- The paper introduces a hybrid-thinking framework that interleaves active perception with text-based reasoning to improve ambiguity resolution in driving scenarios.
- It employs a progressive three-stage training strategy using dual-mode fine-tuning and reinforcement learning to enhance cognitive flexibility and performance.
- Experimental results on Drive-Internal and nuScenes datasets show notable accuracy gains over passive models, validating the method’s real-world applicability.
DriveAgent-R1: Advancing VLM-based Autonomous Driving with Active Perception and Hybrid Thinking
Introduction
DriveAgent-R1 proposes an innovative integration of Vision-LLMs (VLMs) into autonomous driving through active perception and hybrid thinking. While traditional methods rely on passive perception, DriveAgent-R1 actively seeks visual evidence using a tool-based approach to resolve uncertainties inherent in complex driving scenarios. This paper explores how DriveAgent-R1 interleaves text-based reasoning with visual input from a Vision Toolkit, thereby offering enhanced interpretability and reliability in autonomous driving systems.
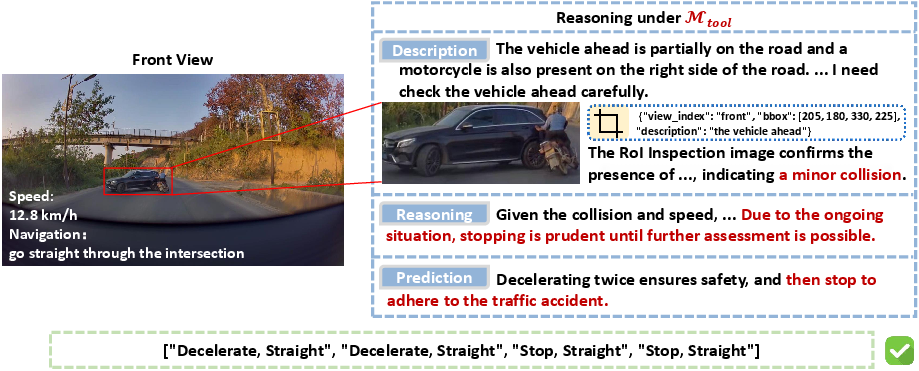
Figure 1: An illustration of DriveAgent-R1's active perception capability. The agent proactively uses RoI Inspection to clarify an uncertain scene, discovering a minor collision between the vehicles ahead.
Hybrid-Thinking Framework
The hybrid-thinking framework allows DriveAgent-R1 to switch between text-only reasoning and tool-augmented visual reasoning. In simple scenarios, text-based reasoning efficiently handles decision making, while complex situations warrant deeper exploration using visual tools.
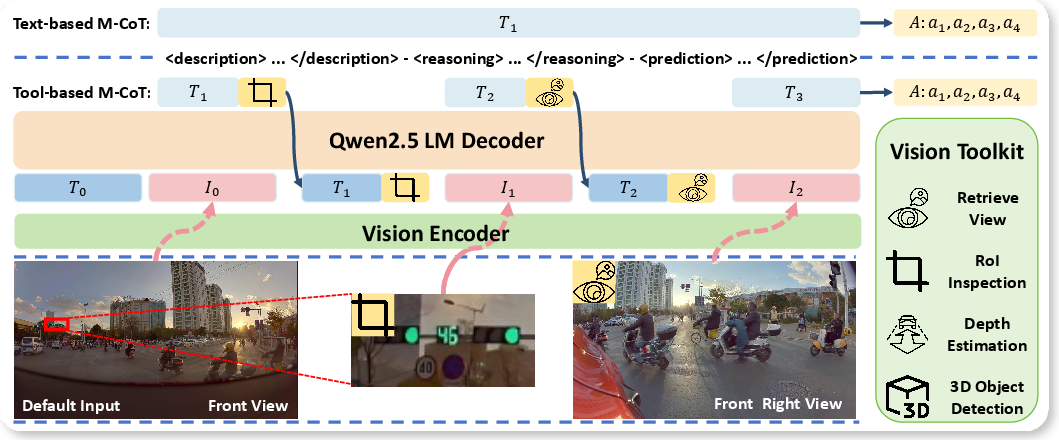
Figure 2: The Hybrid-Thinking architecture of DriveAgent-R1, illustrating the different approaches for simple and complex scenarios.
Progressive Training Strategy
DriveAgent-R1 undergoes a three-stage progressive training strategy, starting with dual-mode supervised fine-tuning (DM-SFT) to establish a foundational understanding. This is followed by cascaded reinforcement learning, strengthening independent mode functionalities and refining adaptive mode selection capabilities.
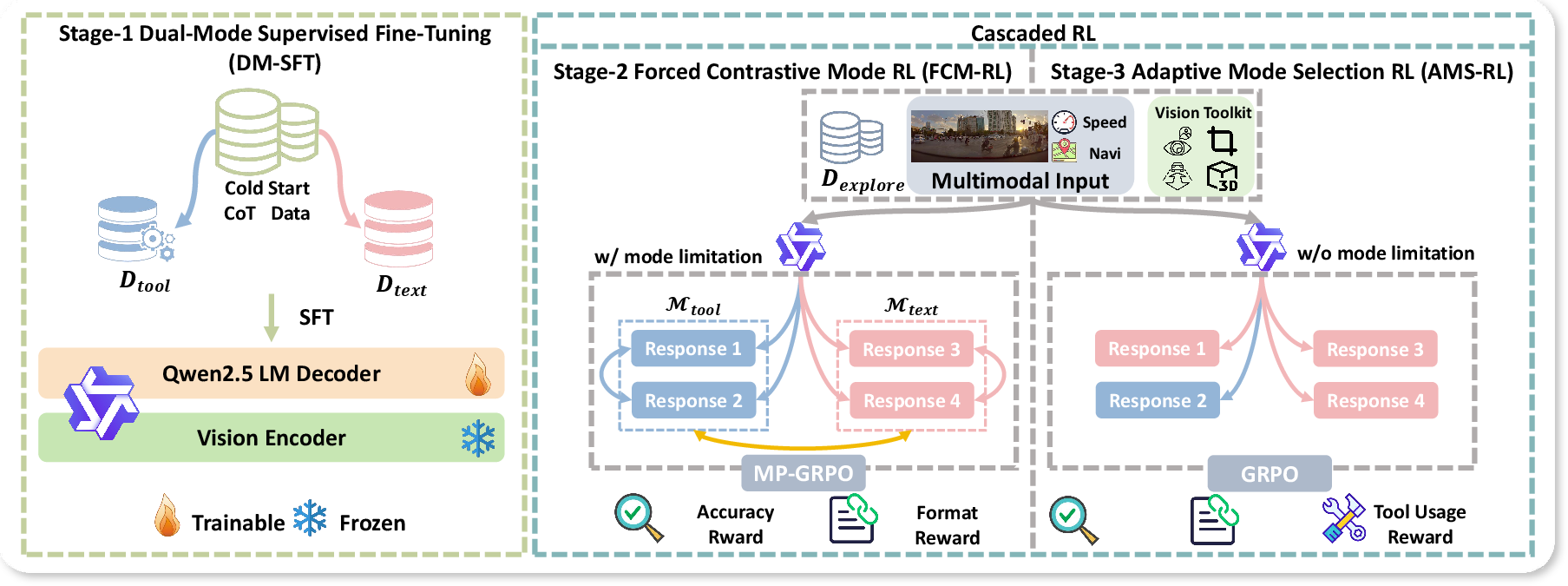
Figure 3: The progressive three-stage training strategy for DriveAgent-R1.
Implementation Details
DriveAgent-R1 is implemented using a hybrid model that leverages active perception tools including RoI Inspection, Depth Estimation, and 3D Object Detection. The agent's reasoning employs multimodal inputs to predict an 8-second meta-action sequence. It uses a Vision Toolkit to dynamically choose the appropriate cognitive strategy based on scene complexity.
Experimental Results
Experiments conducted on the Drive-Internal and nuScenes datasets show that DriveAgent-R1 achieves performance comparable to existing top-tier models like GPT-5, with substantial improvements in tasks requiring complex visual reasoning. Results indicate a notable accuracy gain from active perception and tool usage, validating the hybrid-thinking framework as effective for complex decision-making scenarios.
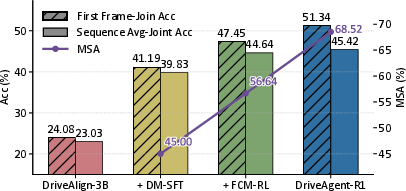
Figure 4: Progressive training gains on Drive-Internaltest. Accuracy in Madaptive mode and MSA improve with each training stage.
Ablation Studies
Ablation studies confirm that DriveAgent-R1's performance is grounded in visual evidence and not reliant on textual shortcuts, highlighting the effectiveness of its domain alignment and hybrid-thinking mechanisms. The active perception framework reliably enhances both planning accuracy and efficiency, showing superior decision-making over passive models.
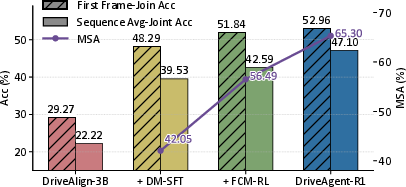
Figure 5: Progressive training gains on nuScenes test set. Accuracy in the adaptive mode (Madaptive) and MSA improve with each training stage.
Conclusion
DriveAgent-R1 presents a significant advancement in VLM-based autonomous driving, demonstrating the potential for active perception and adaptive reasoning in real-world applications. The hybrid-thinking framework not only enhances decision-making accuracy but does so efficiently, ensuring deployment-friendly autonomous systems. Future work will explore refining DriveAgent-R1's perception capabilities and integrating deeper cognitive architectures to address limitations observed in complex intersection navigation.
In summary, DriveAgent-R1 effectively bridges the gap between passive and active cognitive approaches in autonomous systems, setting a precedent for future enhancements in intelligent driving technologies.






