- The paper demonstrates that the Epistemic Alignment Framework bridges the gap between user knowledge delivery preferences and LLM system capabilities.
- It employs empirical analysis of Reddit discussions and platform comparisons to identify ten challenges in epistemic responsibility, personalization, and testimonial reliability.
- The framework’s insights advocate for interface designs that enable structure, feedback, and adaptive personalization to enhance LLM user interactions.
Epistemic Alignment: Bridging User Preferences and LLM System Capabilities
Introduction to Epistemic Alignment
The paper "Epistemic Alignment: A Mediating Framework for User-LLM Knowledge Delivery" (2504.01205) presents a comprehensive framework to address the gap between user expectations and the capabilities of LLMs in delivering knowledge. This disparity arises as users often lack structured means to articulate how they want information presented, leading to a reliance on informal and inconsistent prompt-sharing practices. The Epistemic Alignment Framework is designed to bridge this divide by identifying ten challenges across three key dimensions: Epistemic Responsibility, Epistemic Personalization, and Testimonial Reliability.
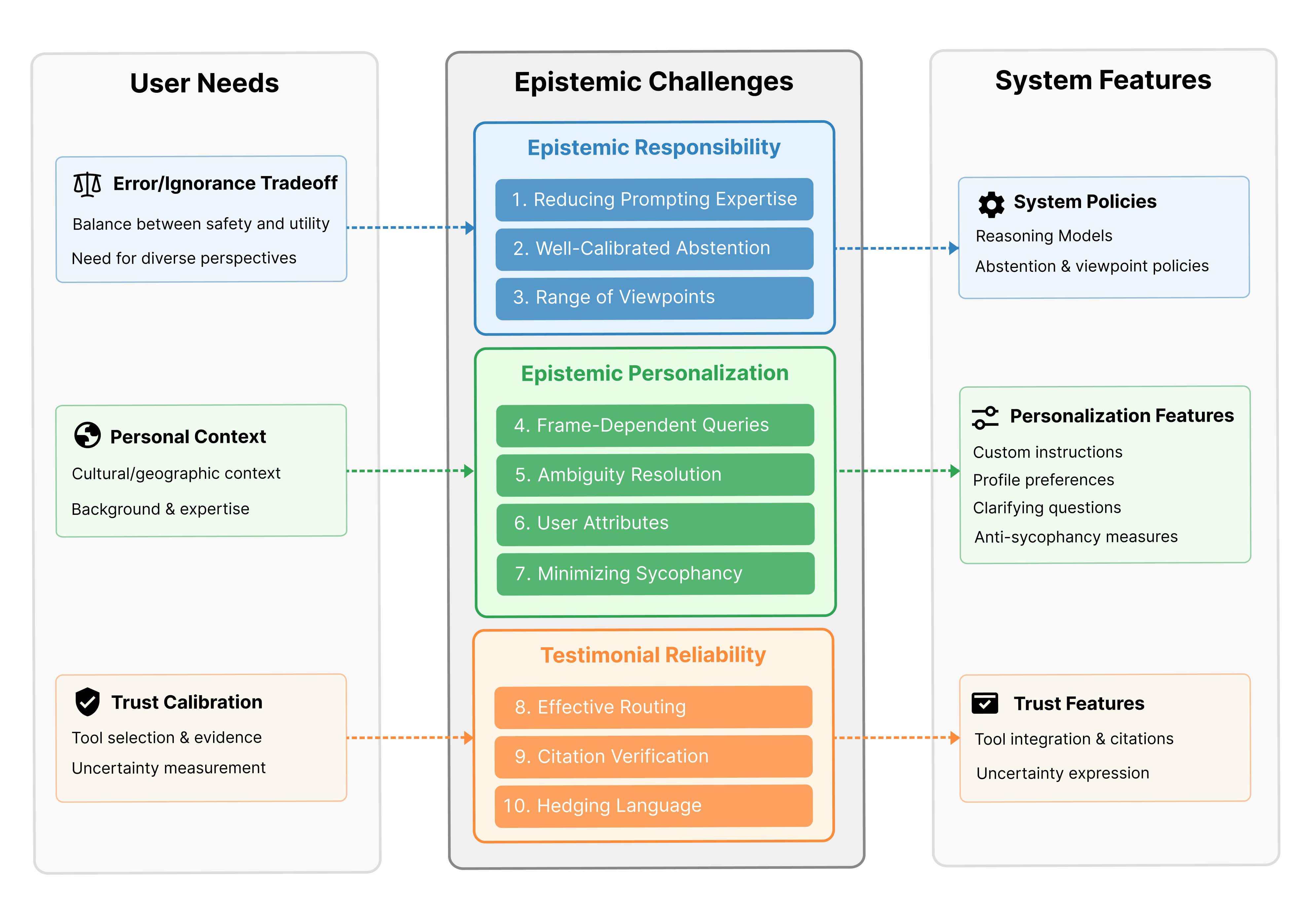
Figure 1: The Epistemic Alignment Framework as a mediating structure between user needs and system implementation.
Theoretical Foundation and Framework
The framework draws on social epistemology and epistemic cognition to explain how users engage with LLMs for knowledge processes. It formalizes the epistemic alignment problem by defining discrepancies between user preferences and system delivery profiles. The paper argues for a structured interface that supports explicit user specification of knowledge delivery parameters, facilitating transparency and feedback.
Epistemic Responsibility addresses the trade-off between error reduction and ignorance avoidance through practices like well-calibrated abstention and pluralism. For instance, LLMs need to find a balance in refusal rates to avoid both harmful content dissemination and unnecessary refusals, thereby maintaining utility without compromising safety.
Epistemic Personalization deals with user-driven inquiry processes. It examines the challenges of specifying preferences and resolving ambiguities, highlighting how users bring culturally and contextually diverse strategies when interacting with LLMs. For effective alignment, users must express their unique strategies adequately, while systems should incorporate adaptive personalization to cater to varying needs.
Testimonial Reliability involves the tools and mechanisms that users employ to gauge the trustworthiness of LLM outputs. This encompasses the citation of sources as a means of verifiability and the integration of tool-assisted workflows for complex tasks, enhancing the credibility and utility of LLM responses.
Empirical Analysis and Findings
The paper's empirical analysis includes a thematic review of Reddit discussions to validate the framework's relevance. Users often develop their own systems of prompts and instructions to tackle the epistemic challenges identified, indicating a strong need for more sophisticated alignment methods.
When evaluating OpenAI and Anthropic's platforms, the paper observes that while both have made strides in addressing epistemic challenges, significant gaps remain. For example, OpenAI’s model specifications overtly engage with abstention and sycophancy concerns, but lack comprehensive user-customizable settings for citation verification and perspective balancing.
Implications and Future Directions
The proposed Epistemic Alignment Framework serves as a concrete guide for AI developers and researchers focused on improving LLM interactions. By mapping user knowledge delivery needs to system capabilities, developers can create more targeted solutions that enhance both safety and user satisfaction.
The paper suggests future interfaces should integrate structured preference settings, transparency through visual annotations indicating preference impacts, and adaptive systems capable of learning user-specific strategies, thereby fostering greater user agency and alignment.
Conclusion
The Epistemic Alignment Framework effectively addresses critical epistemological issues in human-LLM interactions by unifying diverse user preferences with system functionalities. By providing both theoretical and empirical insights, it lays a foundation for bridging the current alignment gap, steering AI systems towards more personalized and reliable knowledge delivery.
In summary, the framework not only contributes theoretical clarity but also offers practical tools for advancing LLM capabilities, paving the way for more nuanced and effective artificial epistemic interactions.


