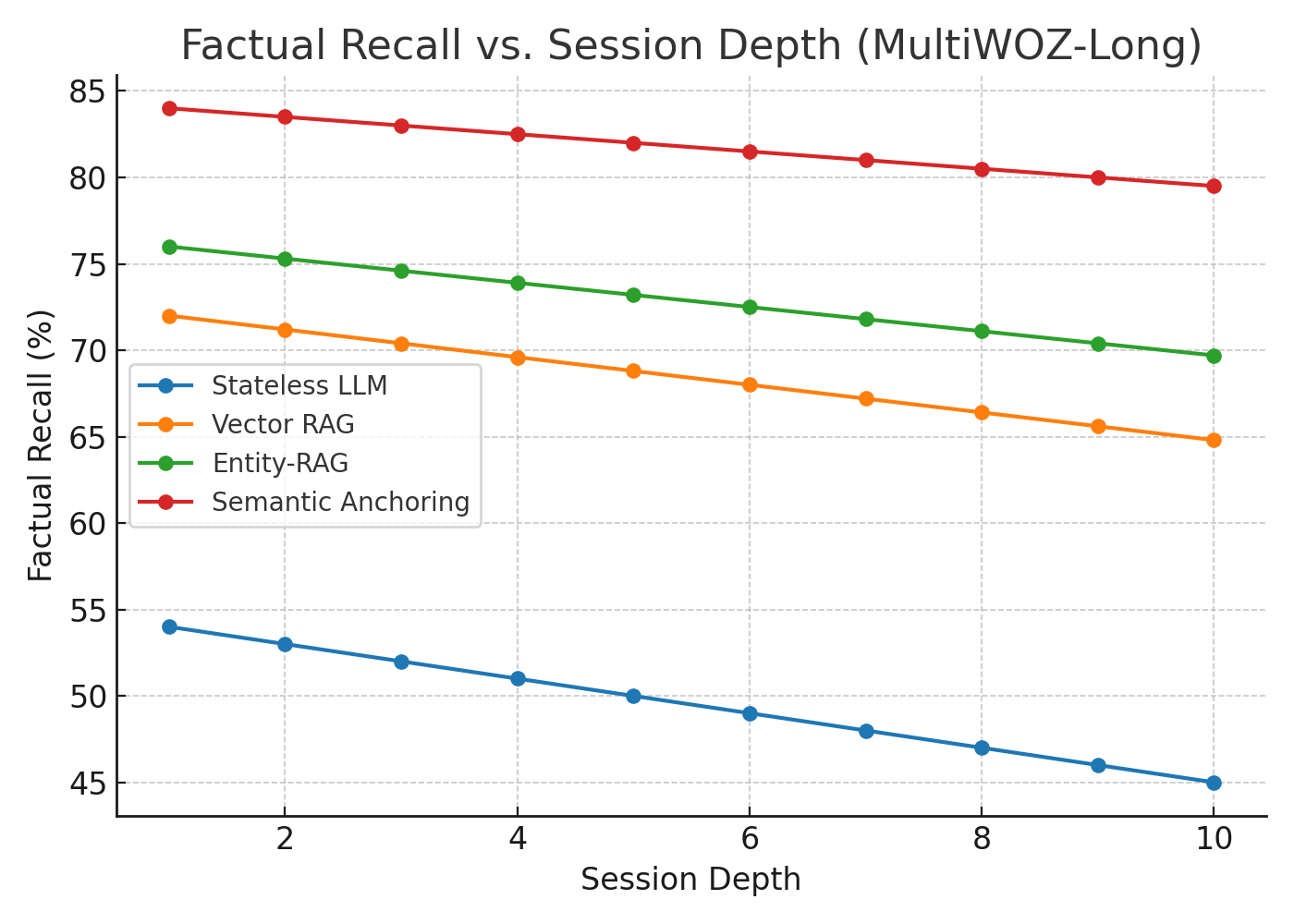
Semantic Anchoring is evaluated against several baselines, including a stateless LLM and different RAG configurations. The principal datasets used are MultiWOZ-Long, adapted from the MultiWOZ 2.2 dataset, and DialogRE-L, an extended version of the DialogRE dataset. Compared to baselines, the model achieves significant improvements in Factual Recall (FR) and Discourse Coherence (DC):
Ablation studies highlight the importance of symbolic features, showing reduced performance when components like discourse tagging and coreference resolution are omitted.
Implementation Considerations
For practical deployment, Semantic Anchoring demands significant computational resources due to its reliance on both neural networks and symbolic processing pipelines. Implementers should ensure proper infrastructure, such as high-capacity GPUs and robust indexing systems, to manage index fusion and real-time querying efficiently.
Conclusion
Semantic Anchoring offers a promising advance in conversational AI by unifying symbolic and neural representations to enhance memory persistence and integrity. Future work may explore integration with incremental parsing for real-time adaptability, user-editable memories, and multilingual support, aiming to pave the way for more globally accessible, persistent conversational agents.