- The paper introduces CSD-JWT, a protocol that uses ECC-based cryptographic accumulators to enable compact verifiable credentials.
- It achieves significant efficiency gains, including up to 46% reduction in memory usage and 27-93% smaller presentations.
- The design mitigates privacy risks and replay attacks, making it ideal for SSI applications in resource-constrained environments.
Compact and Selective Disclosure for Verifiable Credentials
Introduction
The paper "Compact and Selective Disclosure for Verifiable Credentials" introduces CSD-JWT, a mechanism for enhancing privacy and efficiency in the Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) model through compact and selective disclosure of Verifiable Credentials (VCs). The paper addresses current limitations and privacy concerns associated with existing selective disclosure mechanisms, notably the SD-JWT, by utilizing an ECC-based cryptographic accumulator to encode claims. This method provides significant reductions in memory and computational overhead, particularly benefiting resource-constrained environments like IoT devices and hardware wallets.
Self-Sovereign Identity and Verifiable Credentials
SSI models empower individuals by granting them control over their digital identities, relying on VCs issued by trusted authorities. These VCs cryptographically verify specific attributes of the holder. A critical feature of SSI is the ability for users to selectively disclose claims from their credentials, an advancement beyond traditional centralized identity systems, which depend on inflexible and often privacy-invasive data-sharing practices.
CSD-JWT: Methodology and Implementation
The core of the proposed CSD-JWT system is its use of cryptographic accumulators to replace the plaintext list of claims within a VC with a fixed-length encoded value, ensuring compactness and reduced storage needs. During issuance, an issuer generates an accumulator value incorporating hashed claims, and provides claim-specific witnesses to the holder. The holder generates a Verifiable Presentation (VP) by disclosing only selected claims and their proofs, minimizing data exposure and maintaining constant credential size, which guards against inference attacks.
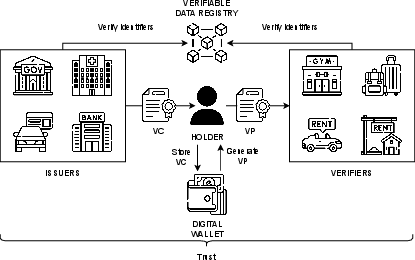
Figure 1: SSI reference system.
Implementation-wise, CSD-JWT allows holders to create VPs devoid of a full claims list, communicating only the necessary claims and corresponding proofs. This approach slashes storage requirements and enhances issuer and verifier operations without inflating computational demands on constrained devices, as shown in performance evaluations.
The performance assessment of CSD-JWT versus the SD-JWT reveals significant storage savings, achieving up to a 46% reduction in memory usage per credential. Network efficiency is similarly enhanced, with CSD-JWT reducing VP sizes by 27-93%, depending on claim disclosure levels.
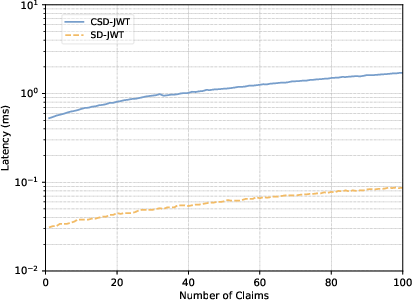
Figure 2: Issuer overhead for generating VCs.
Security-wise, CSD-JWT shields against replay attacks, ensures data minimization, and remains robust against compromised communication channels by employing cryptographic accumulations and well-defined signature checks. Its setup aligns with the Dolev-Yao model, mitigating most common adversarial threats in open communication networks.
Applications and Implications
By effectively marrying privacy preservation with scalability in verifiable credentials, CSD-JWT offers compelling benefits for diverse applications, particularly those requiring lightweight credential handling. Potential use cases span from digital credentials in government-issued IDs to IoT devices requiring rapid, secure identity verification with minimal overhead.
Conclusion
"Compact and Selective Disclosure for Verifiable Credentials" presents a practical, efficient protocol for achieving selective disclosure in SSI systems. Through meticulous evaluation and empirical validation, it establishes CSD-JWT as an advanced alternative to existing systems like SD-JWT. Its design promotes both privacy and practicality, marking a forward step in decentralized identity management, and is especially promising for scalable deployment across IoT and low-resource frameworks, ensuring commitment to future-proofing digital identities amidst rapidly evolving regulatory landscapes.

